Doubly Linked List Program in C
What is a doubly linked list ?
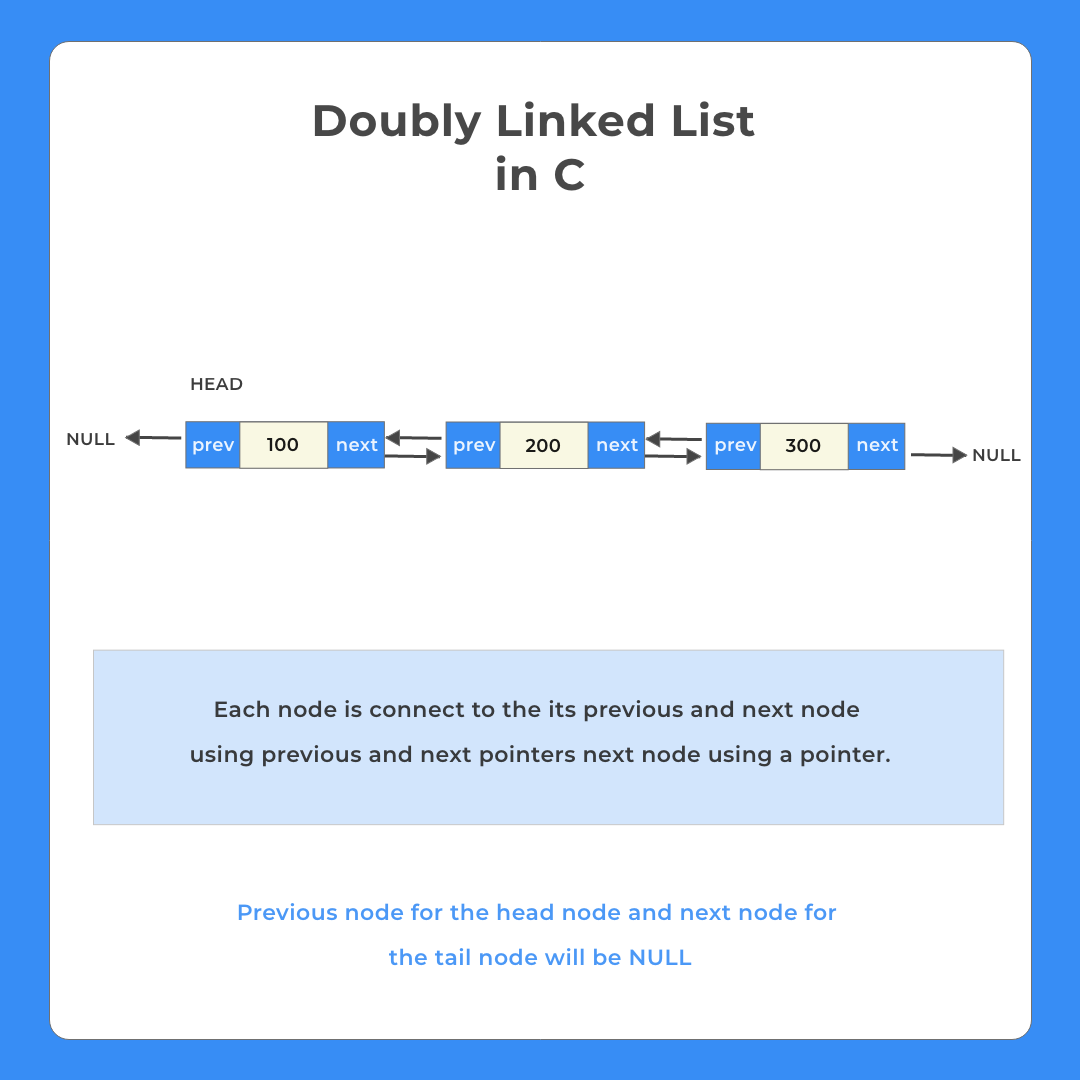
A Doubly Linked List in C is a unique type of Data Structure where there are a chain of nodes, that are connected to one another using pointers, where any individual node has 3 components –
- Data
- Previous Pointer
- Next Pointer
For any node, its previous pointer contains the address of the previous node and the next pointer contains the address of the next node in the chain of nodes.
Components in a Doubly Linked List Program in C
For writing the Doubly Linked List Program we need to know that Doubly Linked List generally has the following components –
- Node – A single unit in Doubly Linked List (DLL) contains – Data, previous and next pointers.
- Next Pointer – Contains the Address to the next node
- Previous Pointer – Contains Addresses to the previous node
- Data – Stores the data value
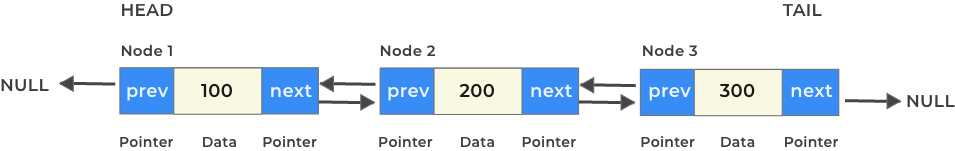
- Head – The first node in DLL
Some variations of DLL also have a tail node pointer, which signifies that this node is the end node in DLL.
Syntax for creating a node
This will create a new node in a doubly linked list which will be storing integer type of data
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
Why doubly linked list?
For Doubly Linked list in Data Structure in C, unlike singly Linked List, which only traverses in one direction. Doubly Linked List can traverse both in forwards and backwards direction.
As for any given node, we have both previous and next node addresses information available.
Insertion operation in doubly linked list
Following insertion operation can be performed on a doubly linked list.
- Insertion at beginning
- Insertion at end
- Insertion in between of nodes
Doubly Linked List Insertion at Beginning
Algorithm of insertion at the beginning
- Create a new node
- Assign its data value
- Assign newly created node’s next ptr to current head reference. So, it points to the previous start node of the linked list address
- Assign newly created node’s previous node to NULL
- Assign the current head’s previous node to this new node
- Change the head reference to the new node’s address.
Objective : Doubly Linked List Program in Data Structure in C
Code (Insertion at Beginning)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// creating memory for newNode
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
// assigning newNode's next as the current head
// Assign data & and make newNode's prev as NULL
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
newNode->prev = NULL;
// if list already had item(s)
// We need to make current head previous node as this new node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// change head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end;
printf ("\nIn Forward Direction\n");
while (node != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\nIn Backward direction \n");
while (end != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", end->data);
end = end->prev;
}
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
// Need '&' i.e. address as we need to change head
insertStart (&head, 1);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 3);
// no need for '&' as head need not be changed
// only doing traversal
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
In Forward Direction 3 2 1 In Backward direction 1 2 3
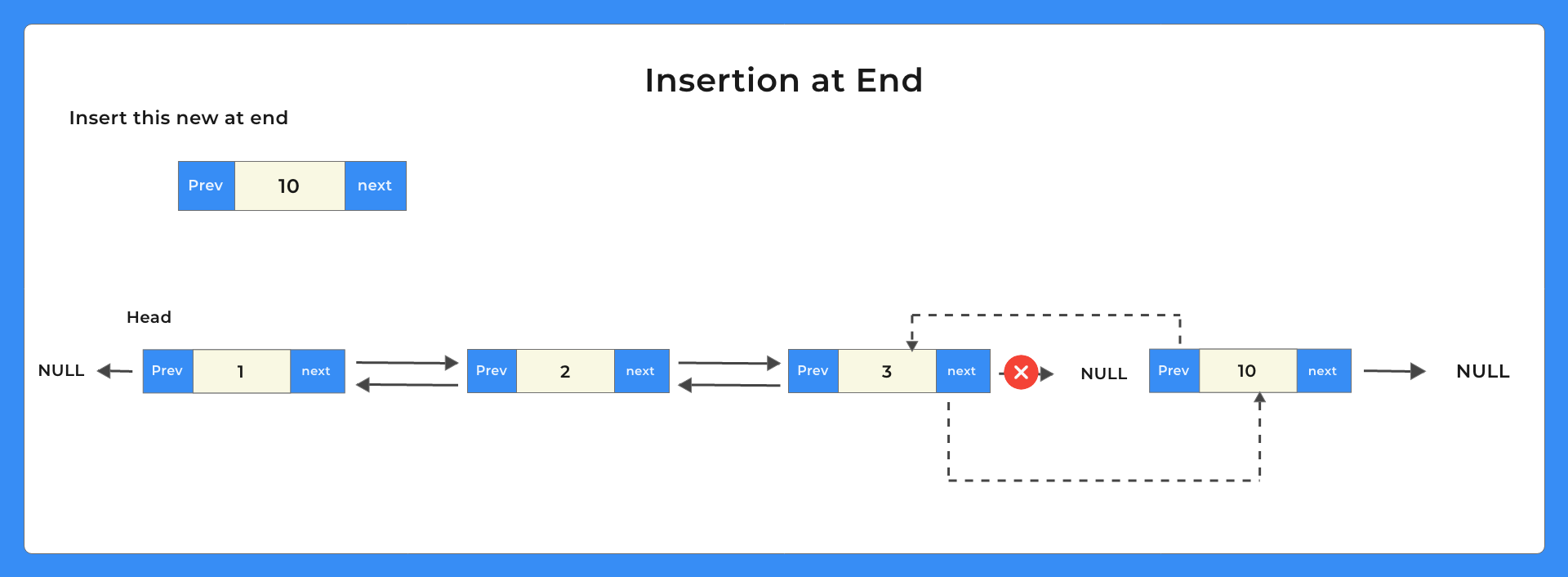
Doubly Linked List Insertion at the end
Algorithm of insertion at the beginning
- Create a new node
- Assign its data value
- Traverse till the end of the Linked List call this node temp
- Assign newly created node’s next node to NULL
- Assign newly created node’s previous node to temp
- Assign Temp’s next node to this newly created node.
Code in C (Insertion at the End)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// creating memory for newNode
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
// assigning newNode's next as the current head
// Assign data & and make newNode's prev as NULL
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
newNode->prev = NULL;
// if list already had item(s)
// We need to make current head previous node as this new node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// change head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
}
void insertLast (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
//need this if there is no node present in linked list at all
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
newNode->prev = NULL;
return;
}
struct Node *temp = *head;
// traverse till the last node
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
// assign last node's next to this new Node
temp->next = newNode;
// assign this new Node's previous to last node(temp)
newNode->prev = temp;
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end;
printf ("\nIn Forward Direction\n");
while (node != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\nIn Backward direction \n");
while (end != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", end->data);
end = end->prev;
}
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
// Need '&' i.e. address as we need to change head
insertStart (&head, 1);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 3);
insertLast (&head, 10);
insertLast (&head, 20);
// no need for '&' as head need not be changed
// only doing traversal
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
In Forward Direction 3 2 1 10 20 In Backward direction 20 10 1 2 3
Doubly Linked List Insertion after a position
Algorithm of insertion at the beginning
- Create a new node
- Assign its data value
- Traverse till nth(pos) node lets call this temp
- Assign newly created node’s next node to temp’s next node
- Assign newly created node’s previous node to temp
- Assign Temp’s next node to this newly created node.
Code in C (Insertion After a certain Position)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// creating memory for newNode
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
// assigning newNode's next as the current head
// Assign data & and make newNode's prev as NULL
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
newNode->prev = NULL;
// if list already had item(s)
// We need to make current head previous node as this new node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// change head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
}
void insertLast (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
//need this if there is no node present in linked list at all
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
newNode->prev = NULL;
return;
}
struct Node *temp = *head;
// traverse till the last node
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
// assign last node's next to this new Node
temp->next = newNode;
// assign this new Node's previous to last node(temp)
newNode->prev = temp;
}
int calcSize (struct Node *node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void insertPosition (int pos, int data, struct Node **head)
{
int size = calcSize (*head);
//If pos is 0 then should use insertStart method
//If pos is less than 0 then can't enter at all
//If pos is greater than size then bufferbound issue
if (pos < 1 || size < pos)
{
printf ("Can't insert, %d is not a valid position\n", pos);
}
else
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
// traverse till pos
while (--pos)
{
temp = temp->next;
}
// assign prev/next of this new node
newNode->next = temp->next;
newNode->prev = temp;
// change next of temp node
temp->next = newNode;
}
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end;
printf ("\nIn Forward Direction\n");
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n\nIn Backward direction \n");
while (end != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", end->data);
end = end->prev;
}
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
// Need '&' i.e. address as we need to change head
insertStart (&head, 1);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 3);
insertLast (&head, 10);
insertLast (&head, 20);
insertPosition (2, 100, &head);
// no need for '&' as head need not be changed
// only doing traversal
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
In Forward Direction 3 2 100 1 10 20 In Backward direction 20 10 1 2 3
Advantages of using doubly linked list
- It saves time as we can traverse in both directions.
- It utilizes memory as we can construct and delete nodes according to our needs.
- Insertion and deletion of the node become efficient if the position is given.
Disadvantages of using doubly linked list
- Uses more memory per node.
- Insertion and deletion take more time because extra pointers need to be maintained.
Also, check the following page –
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :






Login/Signup to comment