JAVA Program for Deletion in Doubly Linked List
Deletion in Doubly Linked List in Java
Java Program for Deletion in Doubly Linked List in Java is an important data structure problem that deals with removing a node from a doubly linked list while maintaining both forward and backward links. Since each node points to both the previous and the next node, deletion becomes more controlled compared to a singly linked list but also requires more careful pointer updates.

Java Program for Deletion in Doubly Linked List
What is Deletion in a Doubly Linked List?
A doubly linked list contains nodes with three parts:
- prev (pointer to the previous node)
- next (pointer to the next node)
Deletion means removing a specific node from the list and reconnecting the surrounding nodes so the list remains intact.
Example:
Original list:
10 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 30 ⇆ 40
Delete node 30
Result:
10 ⇆ 20 ⇆ 40
Next pointer of 20 is connected to 40 and the prev pointer of 40 is connected to 20.
Depending on the position, deletion can be done in three main ways:
- Deletion from the beginning
- Deletion from the end
- Deletion from a given position (Nth node)
Understanding Deletion in a Doubly Linked List in Java helps you learn:
- How bidirectional pointers work?
- How to safely remove nodes?
- Edge case handling. (first node, last node, middle node)
- Memory cleanup through reference removal.
- Efficient list manipulation for real time systems.
Basic rules for deletion:
- If deleting the first node, move the head to head.next
- If deleting the last node, update tail.prev.next = null
- If deleting a middle node, link prev.next with next and next.prev with prev.
Methods for Deletion in a Doubly Linked List using Java
Here we have mentioned 3 different ways for Deletion in a Doubly Linked List in Java:
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Method for Deletion in a Doubly Linked List using Java
Method 1: Deletion at the Beginning
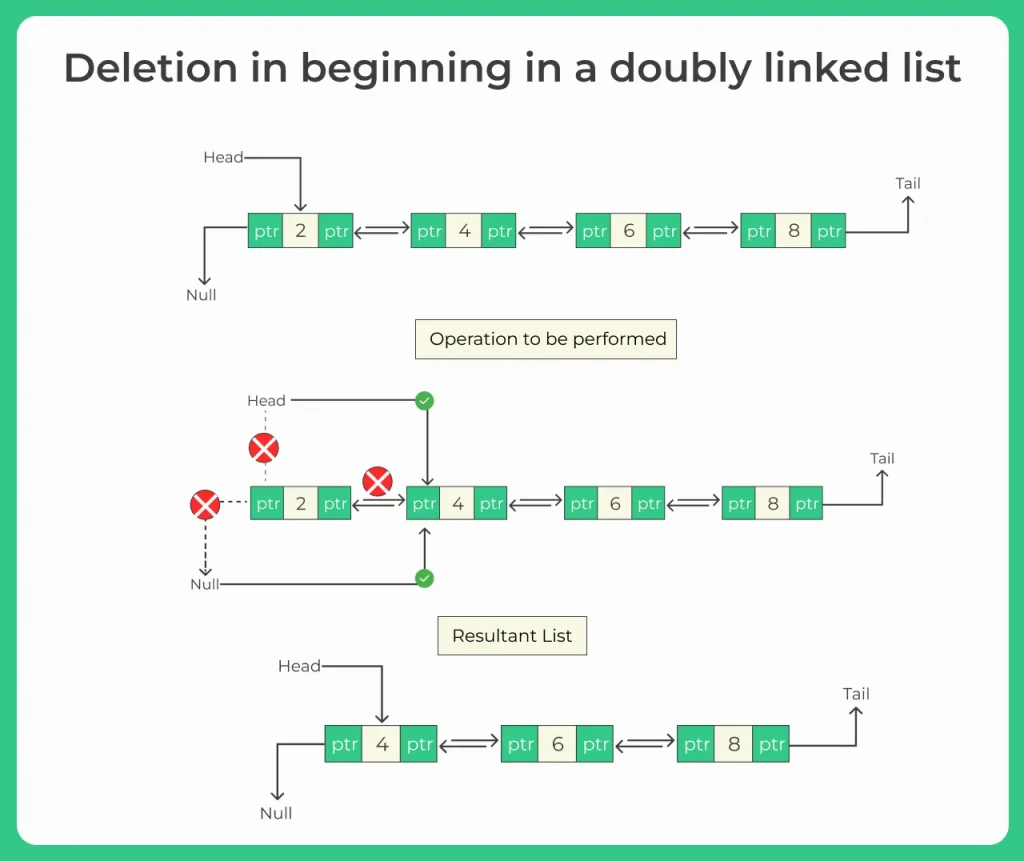
Algorithm:
- If head == null, return null (list is empty)
- If head.next == null, return null (only one node)
- Move head = head.next
- Set head.prev = null
- Return updated head
Java Code:
class DeleteBeginningDoubly {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public static Node deleteAtBeginning(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(10);
Node second = new Node(20);
Node third = new Node(30);
head.next = second;
second.prev = head;
second.next = third;
third.prev = second;
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
printList(head);
head = deleteAtBeginning(head);
System.out.println("After deletion from beginning:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
10 20 30
Output:
10 20
Space Complexity: O(1)
Method for Deletion in a Doubly Linked List in Java
Method 2: Deletion at the End
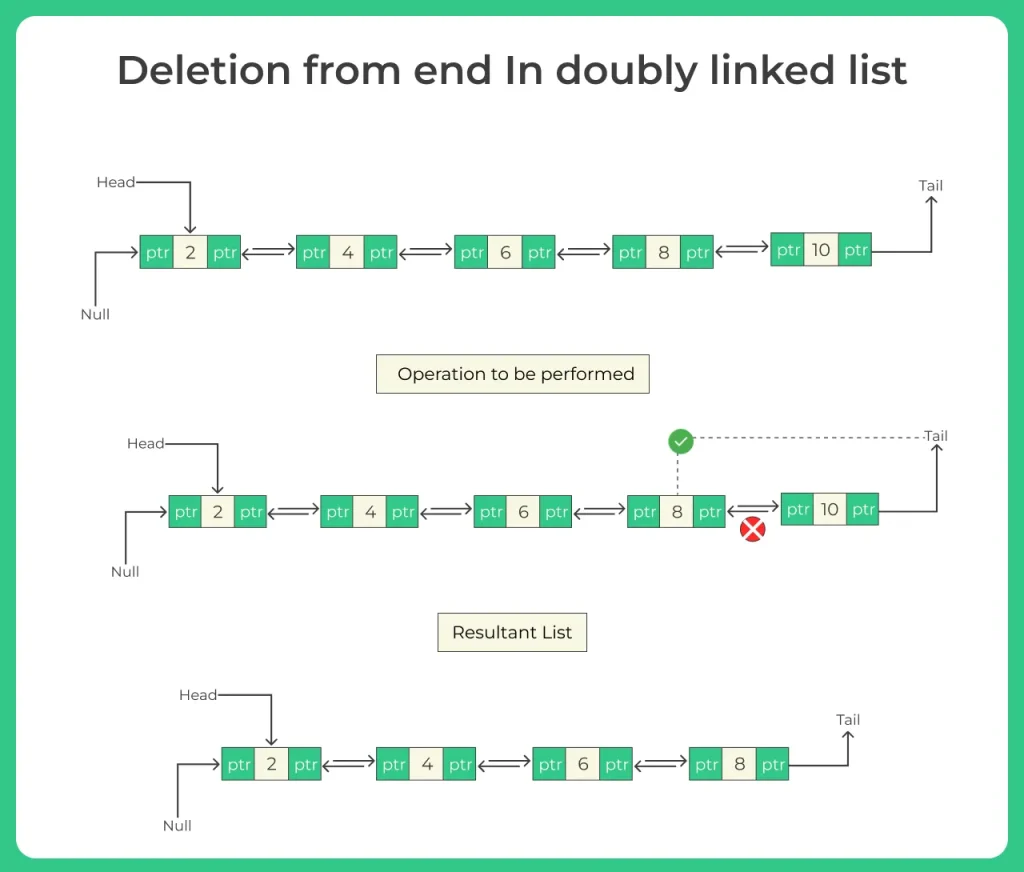
Algorithm:
- If head == null, return null
- If head.next == null, return null
- Traverse to the last node using temp
- Set temp.prev.next = null
- Set temp.prev = null
- Return head
Java Code:
class DeleteEndDoubly {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public static Node deleteAtEnd(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.prev.next = null;
temp.prev = null;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(5);
Node second = new Node(15);
Node third = new Node(25);
head.next = second;
second.prev = head;
second.next = third;
third.prev = second;
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
printList(head);
head = deleteAtEnd(head);
System.out.println("After deletion from end:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
10 20 30
Output:
10 20
Space Complexity: O(1)
Method 3: Deletion at the Nth Position
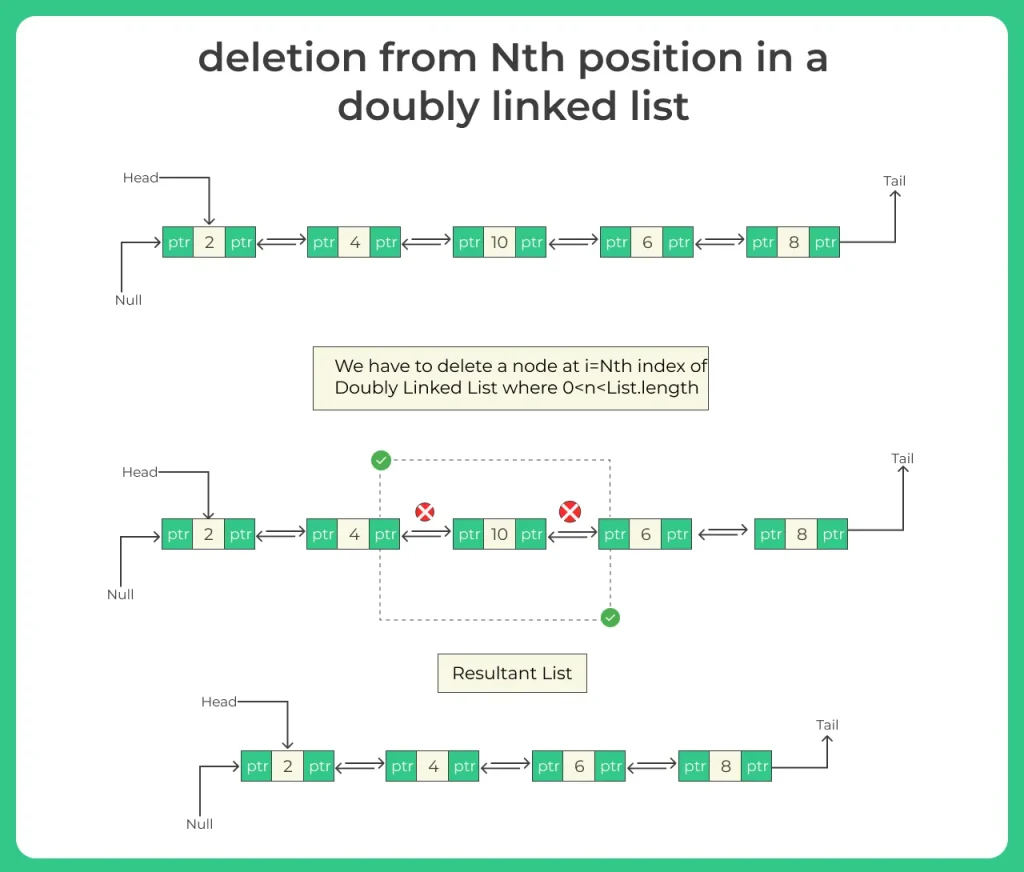
Algorithm:
- If list is empty, return null
- If position == 1, call delete at beginning
- Traverse to the Nth node using temp
- If temp == null, position is invalid
- If temp.next != null, set temp.next.prev = temp.prev
- If temp.prev != null, set temp.prev.next = temp.next
- Disconnect temp
- Return head
class DeleteNthDoubly {
static class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public static Node deleteAtPosition(Node head, int position) {
if (head == null) return null;
if (position == 1) {
if (head.next != null) {
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
} else {
return null;
}
return head;
}
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i < position && temp != null; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp == null) return head;
if (temp.next != null) {
temp.next.prev = temp.prev;
}
if (temp.prev != null) {
temp.prev.next = temp.next;
}
temp.next = null;
temp.prev = null;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(10);
Node second = new Node(20);
Node third = new Node(30);
Node fourth = new Node(40);
head.next = second;
second.prev = head;
second.next = third;
third.prev = second;
third.next = fourth;
fourth.prev = third;
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
printList(head);
head = deleteAtPosition(head, 3);
System.out.println("After deleting 3rd node:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
10 20 30 40 Position: 3
Output:
10 20 40
Space Complexity: O(1)
Comparison between both methods:
| Deletion Type | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| From Beginning | O(1) | O(1) |
| From End | O(n) | O(1) |
| From Nth Position | O(n) | O(1) |
Deletion in a doubly linked list is a critical operation that highlights the true power of bidirectional pointer structures.
- By maintaining both prev and next references, a node can be removed safely without needing to traverse backward from the start.
- Whether deleting from the beginning, end, or a specific position, the key lies in updating the adjacent node connections correctly.
- This operation exposes the core behavior of dynamic memory structures and reinforces how local pointer changes can restructure large parts of the list efficiently.
Understanding Deletion in a Doubly Linked List in Java not only strengthens linked list concepts but also prepares you for designing efficient data handling systems used in real world applications.
FAQ's for Deletion in a Doubly Linked List
Answer:
Deletion in a doubly linked list means removing a node and updating both prev and next pointers of adjacent nodes.
Answer:
Deletion at the beginning is easiest because it only requires updating the head pointer.
Answer:
Yes, especially when deleting middle nodes, because backward links help in pointer adjustment.
Answer:
The list becomes empty and the head becomes null.
Answer:
It is used in browser history, undo redo operations, playlist management, and system navigation apps.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment