Deletion from Beginning in Doubly Linked List in C++
How to delete element from beginning in doubly linked list in C++?
In singly linked list, we can move only in single direction because each node has the address of the next node only.But in doubly linked list there are two pointers, one of these pointers points to the next node and the other points to the previous node so we can move in both directions. A doubly linked list allow deletion from at:-
- Deletion from beginning.
- Deletion from end.
- Deleting any particular node.

Steps to delete from beginning in doubly linked list in C++
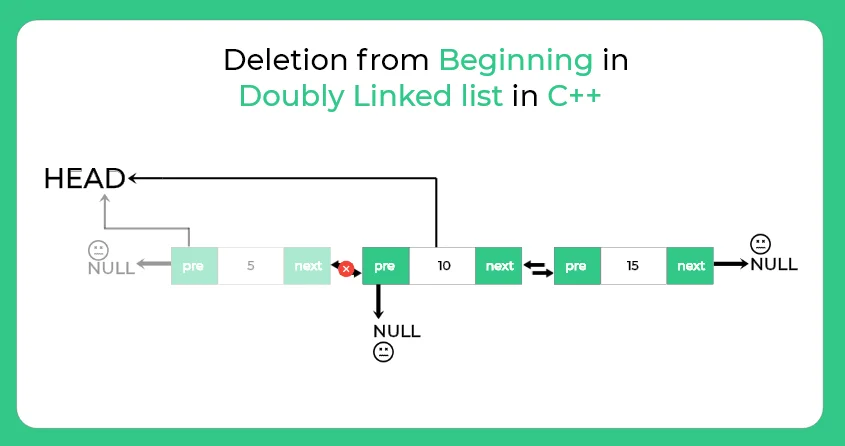
Following steps are involved in deletion of first node from a doubly linked list :-
1.) First node is the head node make next node as head.
2.) Change the previous of next node with null
3.) Delete the node
Defining doubly linked list in C++
struct Node { int Data; Struct Node* next; Struct Node* prev; };
Algorithm to delete from beginning in doubly linked list in C++
- IF HEAD = NULL
- EXIT
- ELSE SET PTR = HEAD
- SET HEAD = HEAD → NEXT
- SET HEAD → PREV = NULL
- FREE PTR
- EXIT
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Program to delete from beginning in doubly linked list in C++
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int num;
struct node *preptr;
struct node *nextptr;
} *start_node, *end_node;
void DlListcreation (int n);
void DeleteFirstNode ();
void displayDlList (int a);
int main ()
{
int n, num1, a, plc;
start_node = NULL;
end_node = NULL;
cout << " Enter the number of nodes: "; cin >> n;
DlListcreation (n);
a = 1;
displayDlList (a);
DeleteFirstNode ();
a = 2;
displayDlList (a);
return 0;
}
void DlListcreation (int n)
{
int i, num;
struct node *fnNode;
if (n >= 1)
{
start_node = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (start_node != NULL)
{
cout << " Enter data for node 1: "; //assigning data in the first node cin >> num;
start_node->num = num;
start_node->preptr = NULL;
start_node->nextptr = NULL;
end_node = start_node;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
fnNode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (fnNode != NULL)
{
cout << " Enter data for node " << i << ": "; cin >> num;
fnNode->num = num;
fnNode->preptr = end_node; // new node is linking with the previous node
fnNode->nextptr = NULL; // set next address of fnnode is NULL
end_node->nextptr = fnNode; // previous node is linking with the new node
end_node = fnNode; // assign new node as last node
}
else
{
cout << " Memory can not be allocated.";
break;
}
}
}
else
{
cout << " Memory can not be allocated.";
}
}
}
void DeleteFirstNode ()
{
struct node *NodeToDel;
if (start_node == NULL)
{
cout << " Deletion is not possible. No data in the list.\n"; } else { NodeToDel = start_node; start_node = start_node->nextptr; // move the next address of starting node to second node
start_node->preptr = NULL; // set previous address of staring node is NULL
free (NodeToDel); // delete the first node from memory
}
}
void displayDlList (int m)
{
struct node *tmp;
int n = 1;
if (start_node == NULL)
{
cout << " No data found in the List yet.";
}
else
{
tmp = start_node;
if (m == 1)
{
cout << "\n Data entered in the list are :\n";
}
else
{
cout << "\n After deletion the new list are :\n";
}
while (tmp != NULL)
{
cout << " node " << n << ": " << tmp->num << endl; n++; tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
}
}
Output:
Enter the number of nodes: 5 Enter data for node 1: 11 Input data for node 2: 22 Input data for node 3: 33 Input data for node 4: 44 Input data for node 5: 55 Data entered in the list are : node 1: 11 node 2: 22 node 3: 33 node 4: 44 node 5: 55 After deletion the new list are : node 1: 22 node 2: 33 node 3: 44 node 4: 55
Explanation:
- The program first creates a doubly linked list dynamically using the DlListcreation() function, where each new node stores data and links to both its previous and next node.
- The DeleteFirstNode() function removes the first node by shifting the start_node pointer to the second node and freeing the memory of the deleted node.
- Each node creation and linking ensures a proper bidirectional connection between previous and next nodes using preptr and nextptr.
- The displayDlList() function traverses the list from the head (start_node) to the end, printing node data before and after deletion.
- Proper memory management is maintained using malloc() for allocation and free() for deletion, ensuring no memory leaks occur when the first node is deleted.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Creation of Doubly Linked List | O(n) | O(n) |
| Deletion of First Node | O(1) | O(1) |
| Traversal / Display | O(n) | O(1) |
| Total Program | O(n) | O(n) |
To wrap it up:
Deleting a node from the beginning of a doubly linked list is a simple yet important operation. It helps maintain proper connectivity by updating the head pointer and ensuring no memory leaks occur during deletion.
By understanding this concept and its implementation, you can easily manage dynamic data structures and perform efficient memory handling in C++. This forms a strong foundation for mastering other complex operations in linked lists.
FAQs
When the first node is deleted, the head pointer moves to the next node, and the previous pointer of this new head is set to NULL. This ensures the list remains properly connected from the new starting point.
Yes, if there is only one node, deleting it will make both the head and tail pointers NULL, effectively making the list empty. It’s important to check this case to prevent accessing invalid memory.
The time complexity is O(1) since deletion from the beginning only requires updating a few pointers, regardless of the list’s size.
Yes, in languages like C++ that don’t have automatic garbage collection, it’s essential to use the delete keyword to free memory occupied by the deleted node and prevent memory leaks.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment