Introduction to Stack in Java
Stack in Java Programming
Stack is a linear data structure that follows the principle of (Last-In-First-Out) LIFO . In Stack there is one end through which insertion and deletion takes place. Whenever an element is added in the stack, it is added on the top of the stack, and the element can be deleted only from the stack. In other words, a stack can be defined as a container in which insertion and deletion can be done from the one end known as the top of the stack.

Introduction to Stack in Java
What is a Stack?
A stack is an abstract data type where insertion and deletion happen only at one end, called the top.
LIFO (Last In, First Out):The element pushed most recently is popped first.
Following are common operations implemented on the stack:
- push():When we insert an element in a stack then the operation is known as a push. If the stack is full then the condition is called overflow condition.
- pop(): When we want to delete an element from the stack, the operation is known as a pop. If the stack is empty means there is no element in the stack, this condition is known as an underflow state.
- isEmpty():When we want to determines whether the stack is empty or not.
- isFull(): when we want to determines whether the stack is full or not.’
- peek(): It returns the element at the given position.
| Stack Operation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Push | Insert an element into the stack. |
| Pop | Remove the top element. |
| Peek / Top | View the top element without removing it. |
| isEmpty | Check whether the stack has no elements. |
| Size | Number of elements in the stack. |
Why Stack Is Important in Java?
Stacks are essential for many internal operations in Java such as:
- Function call stack & recursion
- Expression evaluation (prefix, postfix)
- Undo/redo in editors
- Backtracking algorithms
- Browser back/forward navigation
- Parsing and compiler design
Understanding how a stack works helps you write optimized and structured Java programs.
Implementation of Stack in Java Programming
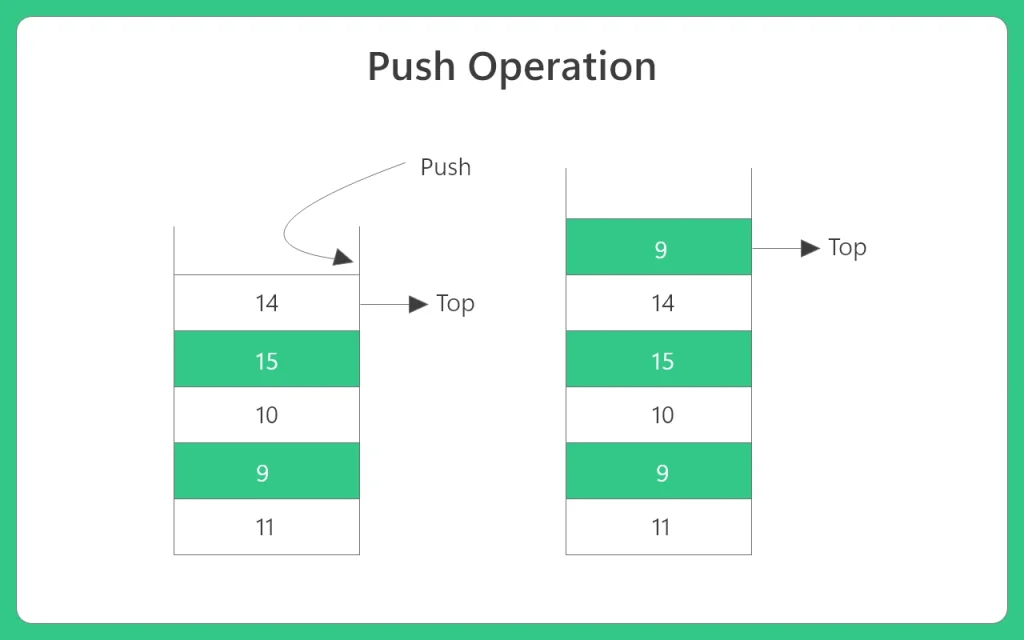
1. Push Operation in Stack
Algorithm:
Push operation consists following two steps:
- Increment Top so that it can now refer to the next memory location.
- Add element at position of incremented top variable . This position is where new element is added.
boolean push (int x)
{
if (top >= (MAX - 1))
{
System.out.println ("Overflow condition reached");
return false;
}
else
{
a[++top] = x;
System.out.println (x + " pushed into stack");
return true;
}
}
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
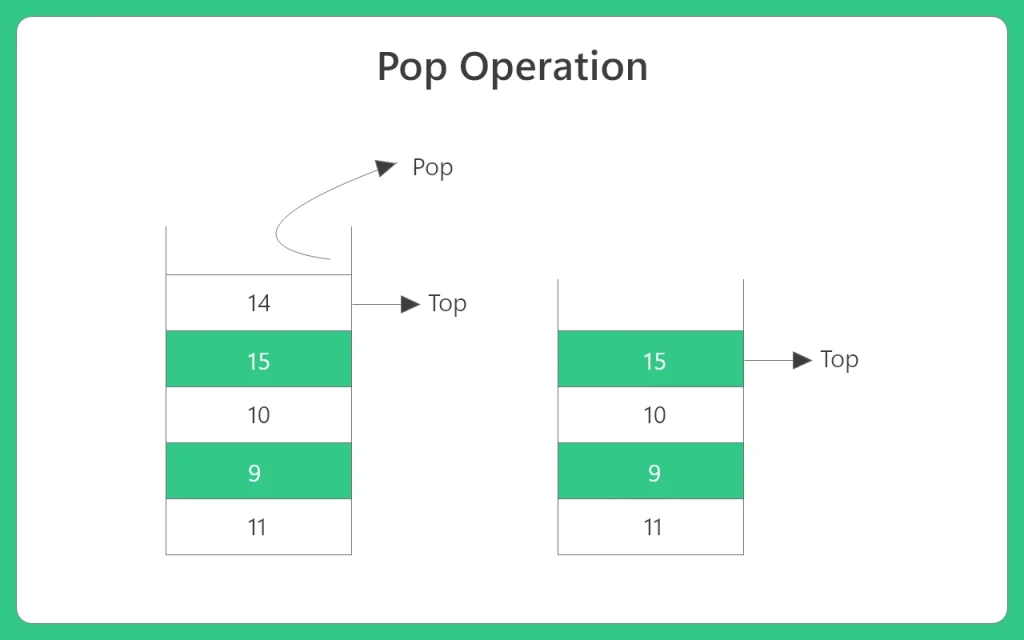
2. Pop Operation in Stack
Algorithm:
Pop operation is used to delete element from top if the stack see code below.
int pop()
{
if (top < 0) {
System.out.println(“Underflow condition reached”);
return 0;
}
else {
int x = a[top–];
return x;
}
} 3. Peek Operation in Stack
Algorithm:
- Peek operation used to return the element which is present at the top of the stack but it does not delete it .
- Underflow condition occur when we try to return the top element in empty stack.
int peek()
{
if (top < 0) {
System.out.println(“Underflow condition”);
return 0;
}
else {
int x = a[top];
return x;
}
} Code to Implement Stack in Java:
// Java program to implement stack operations using array
class Stack {
static final int MAX = 100; // Maximum size of stack
int top;
int[] arr = new int[MAX];
// Constructor
Stack() {
top = -1;
}
// Check if stack is empty
boolean isEmpty() {
return (top < 0);
}
// Push operation
boolean push(int x) {
if (top >= MAX - 1) {
System.out.println("Stack Overflow");
return false;
} else {
arr[++top] = x;
System.out.println(x + " pushed into stack");
return true;
}
}
// Pop operation
int pop() {
if (top < 0) {
System.out.println("Stack Underflow");
return -1;
} else {
return arr[top--];
}
}
// Peek operation
int peek() {
if (top < 0) {
System.out.println("Stack is Empty");
return -1;
} else {
return arr[top];
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stk = new Stack();
stk.push(20);
stk.push(40);
stk.push(60);
System.out.println("Element popped: " + stk.pop());
System.out.println("Top element is: " + stk.peek());
}
}
Output : 20 pushed into stack 40 pushed into stack 60 pushed into stack element poped out : 60
FAQ's Related to Stack in Java
Answer:
A stack is a linear data structure based on LIFO order where insertion and removal happen from the top.
Answer:
The core operations are push, pop, peek, isEmpty, and size.
Answer:
ArrayDeque<E> is considered the best modern stack implementation.
Answer:
Yes, an array based stack can overflow if it exceeds its size. Linked list and ArrayDeque stacks grow dynamically.
Answer:
Stacks are used in recursion, undo redo systems, expression evaluation, parsing, backtracking, and memory management.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment