Representation of a Stack as an Array | C Program

Stack representation as Array:
A Stack is a linear data structure that follows the principle of (Last-In-First-Out) LIFO . In Stack there is one end through which insertion and deletion takes place. Whenever an element is added in the stack, it is added on the top of the stack, and the element can be deleted only from the stack. In other words, a stack can be defined as a container in which insertion and deletion can be done from the one end known as the top of the stack.
An array is used to store an ordered list of elements. Using an array for representation of stack is one of the easy techniques to manage the data. But there is a major difference between an array and a stack.
- Size of an array is fixed.
- While, in a stack, there is no fixed size since the size of stack changed with the number of elements inserted or deleted to and from it.
Representation of a Stack as Array
- Size of an array is fixed.
- While, in a stack, there is no fixed size since the size of stack changed with the number of elements inserted or deleted to and from it.
For Example:
We are given a stack of elements: 12 , 08 , 21 , 33 , 18 , 40.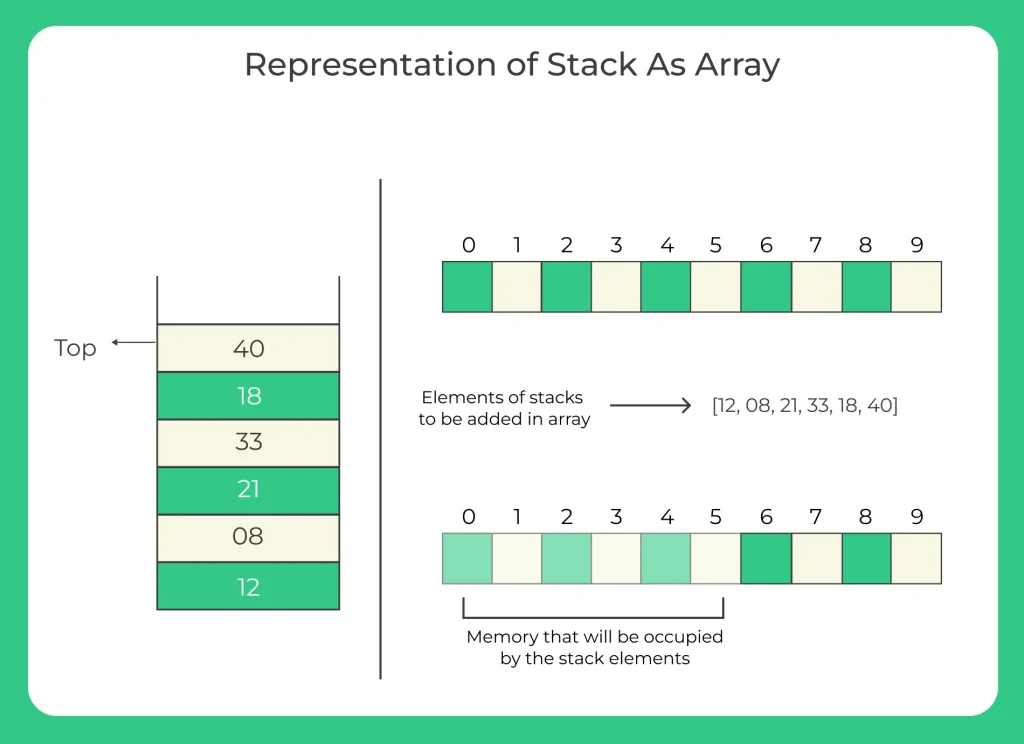
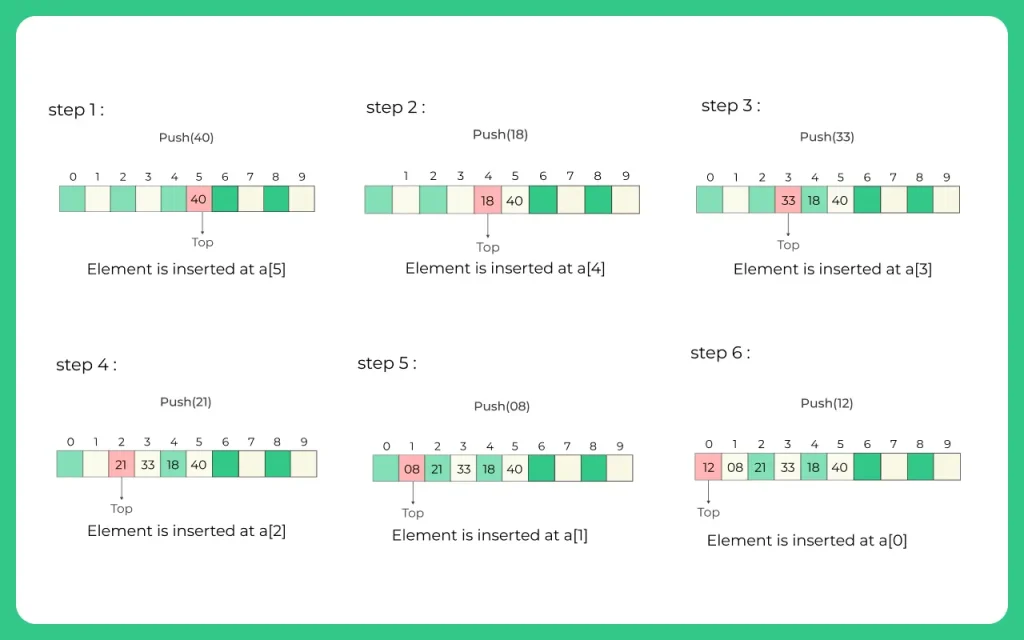
Code for Stack in C Program (using structure)
// C Program for Implmentation of stack (array) using structure
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
// A structure to represent a stack
struct Stack
{
int top;
int maxSize;
int *array;
};
struct Stack *create (int max)
{
struct Stack *stack = (struct Stack *) malloc (sizeof (struct Stack));
stack->maxSize = max;
stack->top = -1;
stack->array = (int *) malloc (stack->maxSize * sizeof (int));
//here above memory for array is being created
// size would be 10*4 = 40
return stack;
}
// Checking with this function is stack is full or not
// Will return true is stack is full else false
//Stack is full when top is equal to the last index
int isFull (struct Stack *stack)
{
if (stack->top == stack->maxSize - 1)
{
printf ("Will not be able to push maxSize reached\n");
}
// Since array starts from 0, and maxSize starts from 1
return stack->top == stack->maxSize - 1;
}
// By definition the Stack is empty when top is equal to -1
// Will return true if top is -1
int isEmpty (struct Stack *stack)
{
return stack->top == -1;
}
// Push function here, inserts value in stack and increments stack top by 1
void push (struct Stack *stack, int item)
{
if (isFull (stack))
return;
stack->array[++stack->top] = item;
printf ("We have pushed %d to stack\n", item);
}
// Function to remove an item from stack. It decreases top by 1
int pop (struct Stack *stack)
{
if (isEmpty (stack))
return INT_MIN;
return stack->array[stack->top--];
}
// Function to return the top from stack without removing it
int peek (struct Stack *stack)
{
if (isEmpty (stack))
return INT_MIN;
return stack->array[stack->top];
}
int main ()
{
struct Stack *stack = create (10);
push (stack, 5);
push (stack, 10);
push (stack, 15);
int flag = 1;
while (flag)
{
if (!isEmpty (stack))
printf ("We have popped %d from stack\n", pop (stack));
else
printf ("Can't Pop stack must be empty\n");
flag = 0;
}
return 0;
}
Output
We have pushed 5 to stack We have pushed 10 to stack We have pushed 15 to stack We have popped 15 from the stack
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment