Infix To Postfix Conversion using Stack in C++
Infix To Postfix Conversion
Infix To Postfix Conversion using Stack in C++ – In the process of Infix To Postfix Converting using Stack in C++, we will use the stack data structure. By scanning the infix expression from left to right, when we will get any operand, simply add them to the postfix form, and for the operator and parenthesis, add them in the stack maintaining the precedence of them.

Basic of Infix and Postfix Notation:-
- Infix Expression: The operator is in between the two operands
- Example: A + B is known as infix expression.
- Postfix Expression: The operator is after the two operands
- Example: BD + is known as postfix expression.
Steps needed for infix to postfix conversion using stack in C++ –
- First Start scanning the expression from left to right
- If the scanned character is an operand, output it, i.e. print it
- Else
- If the precedence of the scanned operator is higher than the precedence of the operator in the stack(or stack is empty or has'(‘), then push operator in the stack
- Else, Pop all the operators, that have greater or equal precedence than the scanned operator. Once you pop them push this scanned operator. (If we see a parenthesis while popping then stop and push scanned operator in the stack)
- If the scanned character is an ‘(‘, push it to the stack.
- If the scanned character is an ‘)’, pop the stack and output it until a ‘(‘ is encountered, and discard both the parenthesis.
- Now, we should repeat steps 2 – 6 until the whole infix i.e. whole characters are scanned.
- Print output
- Do the pop and output (print) until the stack is not empty
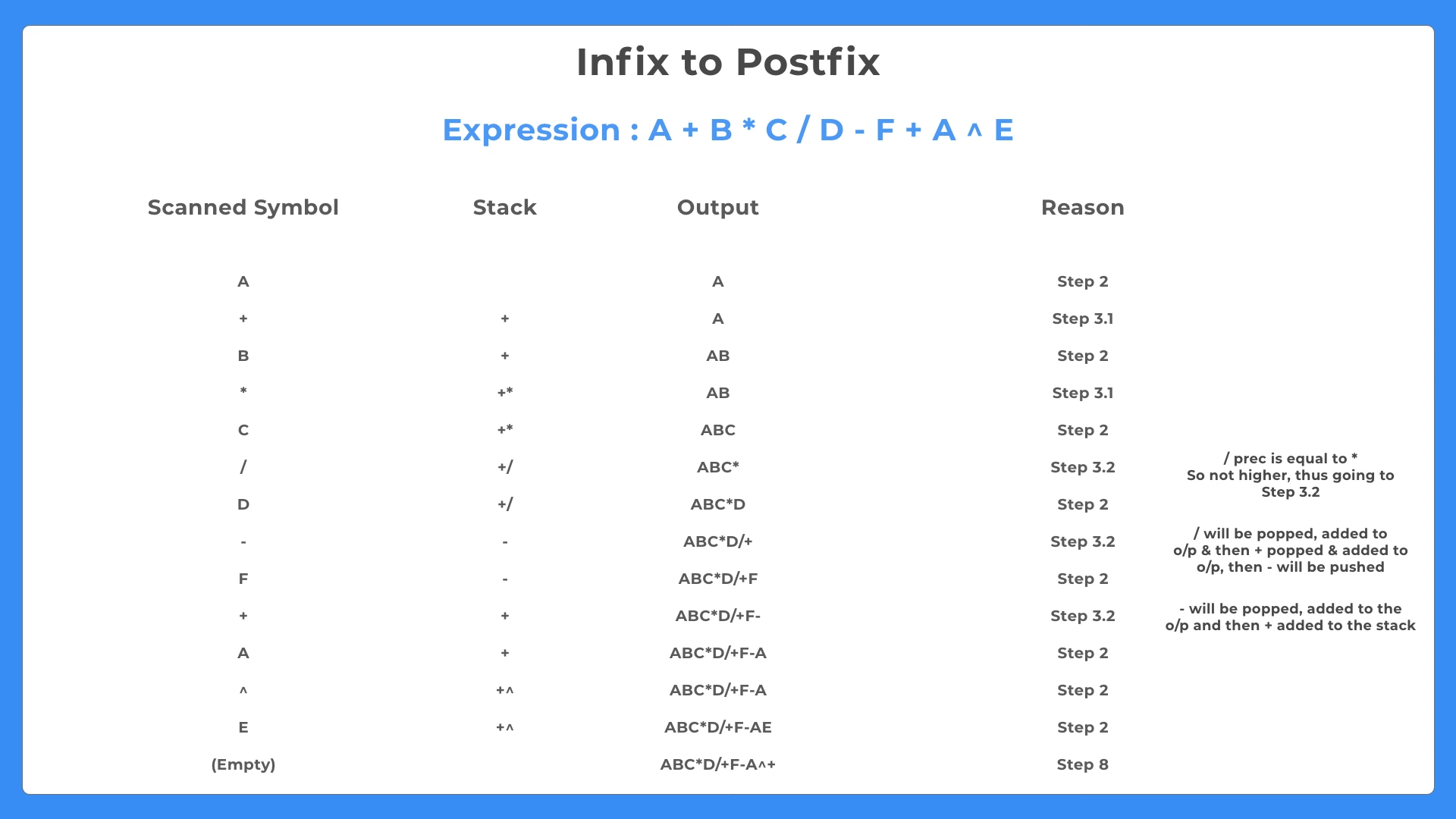
Below are two examples of how Infix to Postfix can be calculated –
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Benefits of Postfix Conversion over Infix Expression
- In postfix any formula can be expressed without parenthesis.
- It is very useful for evaluating formulas on computers with stacks.
- Infix operators have precedence
Infix To Postfix Conversion using Stack in C++
We will look at the following three methods you can choose any of them as per your wish
- Method 1: Stack implemented via inbuilt stack library in C++
- Method 2: Stack created using custom class creation in C++
This method uses inbuilt stack library to create stack
//Using inbuilt stack library to create stack
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int priority (char alpha){
if(alpha == '+' || alpha =='-')
return 1;
if(alpha == '*' || alpha =='/')
return 2;
if(alpha == '^')
return 3;
return 0;
}
string convert(string infix)
{
int i = 0;
string postfix = "";
// using inbuilt stack< > from C++ stack library
stack <int>s;
while(infix[i]!='\0')
{
// if operand add to the postfix expression
if(infix[i]>='a' && infix[i]<='z'|| infix[i]>='A'&& infix[i]<='Z')
{
postfix += infix[i];
i++;
}
// if opening bracket then push the stack
else if(infix[i]=='(')
{
s.push(infix[i]);
i++;
}
// if closing bracket encounted then keep popping from stack until
// closing a pair opening bracket is not encountered
else if(infix[i]==')')
{
while(s.top()!='('){
postfix += s.top();
s.pop();
}
s.pop();
i++;
}
else
{
while (!s.empty() && priority(infix[i]) <= priority(s.top())){
postfix += s.top();
s.pop();
}
s.push(infix[i]);
i++;
}
}
while(!s.empty()){
postfix += s.top();
s.pop();
}
cout << "Postfix is : " << postfix; //it will print postfix conversion
return postfix;
}
int main()
{
string infix = "((a+(b*c))-d)";
string postfix;
postfix = convert(infix);
return 0;
}This method uses custom class for stack creation in C++
// custom class based stack implimentation
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Stack {
int top;
int MAX;
int* a;
public:
Stack(int size){
top = -1;
MAX = size;
a = new int [MAX];
}
bool push(int x);
int pop();
int peek();
bool isEmpty();
bool isFull();
};
bool Stack::isEmpty(){
return (top < 0); } bool Stack::isFull(){ return (top == MAX - 1); } int Stack::peek(){ return a[top]; } bool Stack::push(int x) { if (top >= (MAX - 1)) {
cout << "Stack Overflow";
return false;
}
else {
top++;
a[top] = x;
return true;
}
}
int Stack::pop()
{
if (top < 0) {
cout << "Stack Underflow"; return INT_MIN; } else { int x = a[top]; top--; return x; } } int priority (char alpha) { if(alpha == '+' || alpha =='-') return 1; if(alpha == '*' || alpha =='/') return 2; if(alpha == '^') return 3; return 0; } string convert(string infix) { int i = 0; string postfix = ""; Stack s(20); while(infix[i]!='\0') { // if operand add to the postfix expression if(infix[i]>='a' && infix[i]<='z'|| infix[i]>='A'&& infix[i]<='Z')
{
postfix += infix[i];
i++;
}
// if opening bracket then push the stack
else if(infix[i]=='(') {
s.push(infix[i]);
i++;
}
// if closing bracket encounted then keep popping from stack until
// closing a pair opening bracket is not encountered
else if(infix[i]==')') {
while(s.peek()!='(')
postfix += s.pop();
s.pop();
i++;
}
else {
while (!s.isEmpty() && priority(infix[i]) <= priority(s.peek())){
postfix += s.pop();
}
s.push(infix[i]);
i++;
}
}
while(!s.isEmpty()){
postfix += s.pop();
}
cout << "Postfix is : " << postfix;
//it will print postfix conversion
return postfix;
}
int main() {
string infix = "((a+(b*c))-d)";
string postfix;
postfix = convert(infix);
return 0;
}
Output
Postfix is : abc*+d-
FAQs - Infix To Postfix Conversion using Stack
FAQs - Infix To Postfix Conversion using Stack
A stack is ideal because it provides Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) behavior, which is crucial when dealing with operator precedence and parentheses. It allows efficient temporary storage and retrieval of operators during the traversal of the infix expression.
During conversion, if the incoming operator has lower or equal precedence than the operator on the top of the stack (considering associativity), we pop from the stack to output until this condition breaks. Associativity (left or right) helps determine whether to continue popping or push the current operator.
- On encountering ‘(‘, push it to the stack.
- On encountering ‘)’, pop and append to postfix until ‘(‘ is found.
- Finally, discard the ‘(‘ without appending it to the result.
For multi-digit numbers or variables, instead of character-by-character parsing, tokenization or delimiter-based separation is used. This ensures each operand is treated as a complete unit during the scan.
No, using a stack (explicit or implicit via recursion) is essential to manage nested structures and precedence efficiently. Without it, you’d need a more complex algorithm that replicates stack behavior manually, increasing time and space complexity.
- Mismatched parentheses (e.g., extra ) or ()
- Invalid characters (non-operator, non-operand symbols)
- Incorrect operator placement (e.g., two operators in a row)
- Empty input or null expression
Robust code should check for and handle these before or during conversion.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment