Implementation of Circular Queue using Arrays in java
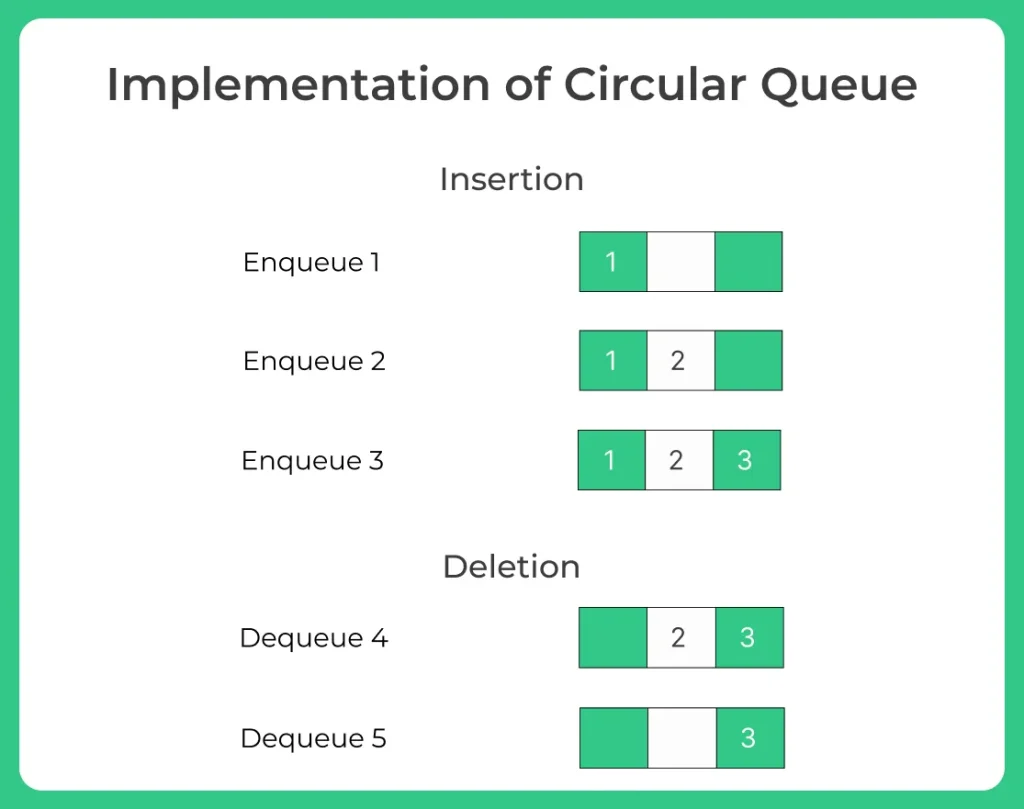
Implementation of Circular Queue using Arrays
Circular Queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position.
Why we need circular queue ??
When we work with normal Queue, we can insert elements till queue is full. But when queue is full, we are not allowed to insert the next element this is the problem with normal queue . To overcome this problem circular queue is used .
Operation In Circular Queue:
The following are the operations that can be performed on a circular queue:
- Front: It is used to get the front item from the Queue.
- Rear: It is used to get the last element from the Queue.
- enQueue(value): This function is used to insert the new value in the Queue. The new element is always inserted from the rear end.
- deQueue(): This function deletes an element from the Queue. The deletion in a Queue always takes place from the front end.
Algorithm for Insertion and Deletion:
- START
- INITIALLY PUT FRONT AND REAR BOTH AS 0
- IN ENQUEUE FUNCTION WRITE
public static void enqueue(int item)
- END
- START
- WRITE dequeue function as
- END
Java code for implementing circular queue using array
import java.util.*;
class CircularQueue {
int SIZE = 5; // Size of Circular Queue
int front, rear;
int items[] = new int[SIZE];
CircularQueue() {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
// Check if the queue is full
boolean isFull() {
if (front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1) {
return true;
}
if (front == rear + 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Check if the queue is empty
boolean isEmpty() {
if (front == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Adding an element
void enQueue(int element) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Queue is full");
} else {
if (front == -1)
front = 0;
rear = (rear + 1) % SIZE;
items[rear] = element;
System.out.println("Inserted " + element);
}
}
// Removing an element
int deQueue() {
int element;
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
return (-1);
} else {
element = items[front];
if (front == rear) {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
} /* Q has only one element, so we reset the queue after deleting it. */ else {
front = (front + 1) % SIZE;
}
return (element);
}
}
void display() {
/* Function to display status of Circular Queue */
int i;
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Empty Queue");
} else {
System.out.println("Items -> ");
for (i = front; i != rear; i = (i + 1) % SIZE)
System.out.print(items[i] + " ");
System.out.println(items[i]);
}
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircularQueue q = new CircularQueue();
q.enQueue(1);
q.enQueue(2);
q.enQueue(3);
q.enQueue(4);
q.enQueue(5);
// Fails to enqueue because front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1
q.enQueue(6);
q.display();
int elem = q.deQueue();
if (elem != -1) {
System.out.println("Deleted Element is " + elem);
}
q.display();
}
}
Output:
Inserted 1 Inserted 2 Inserted 3 Inserted 4 Inserted 5 Queue is full Items -> 1 2 3 4 5 Deleted Element is 1 Items -> 2 3 4 5
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment