Circular Queue using Linked List in Java
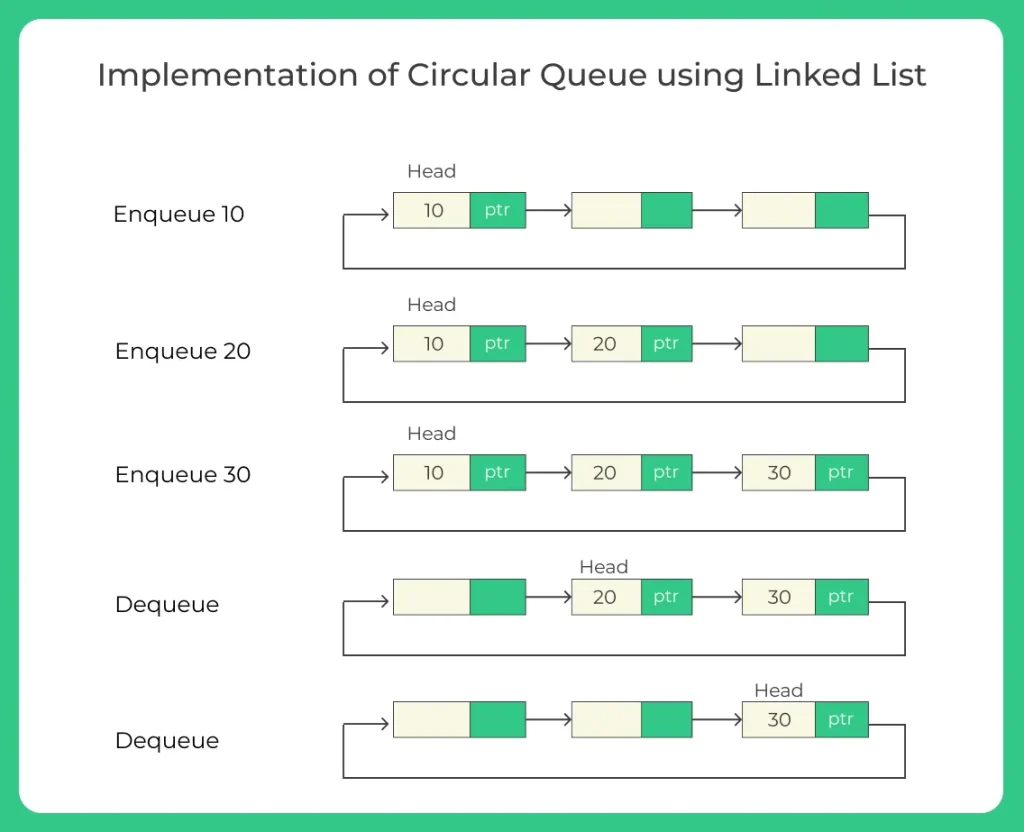
Implementation of Circular Queue using linked list
Circular Queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position.
A circular queue overcomes the problem of unused space in normal queues, and it can be implemented on both arrays and linked list.
Operation In Circular Queue:
The following are the operations that can be performed on a circular queue:
- Front: It is used to get the front item from the Queue.
- Rear: It is used to get the last element from the Queue.
- enQueue() This operation adds a new node after rear and moves rear to the next node.
- deQueue() This operation removes the front node and moves front to the next node.
Algorithm for Insertion and Deletion:
Insertion
Deletion
Insertion
- START
static void enQueue(Queue q, int d)
{
Node tp = new Node();
tp.data =d;
if (q.front == null)
q.front = tp;
else
q.rear.next = tp;
q.rear = tp;
q.rear.next = q.front;
}
- END
Deletion
- START
static int deQueue(Queue q)
{
if (q.front == null) {
System.out.print(“empty queue”);
}
int d;
if (q.front == q.rear)
{
d=q.front.data;
q.front = null;
q.rear = null;
}
else
{
Node tp = q.front;
d=tp.data;
q.front = q.front.next;
q.rear.next = q.front;
}
return d
}
- END
Java code for implementing circular queue using array
Run
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
}
static class Queue
{
Node front, rear;
}
static void enQueue (Queue q, int d)
{
Node tp = new Node ();
tp.data = d;
if (q.front == null)
q.front = tp;
else
q.rear.next = tp;
q.rear = tp;
q.rear.next = q.front;
}
static int deQueue (Queue q)
{
if (q.front == null)
{
System.out.print ("empty queue");
}
int d;
if (q.front == q.rear)
{
d = q.front.data;
q.front = null;
q.rear = null;
}
else
{
Node tp = q.front;
d = tp.data;
q.front = q.front.next;
q.rear.next = q.front;
}
return d;
}
// Function displaying the elements
static void displayQueue (Queue q)
{
Node tp = q.front;
System.out.print ("Elements in Circular Queue are: ");
while (tp.next != q.front)
{
System.out.print (tp.data + " ");
tp = tp.next;
}
System.out.println (tp.data);
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
// Creating a queue
Queue q = new Queue ();
q.front = q.rear = null;
// Inserting elements in Circular Queue
enQueue (q, 20);
enQueue (q, 40);
enQueue (q, 60);
// Display elements
displayQueue (q);
// Deleting elements
System.out.println (deQueue (q));
System.out.println (deQueue (q));
System.out.println ("AFTER DELETING, ELEMENT LEFT ");
// Remaining elements in Circular Queue
displayQueue (q);
System.out.println ("AFTER INSERTING NEW VALUE ");
enQueue (q, 80);
displayQueue (q);
}
}
Output:
Elements in Circular Queue are: 20 40 60 20 40 AFTER DELETING, ELEMENT LEFT Elements in Circular Queue are: 60 AFTER INSERTING NEW VALUE Elements in Circular Queue are: 60 80
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment