Insertion at Beginning in Doubly Linked list in C++
How to insert element at beginning in doubly linked list?
In singly linked list, we can move only in single direction because each node has the address of the next node only.But in doubly linked list there are two pointers, one of these pointers points to the next node and the other points to the previous node so we can move in both directions. A doubly linked list allow insertion at:-
- Insertion at the end of the list.
- Insertion in between the nodes.
- Insertion at the beginning.

Doubly link list definition in C++
struct Node { int Data; Struct Node* next; Struct Node* prev; };
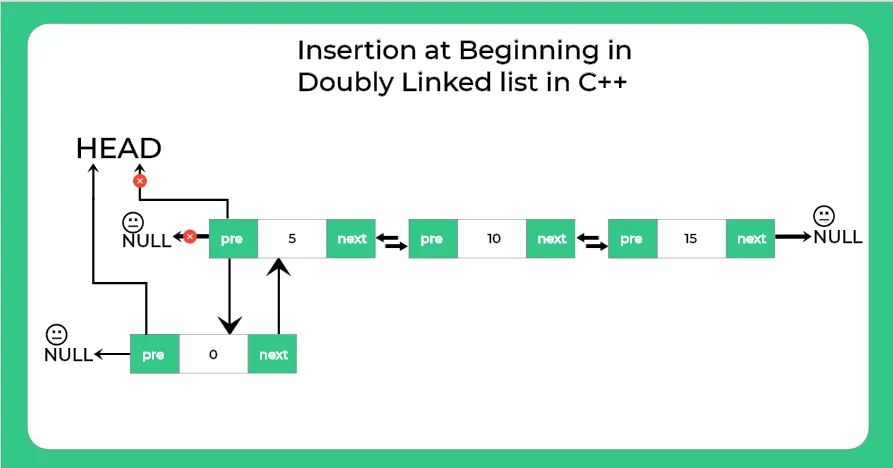
Steps to insert element at beginning in doubly linked list in C++
1.) Allocate node.
2.)Put the data.
3.) Make next node as head and previous as null.
4.)Change previous of head node to the new node.
5.)Move the head to point the new node.
Algorithm for insertion at beginning in doubly linked list in C++
- IF ptr = NULL
- SET NEW_NODE = ptr
- SET ptr = ptr -> NEXT
- SET NEW_NODE -> DATA = VAL
- SET NEW_NODE -> PREV = NULL
- SET NEW_NODE -> NEXT = START
- SET head -> PREV = NEW_NODE
- SET head = NEW_NODE
- EXIT
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Program for insertion at beginning in doubly linked list in C++
In this program, we learn how to insert a new node at the beginning of a doubly linked list using C++. The insertion operation updates the previous and next pointers to ensure the list remains properly linked from both directions.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int num;
struct node *preptr;
struct node *nextptr;
} *stnode, *ennode;
void DlListcreation (int n);
void DlLinsertNodeAtBeginning (int num);
void displayDlList ();
int main ()
{
int n, num1;
stnode = NULL;
ennode = NULL;
cout << "Enter the number of nodes : "; cin >> n;
DlListcreation (n);
displayDlList ();
cout << " Input data for insertion at beginning : "; cin >> num1;
DlLinsertNodeAtBeginning (num1);
displayDlList ();
return 0;
}
void DlListcreation (int n)
{
int i, num;
struct node *fnNode;
if (n >= 1)
{
stnode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (stnode != NULL)
{
cout << " Input data for node 1 : "; // assigning data in the first node cin >> num;
stnode->num = num;
stnode->preptr = NULL;
stnode->nextptr = NULL;
ennode = stnode;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
fnNode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
if (fnNode != NULL)
{
cout << " Input data for node " << i << ": "; cin >> num;
fnNode->num = num;
fnNode->preptr = ennode; // new node is linking with the previous node
fnNode->nextptr = NULL;
ennode->nextptr = fnNode; // previous node is linking with the new node
ennode = fnNode; // assign new node as last node
}
else
{
cout << " Memory can not be allocated.";
break;
}
}
}
else
{
cout << " Memory can not be allocated.";
}
}
}
void DlLinsertNodeAtBeginning (int num)
{
struct node *newnode;
if (stnode == NULL)
{
cout << " No data found in the list\n"; } else { newnode = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node)); newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = stnode; // next address of new node is linking with starting node
newnode->preptr = NULL; // set previous address field of new node is NULL
stnode->preptr = newnode; // previous address of starting node is linking with new node
stnode = newnode; // set the new node as starting node
}
}
void displayDlList ()
{
struct node *tmp;
tmp = stnode;
int n = 1;
while (tmp != NULL)
{
cout << " node " << n << ": " << tmp->num << "\n"; n++; tmp = tmp->nextptr; // current pointer moves to the next node
}
}
Output:
Enter the number of nodes : 5 Input data for node 1 : 11 Input data for node 2: 22 Input data for node 3: 33 Input data for node 4: 44 Input data for node 5: 55 Data entered in the list is : node 1: 11 node 2: 22 node 3: 33 node 4: 44 node 5: 55 Input data for insertion at beginning : 1 After insertion the new list is : node 1: 1 node 2: 11 node 3: 22 node 4: 33 node 5: 44 node 6: 55
Explanation:
- The program creates a doubly linked list where each node stores a number and has pointers to both its previous and next nodes.
- DlListcreation() dynamically allocates memory for each node and links them sequentially using prev and next pointers.
- DlLinsertNodeAtBeginning() inserts a new node at the start by updating the previous and next links appropriately.
- displayDlList() traverses the list from the start node and prints each node’s data in order.
- The code efficiently demonstrates dynamic memory allocation, bidirectional traversal, and insertion operations in a doubly linked list.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| List Creation | O(n) | O(n) |
| Insertion at Beginning | O(1) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
We’ve walked through how to insert a new node at the beginning of a doubly linked list, covering structure definition, step-by-step algorithm, and a full C++ implementation example.
Now that you understand the logic and code, you’re well equipped to apply insertion at the start in your own linked list projects and adapt the approach for more complex operations with confidence.
FAQs
Insertion at the beginning means adding a new node before the current first node of the list. The new node becomes the head, and its next pointer refers to the previous first node.
First, create a new node and assign it the data value. Then set its next pointer to the current head and update the previous pointer of the existing head to this new node before making it the new head.
The operation takes O(1) time because it involves only pointer updates and no traversal through the list.
In a doubly linked list, each node maintains both forward and backward pointers, allowing easy updates at both ends without traversing the entire list, making insertions more efficient.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java





Login/Signup to comment