Circular Queue using Array in C

Implementation of Circular Queues using Array in C
In this post we will learn on how we can implement circular queue using array in C . Circular queues are extension of linear queues where the max size of queue is always available for insertion.
Unlike linear queues which faces the problem of reduction in available size for insertion with each iterative dequeue operation that happens, we will learn more about the same in this post.
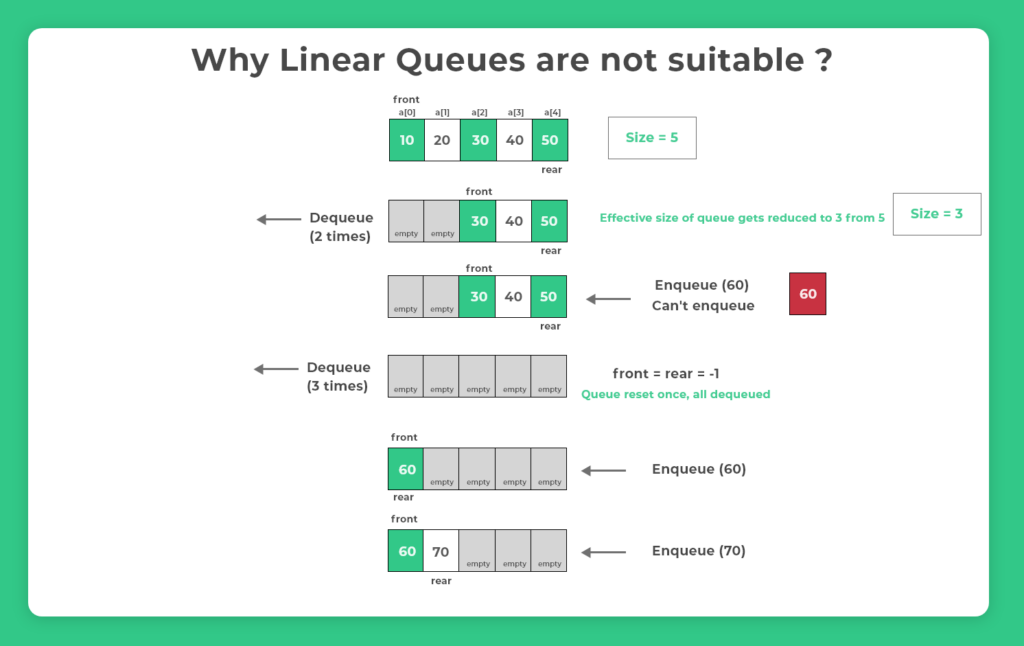
Understanding why Linear Queues are not suitable ?
Linear Queues are not suitable because once the rear reaches the end, no more elements can be inserted even if there’s space at the front (due to dequeued elements). This leads to inefficient memory utilization. Circular Queues solve this limitation by wrapping around the queue.
Everytime we Enqueue something the rear value gets incremented by 1 and every time we decrement something the front value gets incremented by 1 as well.
- Assume that queue had all 5 elements filled completely(as given) in example below
- The rear points at last element i.e. a[4] and front at the first element i.e. a[0]
- If we dequeue the queue 2 times
- This will change the front to a[2]
- Eventhough now there are two array elements that are empty, if we try to Enqueue(insert), it will not be possible
- Now, this happens because rear is pointing towards the last element still and the condition that we have to implement overflow is the following -
if(rear == size - 1)
Overflow condition
/*rear is 4 and size is 5
above condition becomes true
Even with a[0], a[1] being empty we can't use them for enqueueing
this problem is solved by Circular queues*/
Image representation of the above.

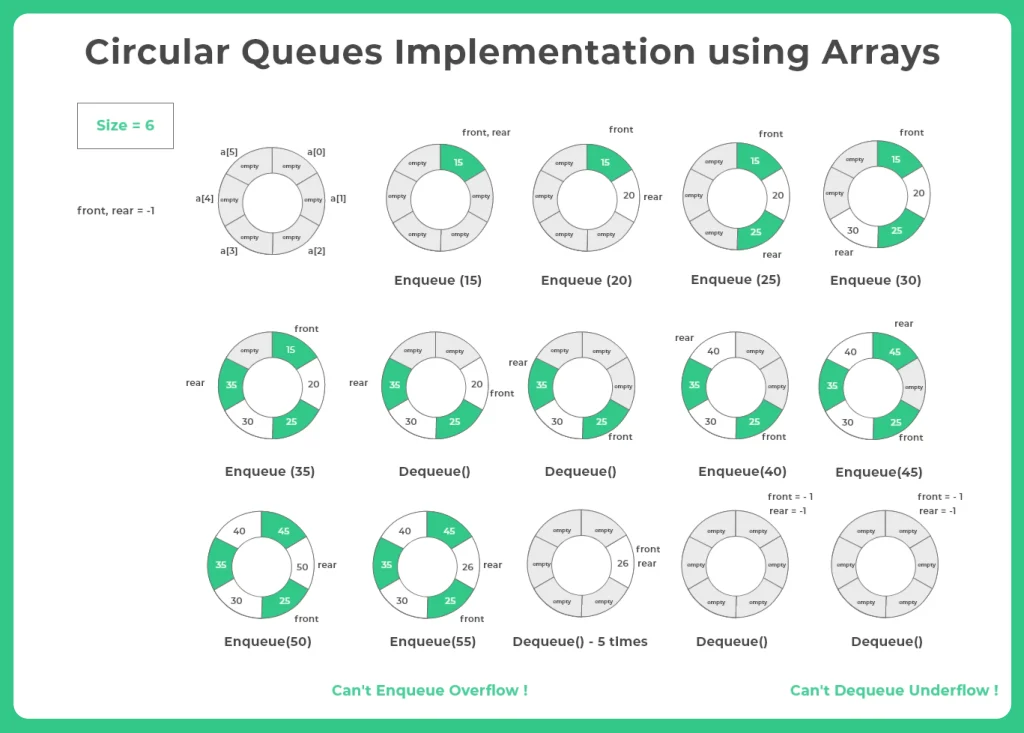
Circular Queues Implementation using Arrays in C
We can make our code circular by making minor adjustment and changes in the code.
For example, our code can try to enter rear item the following ways –
rear = (rear + 1)%size
In this case if the queue is full, it will go to 0th position, if 0th position is empty.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription

Code for Circular Queues implementation using Arrays
#include<stdio.h>
#define capacity 6
int queue[capacity];
int front = -1, rear = -1;
// Here we check if the Circular queue is full or not
int checkFull ()
{
if ((front == rear + 1) || (front == 0 && rear == capacity - 1))
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Here we check if the Circular queue is empty or not
int checkEmpty ()
{
if (front == -1)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// Addtion in the Circular Queue
void enqueue (int value)
{
if (checkFull ())
printf ("Overflow condition\n");
else
{
if (front == -1)
front = 0;
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;
queue[rear] = value;
printf ("%d was enqueued to circular queue\n", value);
}
}
// Removal from the Circular Queue
int dequeue ()
{
int variable;
if (checkEmpty ())
{
printf ("Underflow condition\n");
return -1;
}
else
{
variable = queue[front];
if (front == rear)
{
front = rear = -1;
}
else
{
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
}
printf ("%d was dequeued from circular queue\n", variable);
return 1;
}
}
// Display the queue
void print ()
{
int i;
if (checkEmpty ())
printf ("Nothing to dequeue\n");
else
{
printf ("\nThe queue looks like: \n");
for (i = front; i != rear; i = (i + 1) % capacity)
{
printf ("%d ", queue[i]);
}
printf ("%d \n\n", queue[i]);
}
}
int main ()
{
// Not possible as the Circular queue is empty
dequeue ();
enqueue (15);
enqueue (20);
enqueue (25);
enqueue (30);
enqueue (35);
print ();
dequeue ();
dequeue ();
print ();
enqueue (40);
enqueue (45);
enqueue (50);
enqueue (55); //Overflow condition
print ();
return 0;
}
Output
Underflow condition 15 was enqueued to circular queue 20 was enqueued to circular queue 25 was enqueued to circular queue 30 was enqueued to circular queue 35 was enqueued to circular queue The queue looks like: 15 20 25 30 35 15 was dequeued from circular queue 20 was dequeued from circular queue The queue looks like: 25 30 35 40 was enqueued to circular queue 45 was enqueued to circular queue 50 was enqueued to circular queue Overflow condition The queue looks like: 25 30 35 40 45 50
In summary
Circular queues effectively resolve the limitations of linear queues by reusing freed-up spaces through a wrap-around approach. This leads to optimal memory usage and avoids overflow even when empty spaces exist at the front.
By modifying insertion and deletion logic using modulo operations, circular queues can be easily implemented in C using arrays. This makes them ideal for situations where fixed-size memory buffers need to be managed efficiently.
FAQs
A circular queue utilizes the entire array by wrapping around, preventing space wastage that occurs in linear queues after multiple deletions.
Overflow occurs if (front == rear + 1) or (front == 0 && rear == size – 1), indicating that no further insertions are possible.
The modulo operator allows the rear and front pointers to wrap around the array, enabling continuous usage of all available space.
Yes, circular queues can also be implemented using linked lists, providing dynamic sizing and eliminating fixed-capacity constraints.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment