Deletion from the End of a Circular Linked List in Java
Java Program for Deletion from the End of a Circular Linked List
In this article, we will learn about Deletion from the End of a Circular Linked List in Java an important operation in linked list manipulation. Circular linked list is a special type of linked list where the last node points back to the first node, forming a closed loop.
Understanding how to delete a node from the end of a circular linked list is crucial because it helps in efficient memory management and is frequently used in problems involving circular queues, scheduling, or data buffering.

Deletion from the End of a Circular Linked List in Java
Problem Statement:
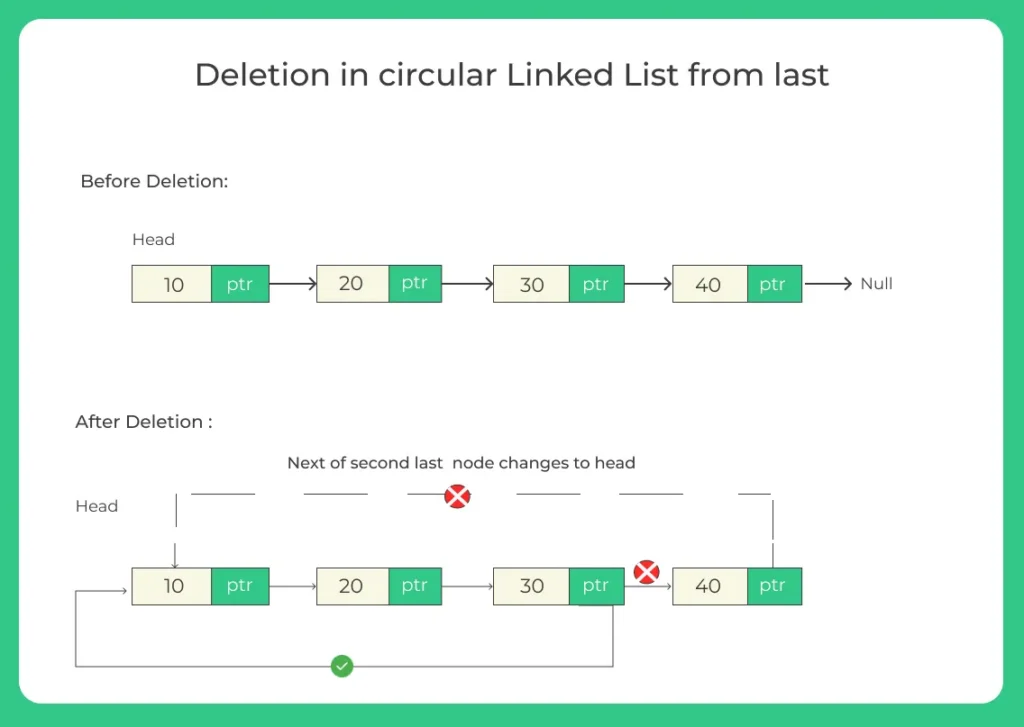
We need to delete the last node of a circular linked list. Let’s take an example:
Example:
1. Initial Circular Linked List:
10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 -> (back to 10)
2. After deleting the last node (40):
10 -> 20 -> 30 -> (back to 10)
Algorithm Deletion from the End of a Circular Linked List in Java
Step 1: Handle Edge Cases
Before performing deletion, check for:
- If the list is empty → Nothing to delete.
- If the list has only one node → Delete it and make head = null.
Step 2: Traverse the List
Use two pointers:
- temp → used to move through nodes
- prev → used to track the node before temp
Traverse the list until temp.next == head (which means temp is the last node).
Step 3: Delete the Last Node
- Change prev.next to point to head (this skips the last node).
- The node pointed to by temp (last node) is deleted.
Algorithm:
Algorithm deleteFromEnd()
1. If head == null
print "List is empty"
return
2. If head.next == head
head = null
return
3. Initialize temp = head
Initialize prev = null
4. While temp.next != head
prev = temp
temp = temp.next
5. prev.next = head
temp = null // free last node
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Java Code for Deletion from the End in a Circular Linked List
Below is the complete executable Java program with example input and output:
public class CircularLinkedListDeletion {
// Node structure
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
static Node head = null;
// Function to insert a node at the end
public static void insertAtEnd(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
newNode.next = head; // circular connection
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != head) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
}
// Function to delete a node from the end
public static void deleteFromEnd() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty. Deletion not possible.");
return;
}
// If only one node
if (head.next == head) {
head = null;
System.out.println("Last node deleted. List is now empty.");
return;
}
Node temp = head;
Node prev = null;
while (temp.next != head) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// 'temp' is the last node, 'prev' is the second last
prev.next = head; // bypass the last node
temp = null; // delete last node
System.out.println("Last node deleted successfully.");
}
// Function to display the circular linked list
public static void display() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty.");
return;
}
Node temp = head;
System.out.print("Circular Linked List: ");
do {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Inserting nodes
insertAtEnd(10);
insertAtEnd(20);
insertAtEnd(30);
insertAtEnd(40);
System.out.println("Before deletion:");
display();
// Deleting from end
deleteFromEnd();
System.out.println("After deletion:");
display();
}
}
Output:
Before deletion: Circular Linked List: 10 20 30 40 Last node deleted successfully. After deletion: Circular Linked List: 10 20 30
Time and Space Complexity Analysis for Deletion from the end of Circular Linked List in Java
Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deletion from end | O(n) | O(1) | We traverse the list once to find the last node |
| Insertion | O(n) | O(1) | Traversal till end required |
| Display | O(n) | O(1) | Visits each node once |
- In a circular linked list, the last node always points to the head.
- When deleting from the end, ensure that the second last node now points to the head.
- Always handle edge cases such as empty list or single node list.
- Circular linked lists are useful in round robin scheduling, circular buffers, and real time applications.
We explored Deletion from the End of a Circular Linked List in java with a clear step by step explanation, algorithm, and complete Java implementation.
By understanding this concept, you can handle node manipulation efficiently in circular structures, which are common in many real world scenarios like scheduling systems and circular queues.
FAQ's Related to Deletion from the End of a Circular Linked List
Answer:
Circular linked list in Java is a data structure where the last node points back to the first node, forming a loop. It can be singly or doubly linked.
Answer:
To delete from the end, traverse the list using two pointers until you reach the last node, then make the previous node’s next pointer point to the head.
Answer:
Time complexity is O(n) because you must traverse the list to find the last node.
Answer:
If the list is empty, there’s no node to delete, and the operation should safely handle this condition by displaying a message or returning null.
Answer:
Circular linked lists are efficient for applications that require continuous looping, such as buffering data, playlist rotations, or round robin scheduling.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment