Deletion from End in Doubly Linked List in C++
How to delete element from end in doubly linked list in C++?
Doubly Linked list is one of the variation of Linked list which is a linear data structure. Double Linked List was introduced because of one major drawback of singly linked list, i.e; we can only traverse the singly linked list in a single direction as it only hold the address of the next node, but not of the previous node.
But in Doubly Linked List, there are two pointer variables and hence we store the data of both the previous node and of the next node, which makes it more suitable to use than its predecessor.

Steps to delete from end in doubly linked list in C++
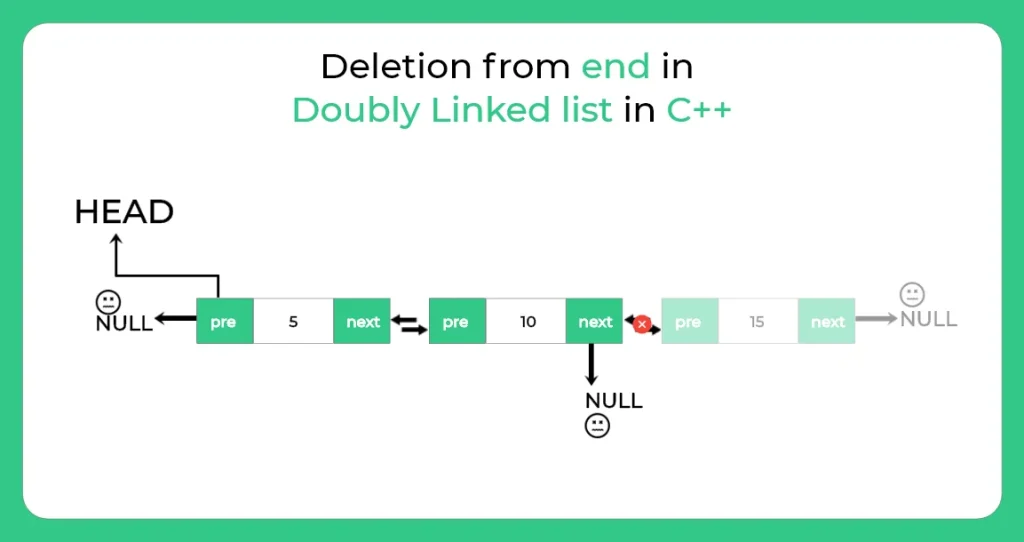
Following steps are involved in deletion of last node from a doubly linked list :-
1.) Traverse till the last node
2.) Change the next of last second node with null.
3.) Delete the last node
Defining doubly linked list in C++
struct Node { int Data; Struct Node* next; Struct Node* prev; };
Algorithm to delete from end in doubly linked list in C++
- IF HEAD = NULL
- EXIT
- ELSE SET TEMP = HEAD
- REPEAT WHILE TEMP->NEXT != NULL
- SET TEMP = TEMP->NEXT
- SET TEMP ->PREV-> NEXT = NULL
- FREE TEMP
- EXIT
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Program to delete from end in doubly linked list in C++
The program to delete a node from the end in a doubly linked list in C++ removes the last node while maintaining proper linkage between remaining nodes. It updates the end pointer to the previous node and ensures the list remains consistent and accessible. This operation helps in efficient memory management and dynamic data handling.
#include< iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int num;
struct node *preptr;
struct node *nextptr;
}
*stnode, *ennode;
void DlListcreation (int n);
void DeleteLastnode ();
void displayDlList ();
int main ()
{
int n, num1, insPlc;
stnode = NULL;
ennode = NULL;
cout << " Enter the number of nodes: "; cin >> n;
DlListcreation (n);
cout << "Linked list before deletion is:" << "\n";
displayDlList ();
DeleteLastnode ();
cout << "Linked list after deletion of node from end is :" << "\n"; displayDlList (); return 0; } void DlListcreation (int n) { int i, num; struct node *fnNode; if (n >= 1)
{
stnode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (stnode != NULL)
{
cout << " Enter data for node 1: "; // assigning data in the first node cin >> num;
stnode->num = num;
stnode->preptr = NULL;
stnode->nextptr = NULL;
ennode = stnode;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
fnNode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (fnNode != NULL)
{
// int t;
cout << " Enter data for node " << i <<": "; cin>>num;
fnNode->num = num;
fnNode->preptr = ennode; // new node is linking with the previous node
fnNode->nextptr = NULL; // set next address of fnnode is NULL
ennode->nextptr = fnNode; // previous node is linking with the new node
ennode = fnNode; // assign new node as last node
}
else
{
cout << " Memory can not be allocated.";
break;
}
}
}
else
{
cout << " Memory can not be allocated.";
}
}
}
void DeleteLastnode ()
{
struct node *NodeToDel;
if (ennode == NULL)
{
cout << " Delete is not possible. No data in the list.\n"; } else { NodeToDel = ennode; ennode = ennode->preptr; // move the previous address of the last node to second last node
ennode->nextptr = NULL; // set the next address of last node to NULL
free (NodeToDel); // delete the last node
}
}
void displayDlList ()
{
struct node *tmp;
tmp = stnode;
int n = 1;
while (tmp != NULL)
{
cout << " node " << n << ": " << tmp->num << "\n"; n++; tmp = tmp->nextptr; // current pointer moves to the next node
}
}Output:
Enter the number of nodes: 5 Enter data for node 1: 11 Enter data for node 2: 22 Enter data for node 3: 33 Enter data for node 4: 44 Enter data for node 5: 55 Data entered in the list are : node 1: 11 node 2: 22 node 3: 33 node 4: 44 node 5: 55 After deletion the new list are : node 1: 11 node 2: 22 node 3: 33 node 4: 44
Explanation:
- The function creates n nodes dynamically, linking them in both directions using preptr and nextptr.
- In deletion, it moves ennode to the previous node, sets its nextptr to NULL, and frees the last node.
- The display function traverses from stnode to NULL, printing all node values.
- The main function handles list creation, deletion from the end, and displays the list before and after deletion.
- Memory is efficiently managed, but freeing all nodes at the end would prevent leaks.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| List Creation | O(n) | O(n) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
| Delete Last Node | O(1) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
Understanding how to delete the last node in a doubly linked list gives you a clear sense of how bidirectional pointers work in data structures. You see how the prev and next links are adjusted to safely remove the tail node, and how edge cases (such as an empty list or a single-node list) must be handled to maintain list integrity.
By mastering this deletion process you’re laying the groundwork for more advanced list operations such as insertion at arbitrary positions, reverse traversal, and complex memory management in C++. With these fundamentals firm, you’ll be better equipped to confidently apply or adapt linked list logic in real world code and interviews.
FAQs
When the last node is deleted, the second last node’s next pointer is set to NULL, marking it as the new end of the list.
If the list has only one node, both start and end pointers are set to NULL after deletion to indicate an empty list.
A doubly linked list allows direct backward traversal using prev pointers, making deletion from the end or middle faster and easier.
The time complexity is O(1) since the last node can be directly accessed through the end pointer without traversal.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment