Deletion from Beginning of a Circular Linked List in Java
Deletion from Beginning of Circular Linked List in Java
In this article, we will focus on a specific operation, Deletion from Beginning of Circular Linked List using Java.
In the world of data structures, linked lists play a crucial role in efficiently organizing and managing dynamic sets of data. Among the various types of linked lists, the Circular Linked List (CLL) stands out due to its circular nature, where the last node points back to the first node.

Deletion from Beginning of Circular Linked List using Java
1. Each node contains data and a pointer to the next node.
2. The last node’s next pointer points back to the first node, forming a circle.
There is no NULL at the end, which allows continuous traversal.
Example:
head → 10 → 20 → 30 →
↑ ↓
← ← ← ← ← ← ←
Problem Statement: Deletion from Beginning of a Circular Linked List.
The goal is to delete the first node of a circular linked list while maintaining the circular property.
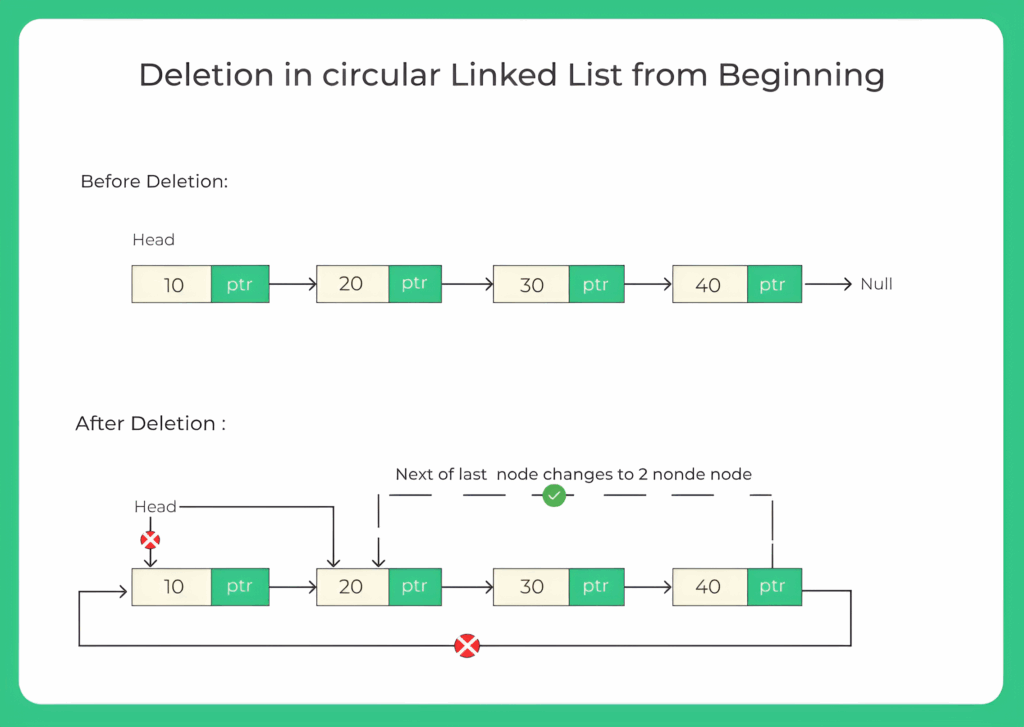

Deletion from Beginning of a Circular Linked List Approach Overview:
We’ll explore the following methods:
Each method will maintain the circular link after deletion and update the head node accordingly.
Algorithm for Deletion from beginning:
Let’s assume we have:
- A class Node that holds data and next reference.
- A tail node pointing to the last node in the list (so tail.next is the head).
Case 1: Deletion When Only One Node is Present
- If tail.next == tail, it means the list has only one node.
- After deletion, set tail = null.
Case 2: Deletion When Multiple Nodes are Present
- Set tail.next = tail.next.next to skip the head node.
- This effectively deletes the first node.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Method 1: Single Node Case for Deletion from beginning
public class SingleNodeCircularList {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
private Node tail;
// Insert single node only
public void insert(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
tail = newNode;
tail.next = tail;
}
public void display() {
if (tail == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty.");
return;
}
System.out.print(tail.data + " ");
System.out.println();
}
public void deleteFromBeginning() {
if (tail == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty. Nothing to delete.");
} else if (tail.next == tail) {
System.out.println("Deleted node: " + tail.data);
tail = null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleNodeCircularList cll = new SingleNodeCircularList();
cll.insert(100);
System.out.println("Original List:");
cll.display();
cll.deleteFromBeginning();
cll.display();
cll.deleteFromBeginning(); // extra deletion
}
}
Input:
insert(100)
Output:
Original List:
100
Deleted node: 100
List is empty.
List is empty. Nothing to delete.
Time Complexity: O(1)
Method 2: Multiple Node Case (Using Tail Reference)
public class MultiNodeCircularList {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
private Node tail;
public void insert(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (tail == null) {
tail = newNode;
tail.next = tail;
} else {
newNode.next = tail.next;
tail.next = newNode;
tail = newNode;
}
}
public void display() {
if (tail == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty.");
return;
}
Node temp = tail.next;
do {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != tail.next);
System.out.println();
}
public void deleteFromBeginning() {
if (tail == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty. Nothing to delete.");
} else if (tail.next == tail) {
System.out.println("Deleted node: " + tail.data);
tail = null;
} else {
Node head = tail.next;
System.out.println("Deleted node: " + head.data);
tail.next = head.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiNodeCircularList cll = new MultiNodeCircularList();
cll.insert(10);
cll.insert(20);
cll.insert(30);
cll.insert(40);
System.out.println("Original List:");
cll.display();
cll.deleteFromBeginning();
cll.display();
cll.deleteFromBeginning();
cll.display();
}
}
Input:
insert(10), insert(20), insert(30), insert(40)
Output:
Original List: Original List: 10 20 30 40 Deleted node: 10 20 30 40 Deleted node: 20 30 40
Time Complexity: O(1)
Conclusion….
Understanding how to delete a node from the beginning of a circular linked list is crucial for mastering dynamic data structures.
- In this guide, we broke down the concept, provided multiple scenarios, implemented the solution in Java, and explained the steps with examples.
- By practicing such basic yet powerful operations, you lay a strong foundation for solving more complex problems in data structures and algorithms.
FAQ's related to Deletion from Beginning of Circular Linked List
Answer:
A circular linked list in Java is a linked list where the last node points back to the first node, forming a circular chain. It allows continuous traversal and is used in scenarios like CPU scheduling or buffering.
Answer:
You can delete the first node by updating the tail’s next pointer to the second node (tail.next = tail.next.next). This effectively removes the reference to the original head node.
Answer:
Yes, deletion from the beginning in a circular linked list is efficient with a time complexity of O(1). It involves just one pointer update.
Answer:
Yes, you can use a head reference, but using a tail makes some operations (like insertion at end and deletion from beginning) easier and more efficient.
Answer:
Yes, Java’s garbage collector automatically reclaims memory for unreferenced objects. When a node is removed from the list and has no references pointing to it, it’s eligible for garbage collection.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment