Implementation of Priority Queue Using Linked List in C++
Priority Queue using linked list in C++
In this section we will implement the priority queue using linked list. Priority Queue implementation using linked list is more efficient than using array. As Linked list provide you the facility of Dynamic memory allocation .If we use Linked List for implementing Priority Queue then memory is not going to waste. We can free the memory which is not in use anymore.

Algorithm for Priority Queue Implementation using Linked List:
- Create a node structure for creating nodes of the linked list.
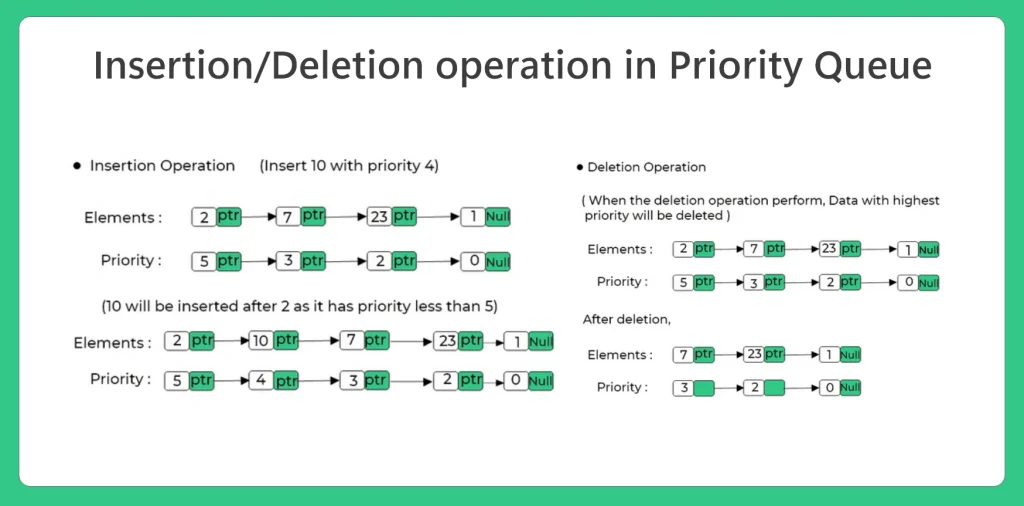
- insert() : This function is used to insert the elements based on the priority level in linked list.
- delete() : This function delete the head node of the linked list, and make free that memory and then the next node will become the head node of the linked list.
- display() : This function is used to display the elements of the priority queue that is implemented using linked list.
- peak() : This function is used to display the top element of the priority queue.
Prime Course Trailer
Code Implementation for Priority Queue using Linked List
Implementing a priority queue with a linked list ensures that each new element is placed in its proper priority order without needing array shifts. This method maintains a sorted structure, making deletion of the highest priority element quick and efficient. It also adapts well to dynamic data sizes due to linked list flexibility.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
int priority;
Node *next;
};
Node *front = NULL;
void insert (int data, int priority)
{
Node *temp, *curr, *pre = NULL;
temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->priority = priority;
if (front == NULL or priority >= front->priority)
{
temp->next = front;
front = temp;
}
else
{
curr = front;
while (curr and priority <= curr->priority)
{
pre = curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
temp->next = pre->next;
pre->next = temp;
}
}
void Delete ()
{
if (front == NULL)
{
cout << "Priority Queue is underflow" << endl;
return;
}
else
{
Node *temp;
temp = front;
cout << "Deleted item is " << temp->data << endl; front = temp->next;
free (temp);
}
}
void display ()
{
if (front == NULL)
cout << "Priority-Queue is empty" << endl;
Node *curr = front;
cout << "\nPriority-Queue elements are : ";
while (curr)
{
cout << curr->data << " "; curr = curr->next;
}
cout << endl;
return;
}
void peak ()
{
cout << "Peak element is :" << front->data << endl;
}
int main ()
{
insert (2, 9);
insert (3, 4);
insert (6, 8);
display ();
peak ();
Delete ();
Delete ();
display ();
return 0;
}
Output:
Priority-Queue elements are :2 6 3 Peak element is : 2 Deleted element : 2 Deleted element : 6 Priority-Queue elements are : 3
Explanation:
- This code implements a priority queue using a singly linked list where each Node stores data, a numeric priority, and a next pointer; nodes with larger priority values are placed toward the front (higher priority = served first).
- insert(data, priority) creates a new node and either places it at the front (if list is empty or new priority ≥ front’s priority) or walks the list to insert it after all nodes with priority ≥ the new node (so existing equal-priority nodes stay ahead — FIFO for ties).
- Delete() removes the front node (the current highest-priority element), prints its data, updates front, and frees the node; this is the queue’s dequeue operation.
- display() prints a message if the queue is empty and then lists all data values from front to end; peak() prints the front element’s data (but neither peak() nor Delete() check for front==NULL before accessing front->data in all code paths, so they assume the queue is non-empty when called).
- Minor issues: nodes are allocated with new but freed with free() (should use delete), and peak() lacks an empty-check (risk of dereferencing NULL); otherwise insertion preserves correct order and deletion is simple O(1).
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space |
|---|---|---|
| Insert | O(n) | O(1) |
| Delete | O(1) | O(1) |
| Peak | O(1) | O(1) |
| Display | O(n) | O(1) |
| Total Space (n elements) | — | O(n) |
To wrap it up:
The article on “Implementation of Priority Queue Using Linked List in C++” provides a clear walk-through of how to use a dynamically allocated linked list to build a priority queue. It shows how insertions respect priority ordering, how the highest priority element is removed, and how the front (peak) can be retrieved efficiently.
By choosing a linked list over a fixed-size array, the implementation avoids wasted memory and supports flexible growth and shrinkage at runtime. With the detailed algorithm steps and complete code sample provided, this serves as a concrete and practical example of applying data-structure fundamentals in C++.
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
FAQs
It compares the new element’s priority with existing nodes and inserts it in the correct sorted position. This ensures the highest-priority element always stays at the front.
A linked list offers dynamic size and avoids overflow issues. It also makes insertions efficient when elements need to be placed in the middle.
Deletion simply removes the first node, which always holds the highest priority. This makes removal a constant-time operation.
Typically, we delete that node and reinsert it with the updated priority. This keeps the ordering of the queue consistent and accurate.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java
Priority Queue
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
- Operations on a Stack
- Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
- Stack Representation in – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as an Array. – C | C++ | Java
- Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to Postfix Conversion – C | C++ | Java
- Infix to prefix conversion in – C | C++ | Java
- Postfix to Prefix Conversion in – C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
- Queues Program in C and implementation
- Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
- Types of Queues in Data Structure
- Application of Queue Data Structure
- Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) – C | C++ | Java
- Reverse a Queue – C | C++ | Java
- Queues using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using Stack – C | C++ | Java
- Implement Queue using two Stacks – C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
- Applications of Circular Queues
- Circular queue in – C | C++ | Java
- Circular queue using Array – C | C++ | Java
- Circular Queue using Linked Lists – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment