Insertion in Doubly Linked List in C++
What is insertion in doubly linked list in C++ programming?
Insertion in Doubly Linked List in C++ refers to the process of adding a new node to an existing doubly linked list. In C++ programming, this can be done in three main way, depending on where you want to insert the new node:
- Insertion at the beginning of the doubly linked list
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list
- Insertion at the end of the doubly linked list
Each method updates the pointers of the neighboring nodes to maintain the bidirectional link structure of the list.
Types of Insertion in Doubly Linked List
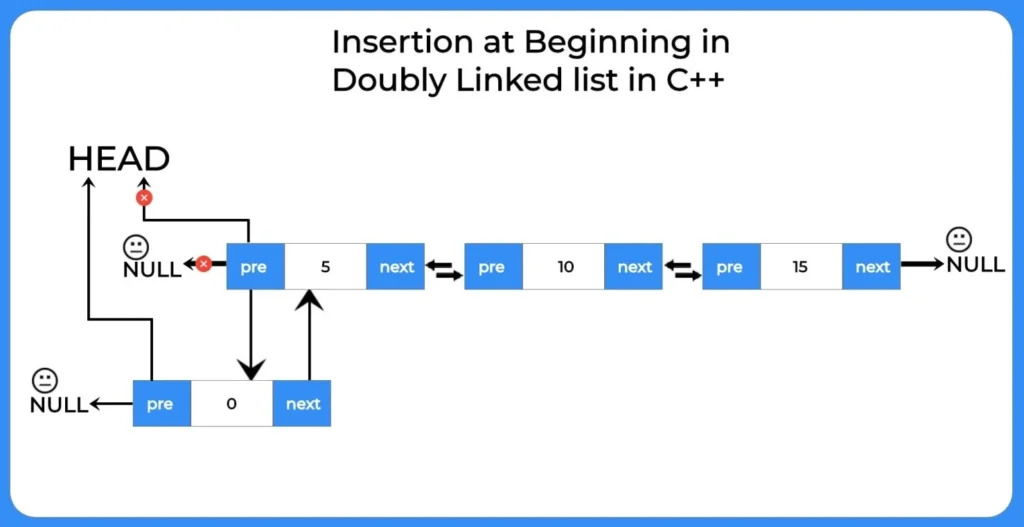
Insertion at Beginning
In this type of insertion in doubly linked list a new node is added before the head of the list i.e. before the first node of the list.
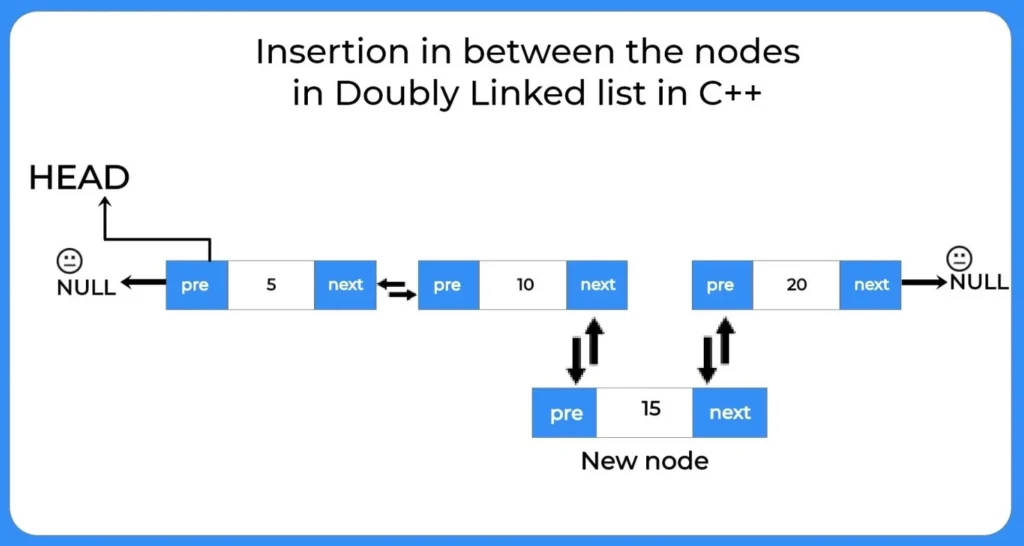
Insertion at specific position
Here we insert a new node at specific position by traversing till the desired position and inserting new node there.
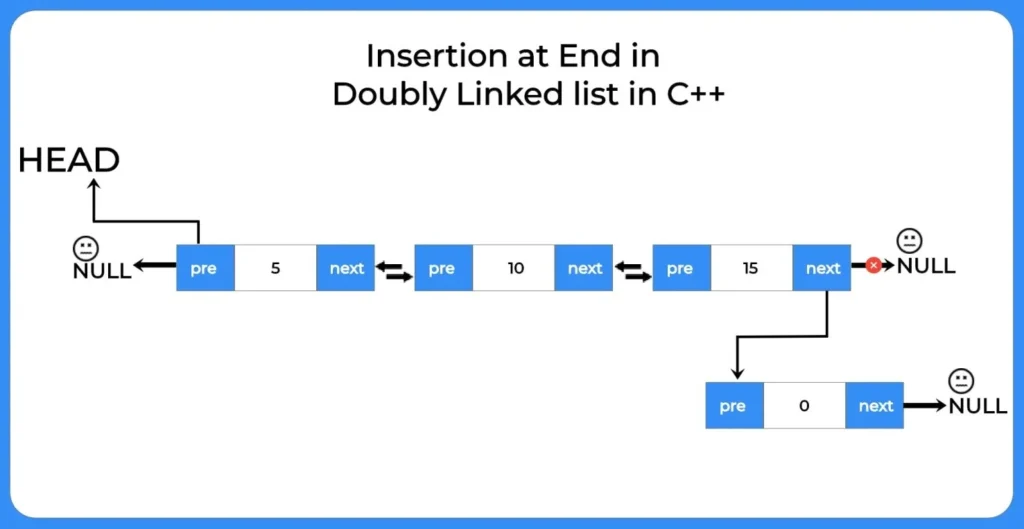
Insertion at end
We insert new node after the last node i.e. after the tail node in the insertion at end doubly linked list.
- You need efficient forward and backward traversal.
- Frequent insertions and deletions are required at both ends or middle of the list.
- You are implementing complex data structures like navigation systems, MRU/LRU caches, or undo-redo functionality.
How to perform insertion at beginning in doubly linked list?
To perform insertion at beginning in doubly linked list we will use the following steps:-
- We will allocate space for the new node at the beginning of the list
- After that we will built a new node on the space created.
- Now we will insert data in the newly created node.
void insertNodeAtBeginning(int num)
{
struct node * newnode;
if(stnode == NULL)
{
cout<<" No data found in the list\n"; } else { newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = stnode;
newnode->preptr = NULL;
stnode->preptr = newnode;
stnode = newnode;
}
}

Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
How to perform insertion at specific position in doubly linked list?
To perform insertion at specific position in doubly linked list we will use the following steps:-- We will traverse till the specific position in the list.
- We will insert a node here by changing linking the next pointer of the previous node to new node.
- Also we will linked the previous pointer of next node with the new node.
void insertSpecific(int num, int pos)
{
int i;
struct node * newnode, *tmp;
if(ennode == NULL)
{
cout<<" No data found in the list!\n";
}
else
{
tmp = stnode;
i=1;
while(inextptr;
i++;
}
if(tmp!=NULL)
{
newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = tmp->nextptr;
newnode->preptr = tmp;
if(tmp->nextptr != NULL)
{
tmp->nextptr->preptr = newnode;
}
tmp->nextptr = newnode;
}
else
{
cout<<" The position you entered, is invalid.\n";
}
}
}
How to perform insertion at end in singly linked list?
To perform insertion at end in singly linked list we will use the following steps:- After creating a linked list with some data in it we will :-- Use a pointer to traverse till the end of the list.
- After that we will create a new node after the last node.
- Insert the data that you want to enter by putting it in the node.
void insertNodeAtEnd(int num)
{
struct node * newnode;
if(ennode == NULL)
{
cout<<" No data found in the list!\n"; } else { newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); newnode->num = num;
newnode->nextptr = NULL;
newnode->preptr = ennode;
ennode->nextptr = newnode;
ennode = newnode;
}
}
Example: Insertion in Doubly Linked List
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
Node(int val) : data(val), prev(nullptr), next(nullptr) {}
};
void insertAtEnd(Node*& head, int val) {
Node* newNode = new Node(val);
if (!head) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node* temp = head;
while (temp->next) temp = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = temp;
}
void display(Node* head) {
while (head) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
Node* head = nullptr;
insertAtEnd(head, 10);
insertAtEnd(head, 20);
insertAtEnd(head, 30);
display(head); // Output: 10 20 30
return 0;
}
Output
10 20 30This example is concise and demonstrates:
- Creating a doubly linked list
- Inserting nodes at the end
- Displaying the list
Explanation:
- A Node structure is defined with three members data, prev, and next, along with a constructor for easy initialization.
- The function insertAtEnd() inserts a new node at the end of the doubly linked list by traversing till the last node and linking the new node accordingly.
- If the list is empty, the new node becomes the head of the list.
- The display() function traverses the list from the head node and prints all elements sequentially.
- In main(), three nodes with values 10, 20, and 30 are inserted, and the final list is displayed as 10 20 30.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at End | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall Program | O(n) | O(n) |
Key Takeaways
Insertion in a doubly linked list in C++ allows efficient addition of nodes at the beginning, end, or any specific position in the list. It maintains bidirectional links by properly updating the prev and next pointers of involved nodes, making it ideal for applications requiring quick and flexible data manipulation.
FAQs
Insertion can be done at the beginning, at a specific position, or at the end of the list.
It supports two-way traversal and efficient insertions/deletions from both ends.
Create a new node, point its next to the current head, update head’s prev, and make it the new head.
Traverse to the desired position, link the new node between the previous and next nodes by updating their pointers.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others



Login/Signup to comment