Java Program to Reverse a Queue
Reverse a Queue in Java
Java Program to Reverse a Queue is a common problem that helps you understand how queues interact with other data structures like stacks and recursion. Since a queue follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle, reversing it means changing the order so that the last element becomes the first.
This problem is frequently asked in interviews and is useful for mastering queue manipulation in Java.
Here you will learn different ways to reverse a queue, including algorithms, Java programs, example input/output, time and space complexity, and important tips.
What is Reversing a Queue means?
Queue stores elements in FIFO order.
Example:
1. Original Queue:
10 20 30 40
2. After reversing:
40 30 20 10
So, reversing a queue means changing its order completely.
2. Scheduling systems
3. Palindrome checking
4. Data reordering
Methods to Reverse a Queue in Java
Here we will study about 4 methods for Reverse a Queue in Java:
Each method includes Concept, Algorithm, Java Code, Input/Output and Time & Space Complexity.
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods to Reverse a Queue in Java
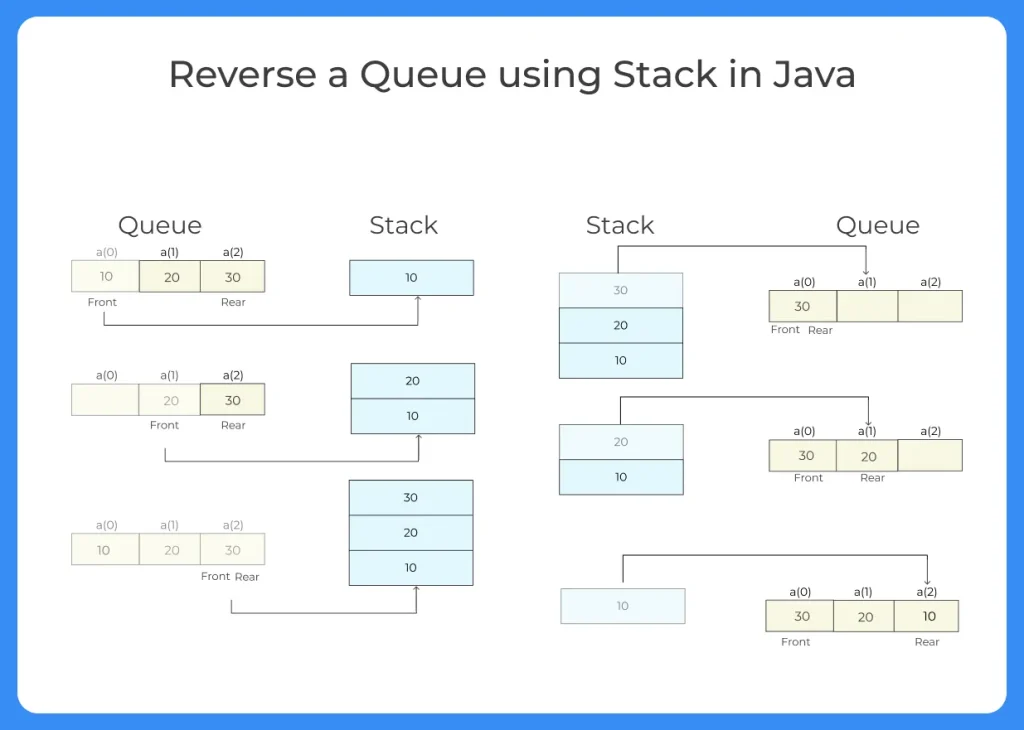
Method 1: Reverse Queue Using Stack
Steps:
- Remove all elements from the queue
- Push them into a stack
- Pop from stack and insert back into queue
Since a stack follows LIFO, it automatically reverses the order. This is the most common and easiest method.
Algorithm:
- Create an empty stack.
- While queue is not empty:
- Remove element and push into stack.
- While stack is not empty:
- Pop element and insert into queue.
Java Code to Reverse a Queue
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class ReverseQueueUsingStack {
public static void reverseQueue(Queue queue) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// Step 1: Move queue elements to stack
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
stack.push(queue.poll());
}
// Step 2: Move stack elements back to queue
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
queue.offer(stack.pop());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(10);
queue.offer(20);
queue.offer(30);
queue.offer(40);
System.out.println("Original Queue: " + queue);
reverseQueue(queue);
System.out.println("Reversed Queue: " + queue);
}
}
Input:
10 20 30 40
Output:
Original Queue: [10, 20, 30, 40] Reversed Queue: [40, 30, 20, 10]
Space Complexity: O(n)
Method to Reverse a Queue in Java
Method 2: Reverse Queue Using Recursion
Steps:
In this method, recursion is used instead of a stack. This works because recursion uses the call stack internally.
- Remove front element
- Recursively reverse remaining queue
- Insert removed element at rear.
Note: May cause stack overflow for very large queues.
Algorithm:
- If queue is empty
- Return
- Remove front element
- Reverse remaining queue recursively
- Insert removed element at rear
Java Code to Reverse a Queue
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class ReverseQueueUsingRecursion {
public static void reverseQueue(Queue queue) {
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
int front = queue.poll();
reverseQueue(queue);
queue.offer(front);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(5);
queue.offer(15);
queue.offer(25);
queue.offer(35);
System.out.println("Original Queue: " + queue);
reverseQueue(queue);
System.out.println("Reversed Queue: " + queue);
}
}
Input:
5 15 25 35
Output:
Original Queue: [5, 15, 25, 35] Reversed Queue: [35, 25, 15, 5]
Space Complexity: O(n)
Method to Reverse a Queue in Java
Method 3: Reverse Queue Using Java Collections
Java provides utility methods in Collections class that can reverse a list.
- Since LinkedList implements both Queue and List, we can use this feature.
- This is the shortest method.
- Works only when using LinkedList (not with all queue types).
Algorithm:
- Create queue using LinkedList
- Use Collections.reverse(queue)
Java Code
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class ReverseQueueUsingCollections {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
System.out.println("Original Queue: " + queue);
Collections.reverse(queue);
System.out.println("Reversed Queue: " + queue);
}
}
Input:
1 2 3 4
Output:
Original Queue: [1, 2, 3, 4] Reversed Queue: [4, 3, 2, 1]
Space Complexity: O(1)
Before reversing a queue, check:
- Queue is not null
- Queue is not empty
- Recursion depth is safe
- Correct data type is used
Example:
if (queue == null || queue.isEmpty())
return;
Comparison of All Methods
| Method | Extra Space | Time | Space |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stack | Yes | O(n) | O(n) |
| Recursion | Yes | O(n) | O(n) |
| Collections | No | O(n) | O(1) |
Frequently Asked Questions
Answer:
It is a program that changes the order of elements in a queue so that the last element becomes first.
Answer:
Using a stack is the most common and safest method for reversing a queue.
Answer:
All standard methods take O(n) time.
Answer:
Using Collections.reverse() on LinkedList works in place, but most methods need extra space.
Answer:
Yes, for learning, but not recommended for very large queues due to stack overflow risk.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Stacks
- Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
Click Here - Operations on a Stack
Click Here - Stack: Infix, Prefix and Postfix conversions
Click Here - Stack Representation in –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as an Array. –
C | C++ | Java - Representation of a Stack as a Linked List. –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to Postfix Conversion –
C | C++ | Java - Infix to prefix conversion in –
C | C++ | Java - Postfix to Prefix Conversion in –
C | C++ | Java
Queues
- Queues in Data Structures (Introduction)
Click Here - Queues Program in C and implementation
Click Here - Implementation of Queues using Arrays | C Program
Click Here - Types of Queues in Data Structure
Click Here - Application of Queue Data Structure
Click Here - Insertion in Queues Program (Enqueuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Deletion (Removal) in Queues Program(Dequeuing) –
C | C++ | Java - Reverse a Queue –
C | C++ | Java - Queues using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using Stack –
C | C++ | Java - Implement Queue using two Stacks –
C | C++ | Java
Circular Queues
- Circular queue in Data Structure
Click Here - Applications of Circular Queues
Click Here - Circular queue in –
C | C++ | Java - Circular queue using Array –
C | C++ | Java - Circular Queue using Linked Lists –
C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment