Doubly Linked List Insertion and Deletion Program in C++
Doubly Linked List Insertion and Deletion in C++
We will explore all the different methods to do insertion and deletion in a doubly-linked list in C++ using struct, classes and class functions. Let us go!

A doubly Linked list is sometimes used over the singly Linked list in C++ since they allow traversal in both forward and backward directions. While singly linked list allowed traversal in backward direction only.
Definition
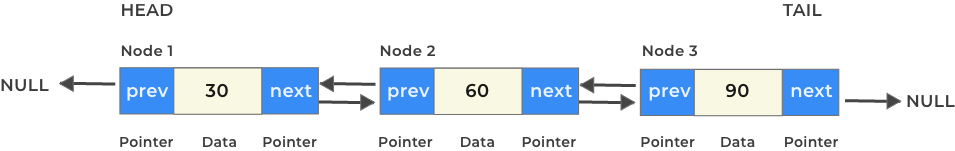
A Doubly Linked list is a data structure that contains a chain of nodes connected to one another and where each node has a data value two pointers: next and previous where the next node contains the address to the next node in the linked list and the previous node contains the address to the previous node in the chained linked list.
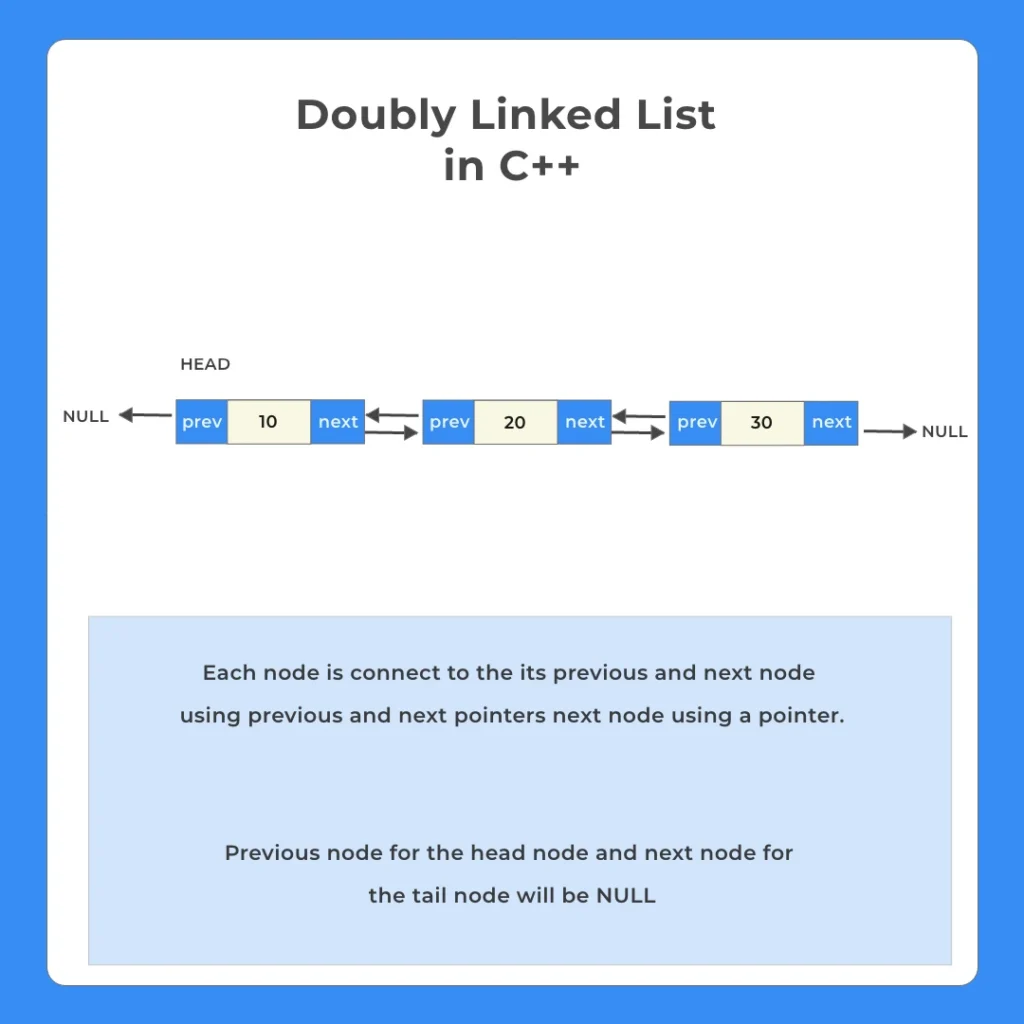
A doubly linked has the following –
- Data value
- Next Pointer
- Previous Pointer
Each unit of the above is called a node.
The start of Linked List is denoted by a special additional pointer called head.
Some versions of doubly-linked lists may also have trail pointer that denotes the end of the linked list.
Structure of a Node in Doubly Linked List
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node *prev;
};
Operations
We can do delete and insertion operations on the doubly linked list at various positions which are –
- At beginning
- At the end
- In the middle
Let us now look at the programs for the same. First with insertion operations.
Doubly Linked List Insertion in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node *prev;
};
void insertStart (Node ** head, int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node ();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = *head;
new_node->prev = NULL;
// if DLL had already >=1 nodes
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = new_node;
// changing head to this
*head = new_node;
}
void insertLast (Node ** head, int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node ();
// assign data
// since this will be the last node its next will be NULL
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
//if we are entering the first node
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = new_node;
new_node->prev = NULL;
return;
}
struct Node *last = *head;
// traverse to the current last node
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
// assign current last node's next to this new node
// also assign new node's prev to this 'last' node
last->next = new_node;
new_node->prev = last;
// new_node becomes the last node now
}
int countItems (Node * node)
{
int count = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
void insertAfter (int n, int data, Node ** head)
{
int len = countItems (*head);
// if insertion position is 0 means entering at start
if (n == 0)
{
insertStart (head, data);
return;
}
// means inserting after last item
if (n == len)
{
insertLast (head, data);
return;
}
// else insertion will happen somewhere in the middle
if (n < 1 || len < n)
cout << "Invalid position" << endl; else { Node *new_node = new Node (); new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
new_node->prev = NULL;
// nthNode used to traverse the Linked List
struct Node *nthNode = *head;
// traverse till the nth node
while (--n)
{
nthNode = nthNode->next;
}
struct Node *nextNode = nthNode->next; // (n+1)th node
// assigning (n+1)th node's previous to this new node
nextNode->prev = new_node;
// new_node's next assigned to (n+1)th node
new_node->next = nextNode;
// new_node's previous assigned to nth node
new_node->prev = nthNode;
// assign nth node's next to new_node
nthNode->next = new_node;
}
}
void display (Node * node)
{
Node *end = NULL;
cout << "Reading DLL Forward: ";
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " "; end = node; node = node->next;
}
cout << "\nReading DLL Backward: ";
while (end != NULL)
{
cout << end->data << " "; end = end->prev;
}
cout << "\n\n";
}
int main ()
{
Node *head = NULL;
insertStart (&head, 6);
insertStart (&head, 4);
insertStart (&head, 2);
display (head);
insertLast (&head, 8);
insertLast (&head, 12);
insertLast (&head, 14);
display (head);
//Inserts after 4th position
insertAfter (4, 10, &head);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Reading DLL Forward: 2 4 6 Reading DLL Backward: 6 4 2 Reading DLL Forward: 2 4 6 8 12 14 Reading DLL Backward: 14 12 8 6 4 2 Reading DLL Forward: 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Reading DLL Backward: 14 12 10 8 6 4 2
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next, *prev;
};
class DoublyLinkedList
{
private:
Node * head;
public:
DoublyLinkedList ()
{ // constructor
head = NULL;
}
int countItems ();
void insertStart (int data);
void insertLast (int data);
void insertAfter (int pos, int data);
void display ();
};
void DoublyLinkedList::insertStart (int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node ();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = head;
new_node->prev = NULL;
// if DLL had already >=1 nodes
if (head != NULL)
head->prev = new_node;
// changing head to this
head = new_node;
}
void DoublyLinkedList::insertLast (int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node ();
// assign data
// since this will be the last node its next will be NULL
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
//if we are entering the first node
if (head == NULL)
{
head = new_node;
new_node->prev = NULL;
return;
}
Node *last = head;
// traverse to the current last node
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
// assign current last node's next to this new node
last->next = new_node;
new_node->prev = last;
// new_node becomes the last node now
}
void DoublyLinkedList::insertAfter (int n, int data)
{
int len = countItems ();
// if insertion position is 0 means entering at start
if (n == 0)
{
insertStart (data);
return;
}
// means inserting after last item
if (n == len)
{
insertLast (data);
return;
}
// else insertion will happen somewhere in the middle
if (n < 1 || len < n)
cout << "Invalid position" << endl; else { Node *new_node = new Node (); new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
new_node->prev = NULL;
// nthNode used to traverse the Linked List
Node *nthNode = head;
// traverse till the nth node
while (--n)
{
nthNode = nthNode->next;
}
Node *nextNode = nthNode->next; // (n+1)th node
// assigning (n+1)th node's previous to this new node
nextNode->prev = new_node;
// new_node's next assigned to (n+1)th node
new_node->next = nextNode;
// new_node's previous assigned to nth node
new_node->prev = nthNode;
// assign nth node's next to new_node
nthNode->next = new_node;
}
}
int DoublyLinkedList::countItems ()
{
Node *node = new Node ();
node = head;
int items = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
items++;
}
return items;
}
void DoublyLinkedList::display ()
{
Node *node = head;
Node *end = NULL;
cout << "Reading DLL Forward: ";
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " "; end = node; node = node->next;
}
cout << "\nReading DLL Backward: ";
while (end != NULL)
{
cout << end->data << " "; end = end->prev;
}
cout << "\n\n"; } int main () { DoublyLinkedList *dll = new DoublyLinkedList (); dll->insertStart (6);
dll->insertStart (4);
dll->insertStart (2);
dll->display ();
dll->insertLast (8);
dll->insertLast (12);
dll->insertLast (14);
dll->display ();
// delete 3rd node
dll->insertAfter (3, 10);
dll->display ();
return 0;
}
Output
Reading DLL Forward: 2 4 6 Reading DLL Backward: 6 4 2 Reading DLL Forward: 2 4 6 8 12 14 Reading DLL Backward: 14 12 8 6 4 2 Reading DLL Forward: 2 4 6 10 8 12 14 Reading DLL Backward: 14 12 8 10 6 4 2
Doubly Linked List deletion in C++
Let us look at all variations of the program for the same –
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
int countItems (struct Node *node);
void insert (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *new_node = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = *head;
new_node->prev = NULL;
// If the linked list already had atleast 1 node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = new_node;
// new_node will become head
*head = new_node;
}
void deleteStart (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
// if DLL is empty
if (*head == NULL)
{
cout << "Linked List Empty, nothing to delete\n";
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (temp->next == NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " deleted\n";
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
// assign head node's previous to NULL
(*head)->prev = NULL;
cout << temp->data << " deleted\n";
free (temp);
}
void deleteLast (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
// if DLL is empty
if (*head == NULL)
{
cout << ("DLL empty can't delete\n");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (temp->next == NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " deleted\n";
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// else traverse to the last node
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
struct Node *secondLast = temp->prev;
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to Null
secondLast->next = NULL;
cout << temp->data << " deleted\n";
free (temp);
}
void deleteNthNode (struct Node **head, int n)
{
//if the head node itself needs to be deleted
int len = countItems (*head);
// not valid
if (n < 1 || n > len)
{
cout << "Not a valid position\n";
return;
}
// delete the first node
if (n == 1)
{
deleteStart (head);
return;
}
if (n == len)
{
deleteLast (head);
return;
}
struct Node *temp = *head;
// traverse to the nth node
while (--n)
{
temp = temp->next;
}
struct Node *previousNode = temp->prev; // (n-1)th node
struct Node *nextNode = temp->next; // (n+1)th node
// assigning (n-1)th node's next pointer to (n+1)th node
previousNode->next = temp->next;
// assigning (n+1)th node's previous pointer to (n-1)th node
nextNode->prev = temp->prev;
// deleting nth node
cout << temp->data << " deleted\n";
free (temp);
}
// required for deleteNthNode
int countItems (struct Node *node)
{
int items = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
items++;
}
return items;
}
//function to print the doubly linked list
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end = NULL;
cout << "Reading DLL Forward: ";
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
cout << "\nReading DLL Backward: ";
while (end != NULL)
{
cout << end->data << " ";
end = end->prev;
}
cout << "\n\n";
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
insert (&head, 2);
insert (&head, 4);
insert (&head, 8);
insert (&head, 10);
insert (&head, 12);
insert (&head, 14);
display (head);
deleteStart (&head);
display (head);
deleteLast (&head);
display (head);
// delete 3rd node
deleteNthNode (&head, 3);
display (head);
// delete 1st node
deleteNthNode (&head, 1);
display (head);
// delete 1st node
deleteLast (&head);
display (head);
// delete 1st node
deleteStart (&head);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Reading DLL Forward: 14 12 10 8 4 2 Reading DLL Backward: 2 4 8 10 12 14 14 deleted Reading DLL Forward: 12 10 8 4 2 Reading DLL Backward: 2 4 8 10 12 2 deleted Reading DLL Forward: 12 10 8 4 Reading DLL Backward: 4 8 10 12 8 deleted Reading DLL Forward: 12 10 4 Reading DLL Backward: 4 10 12 12 deleted Reading DLL Forward: 10 4 Reading DLL Backward: 4 10 4 deleted Reading DLL Forward: 10 Reading DLL Backward: 10 10 deleted Reading DLL Forward: Reading DLL Backward:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next, *prev;
};
class DoublyLinkedList
{
private:
Node * head;
public:
DoublyLinkedList ()
{ // constructor
head = NULL;
}
int countItems ();
void insert (int data);
void deleteStart ();
void deleteLast ();
void deleteNthNode (int pos);
void display ();
};
void DoublyLinkedList::insert (int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node ();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = head;
new_node->prev = NULL;
// if DLL had already >=1 nodes
if (head != NULL)
head->prev = new_node;
// changing head to this
head = new_node;
}
void DoublyLinkedList::deleteStart ()
{
Node *temp = head;
// if DLL is empty
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << "Linked List Empty, nothing to delete\n";
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (temp->next == NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " deleted\n";
head = NULL;
return;
}
// move head to next node
head = head->next;
// assign head node's previous to NULL
head->prev = NULL;
cout << temp->data << " deleted\n";
free (temp);
}
void DoublyLinkedList::deleteLast ()
{
Node *temp = head;
// if DLL is empty
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << ("DLL empty can't delete\n");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (temp->next == NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " deleted\n";
head = NULL;
return;
} // else traverse to the last node
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
Node *secondLast = temp->prev;
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to Null
secondLast->next = NULL;
cout << temp->data << " deleted\n";
free (temp);
}
void DoublyLinkedList::deleteNthNode (int n)
{
//if the head node itself needs to be deleted
int len = countItems ();
// not valid
if (n < 1 || n > len)
{
cout << "Not a valid position\n";
return;
}
// delete the first node
if (n == 1)
{
deleteStart ();
return;
}
if (n == len)
{
deleteLast ();
return;
}
Node *temp = head;
// traverse to the nth node
while (--n)
{
temp = temp->next;
}
Node *previousNode = temp->prev; // (n-1)th node
Node *nextNode = temp->next; // (n+1)th node
// assigning (n-1)th node's next pointer to (n+1)th node
previousNode->next = temp->next;
// assigning (n+1)th node's previous pointer to (n-1)th node
nextNode->prev = temp->prev;
// deleting nth node
cout << temp->data << " deleted\n";
free (temp);
}
int DoublyLinkedList::countItems ()
{
Node *node = new Node ();
node = head;
int items = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
items++;
}
return items;
}
void DoublyLinkedList::display ()
{
Node *node = head;
Node *end = NULL;
cout << "Reading DLL Forward: ";
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
cout << "\nReading DLL Backward: ";
while (end != NULL)
{
cout << end->data << " ";
end = end->prev;
}
cout << "\n\n";
}
int main ()
{
DoublyLinkedList *dll = new DoublyLinkedList ();
dll->insert (2);
dll->insert (4);
dll->insert (8);
dll->insert (10);
dll->insert (12);
dll->insert (14);
dll->display ();
dll->deleteStart ();
dll->display ();
dll->deleteLast ();
dll->display ();
// delete 3rd node
dll->deleteNthNode (3);
dll->display ();
// delete 1st node
dll->deleteNthNode (1);
dll->display ();
// delete 1st node
dll->deleteLast ();
dll->display ();
// delete 1st node
dll->deleteStart ();
dll->display ();
return 0;
}
Output
Reading DLL Forward: 14 12 10 8 4 2 Reading DLL Backward: 2 4 8 10 12 14 14 deleted Reading DLL Forward: 12 10 8 4 2 Reading DLL Backward: 2 4 8 10 12 2 deleted Reading DLL Forward: 12 10 8 4 Reading DLL Backward: 4 8 10 12 8 deleted Reading DLL Forward: 12 10 4 Reading DLL Backward: 4 10 12 12 deleted Reading DLL Forward: 10 4 Reading DLL Backward: 4 10 4 deleted Reading DLL Forward: 10 Reading DLL Backward: 10 10 deleted Reading DLL Forward: Reading DLL Backward:
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment