Infix to Prefix Conversion in Java
Infix to Prefix Conversion
Infix to Prefix Conversion in Java is a standard stack based transformation used in compilers and expression evaluators.
Infix is the form humans naturally write (example: A+B*C), while prefix places the operator before its operands (example: +A*BC). Prefix is easier for machines to process because operator precedence is already encoded in the structure of the expression.
What is Infix and Prefix?
Infix notation:
Operator is written between operands:
- A + B
- (A + B) * C
Prefix notation (Polish notation):
Operator is written before operands:
- +AB
- *+ABC
Why conversion matters: Compilers often convert infix to postfix or prefix because these forms avoid repeated precedence checks during evaluation.
Approach for Infix to Prefix Conversion in Java
Approach: Reverse + Infix to Postfix + Reverse
- Reverse the infix expression.
- Swap parentheses: replace ( with ) and ) with (.
- Convert the resulting expression to postfix using the standard stack method.
- Reverse the postfix result → this becomes the prefix expression.
This approach is commonly described as a small modification of infix to postfix conversion.
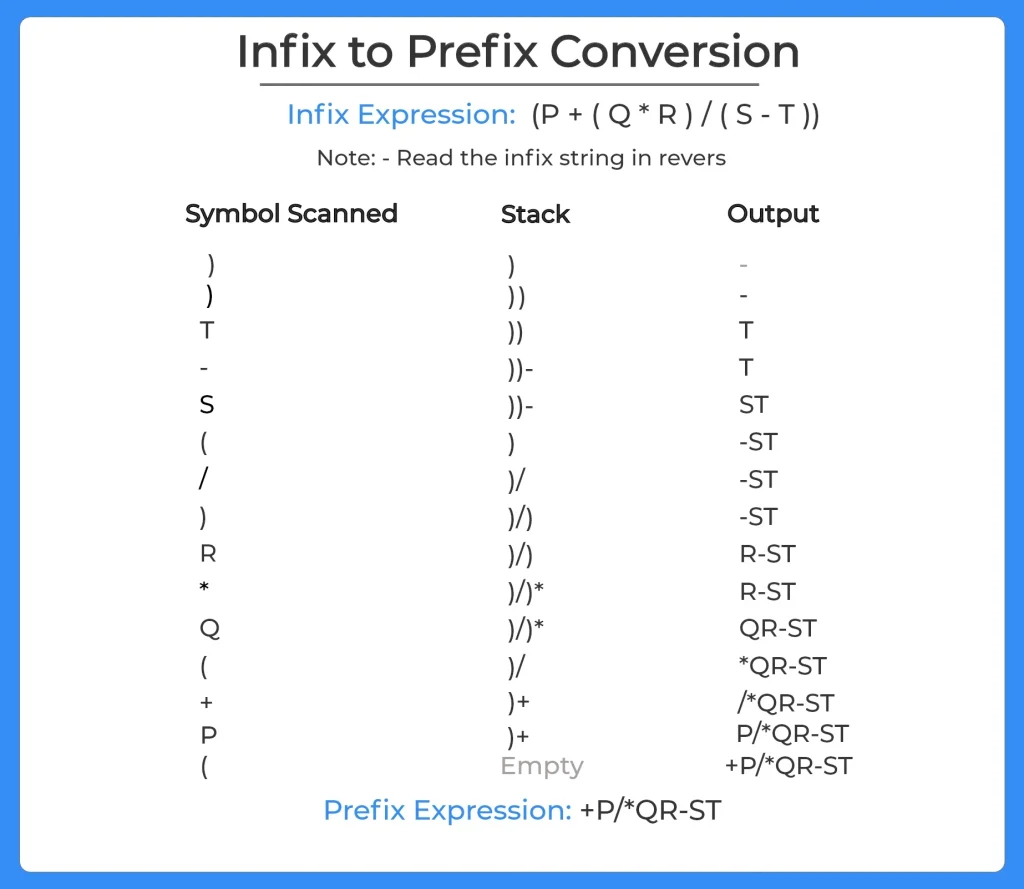
Algorithm for Infix to Prefix Conversion in Java
Variables used:
- String infix → input expression
- String reversed → reversed infix with swapped parentheses
- Stack<Character> ops → operator stack
- StringBuilder postfix → postfix output for reversed expression
- String prefix → final prefix result
Steps:
- Read infix.
- Reverse it into reversed.
- Swap parentheses in reversed:
if ( → make it )
if ) → make it (
- Convert reversed to postfix using stack:
If operand → append to postfix
If ( → push
If ) → pop until ( found
If operator → pop operators from stack based on precedence/associativity, then push current
- Reverse postfix → that becomes prefix.
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Java Code Infix to Prefix Conversion
import java.util.Stack;
public class InfixToPrefix {
private static boolean isOperand(char ch) {
return Character.isLetterOrDigit(ch);
}
private static boolean isOperator(char ch) {
return ch == '+' || ch == '-' || ch == '*' || ch == '/' || ch == '^';
}
private static int precedence(char op) {
switch (op) {
case '^': return 3;
case '*':
case '/': return 2;
case '+':
case '-': return 1;
default: return -1;
}
}
// ^ is right-associative, others are left-associative
private static boolean isRightAssociative(char op) {
return op == '^';
}
private static String reverseAndSwapParentheses(String s) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (ch == '(') sb.append(')');
else if (ch == ')') sb.append('(');
else sb.append(ch);
}
return sb.toString();
}
// Standard infix-to-postfix conversion, used internally after reverse+swap
private static String toPostfix(String infix) {
Stack ops = new Stack<>();
StringBuilder postfix = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < infix.length(); i++) {
char ch = infix.charAt(i);
if (ch == ' ') continue; // ignore spaces
if (isOperand(ch)) {
postfix.append(ch);
} else if (ch == '(') {
ops.push(ch);
} else if (ch == ')') {
while (!ops.isEmpty() && ops.peek() != '(') {
postfix.append(ops.pop());
}
if (!ops.isEmpty() && ops.peek() == '(') ops.pop();
else throw new IllegalArgumentException("Mismatched parentheses");
} else if (isOperator(ch)) {
while (!ops.isEmpty() && isOperator(ops.peek())) {
char top = ops.peek();
// Pop if top has higher precedence
// Or same precedence and current operator is left-associative
if (precedence(top) > precedence(ch) ||
(precedence(top) == precedence(ch) && !isRightAssociative(ch))) {
postfix.append(ops.pop());
} else {
break;
}
}
ops.push(ch);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid character: " + ch);
}
}
while (!ops.isEmpty()) {
if (ops.peek() == '(') throw new IllegalArgumentException("Mismatched parentheses");
postfix.append(ops.pop());
}
return postfix.toString();
}
public static String infixToPrefix(String infix) {
String reversed = reverseAndSwapParentheses(infix);
String postfix = toPostfix(reversed);
return new StringBuilder(postfix).reverse().toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String infix = "(A-B/C)*(A/K-L)";
String prefix = infixToPrefix(infix);
System.out.println("Infix : " + infix);
System.out.println("Prefix : " + prefix);
}
}
Output:
Infix : (A-B/C)*(A/K-L) Prefix : *-A/BC-/AKL
Edge cases for Infix to Prefix Conversion in Java
- Not swapping parentheses after reversing: If you reverse without swapping, parentheses meaning breaks.
- Wrong associativity for ^: Treating ^ as left-associative can change results for expressions like a^b^c.
- Mismatched parentheses: Always detect and report errors when stack still contains ( or a ) can’t find (.
- Multi digit numbers: This simple implementation reads one character at a time. For multi digit support, tokenize the input (numbers as full tokens).
Frequently Asked Questions
Answer:
Infix to Prefix Conversion in Java means converting an expression like A+B*C into prefix form +A*BC using stack rules for precedence and parentheses.
Answer:
A stack temporarily stores operators and parentheses so they can be placed into prefix order based on precedence and associativity.
Answer:
The conversion runs in O(n) time and uses O(n) space in the worst case due to the operator stack and output string building.
Answer:
The most common method is: reverse infix → swap parentheses → convert to postfix → reverse result to get prefix.
Answer:
Exponent ^ is generally right associative, so the algorithm must avoid popping on equal precedence when the current operator is ^, preserving correct grouping.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment