Implementation of Queue using Linked List in C++
Queue using Linked List
In this section, we will learn how the implementation of Queue using Linked List in C++ which is dynamic in nature and it’s size is variable so we do not need to reallocate the entire Linked List. This implementation of the queue is more efficient as compared to the array implementation of the queue.

What is Queue using Linked List?
A Queue using Linked List is a dynamic version of a queue where elements are stored in nodes and linked using pointers. Each node contains two parts:
- The data (value)
- The pointer to the next node
The queue maintains two pointers:
- front: points to the first element of the queue
- rear: points to the last element of the queue
New elements are added at the rear, and elements are removed from the front.
Operations involved in Queue using Linked List
Here are the common operations:
- Enqueue (Insertion) – Add an element at the rear end.
- Dequeue (Deletion) – Remove an element from the front end.
- Peek/Front – Get the value of the front element without removing it.
- IsEmpty – Check whether the queue is empty.
Steps to Implement Queue using Linked List in C++
- We will create a Linked list to perform the operations on the queue.
- Create a linked list to insert the elements .
- Similarly, Perform the deletion operation in Linked List.
- Implement all the methods of the queue in a Linked List.
The Linked List Implementation of queue is also better in terms of
- space
- memory
- time complexity
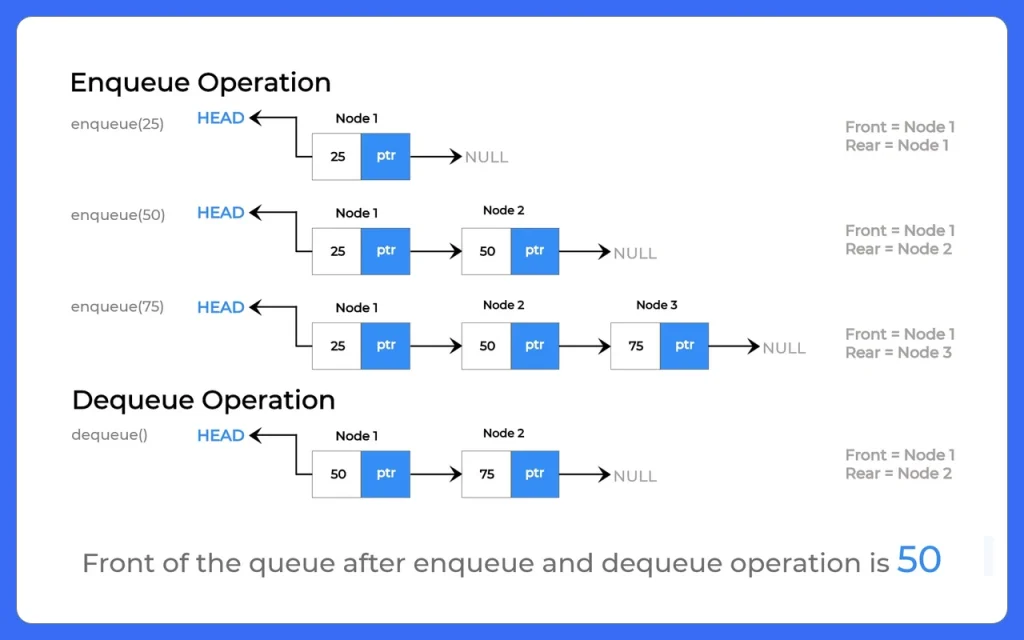
Algorithm for Enqueue:-
- Return Queue full
- Else
- Rear+Rear+1
- Queue[Rear]=Data
- If(Front== -1)
- Front= 0
Algorithm for Dequeue:-
- If(Front==-1||Front==Rear+1)
- Return
- Else
- Queue[Front]=0
- Front=Front+1
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Problem Description :
Problem:
You have to implement a queue using linked list in C++. The program should support the following operations:
- Insertion (enqueue)
- Deletion (dequeue)
- Display the front element
- Check if the queue is empty
Write the code in C++ to achieve this functionality.
Implementation of Queue using Linked List in C++:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
void enqueue (Node ** head, int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node ();
// assign data value
new_node->data = data;
// change the next node of this new_node
// to current head of Linked List
new_node->next = *head;
//changing the new head to this newly entered node
*head = new_node;
}
void dequeue (Node ** head)
{
Node *temp = *head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
cout << ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete"); return; } // move head to next node *head = (*head)->next;
//cout<< ("Deleted: %d\n", temp->data);
delete (temp);
}
void display (Node * node)
{
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main ()
{
Node *head = NULL;
enqueue (&head, 10);
enqueue (&head, 11);
enqueue (&head, 12);
enqueue (&head, 13);
enqueue (&head, 14);
enqueue (&head, 15);
enqueue (&head, 16);
enqueue (&head, 17);
enqueue (&head, 18);
cout << "Queue before deletion: ";
display (head);
dequeue (&head);
cout << endl << "Queue after deletion: ";
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output:-
Queue before deletion: 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 Queue after deletion: 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10
Explanation:
- The program uses a dynamically allocated Node structure where each element stores data and a pointer to the next node.
- The enqueue function inserts every new element at the head of the linked list, making insertion fast and constant in time.
- The dequeue function removes the first node (head) and updates the head pointer, ensuring quick deletion.
- The display function traverses the linked list from head to NULL to print all elements in order.
- Since both insertion and deletion happen at the head, the code behaves more like a stack even though it’s named as a queue.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Enqueue (Insert at head) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Dequeue (Delete head) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Display (Traversal) | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall Space Used | — | O(n) |
To wrap it up:
Implementing a queue using a linked list in C++ is a very practical and efficient approach when the number of elements isn’t fixed. Unlike arrays, linked lists don’t require predefined size and allow dynamic memory allocation.
FAQs - Implementation of Queue using Linked List in C++
FAQs - Implementation of Queue using Linked List in C++
Arrays have a fixed size, which means you need to define the maximum number of elements beforehand. If the array gets full, you either need to resize it (which is expensive) or stop inserting. On the other hand, a linked list is dynamic—it uses memory as needed. You can keep adding elements until system memory is available, making it more efficient and flexible for queue operations.
If we try to remove (dequeue) an element when the queue is already empty, it should not crash the program. Instead, the program should display a proper message like “Queue is empty. Cannot dequeue.” and skip the deletion process. In linked list implementation, this is handled by checking if the front pointer is NULL.
Yes, circular queues can also be implemented using linked lists. In a circular queue, after the last node, the next pointer links back to the first node. This structure is useful in scenarios like memory management, round-robin scheduling, or buffering, where the queue starts over again after reaching the end.
Yes. When we remove a node from the front of the queue, we also free the memory allocated to that node using the delete keyword in C++. This ensures we don’t waste memory or cause memory leaks. It’s one of the benefits of using dynamic memory allocation responsibly in linked lists.
Yes, both enqueue (insertion at rear) and dequeue (deletion at front) operations are performed in O(1) time. This is because they involve only pointer changes and do not require shifting of elements or traversal of the list, unlike array-based implementations where shifting may be needed.
The rear pointer keeps track of the last node in the queue. This allows us to directly add new elements to the end in constant time (O(1)). Without the rear pointer, we would have to start from the front and traverse the entire list every time we wanted to insert a new node, which would be inefficient (O(n) time).
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment