Count Total Nodes in Circular Linked List
Java Program to Count the Number of Nodes in a Circular Linked List
In this page, we’ll take a look at a program to Count Total Nodes in Circular Linked List in Java, a loop is required until the very first element reappears. Circular linked lists have a head and tail.
In this article, we will focus on counting the total number of nodes present in a circular singly linked list using Java. The task involves traversing the list while maintaining a counter until we reach the starting node again.

One Loop iterates through the entire list and increases the value of a counter variable for every passing node.
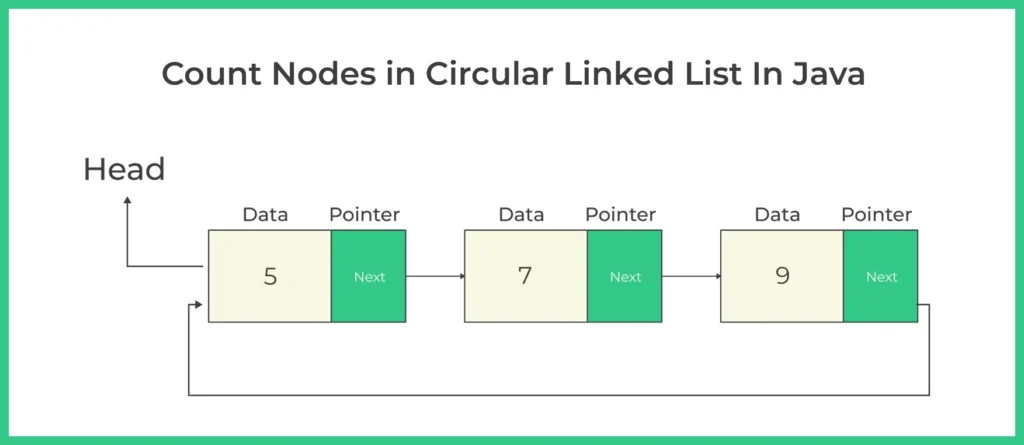
Understanding Circular Linked List
In a singly circular linked list, each node contains two parts:
- data: The value stored in the node
- next: Reference to the next node
In contrast to a singly linked list where the last node’s next is null, in a circular linked list, the last node’s next points back to the head node.
Problem Statement:
Given the head of a circular singly linked list, write a program to count the total number of nodes in the list.
Algorithm:
To count the total nodes in a circular linked list, follow the below steps:
Step by Step Algorithm:
- Check if head is null: If the list is empty, return count as 0
- Initialize a counter: Set count = 1 since the head is the first node
- Create a temporary pointer: Let current = head.next
- Traverse the list until we reach head again
- While current != head
- Increment count
- Move current to current.next
Return the counter value.
Code Implementation:
// Node class definition
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
// CircularLinkedList class
public class CircularLinkedList {
Node head;
// Function to add a node to the circular linked list
public void addToEmpty(int data) {
if (head != null)
return;
Node newNode = new Node(data);
head = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
}
public void addNode(int data) {
if (head == null) {
addToEmpty(data);
return;
}
Node newNode = new Node(data);
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != head) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
}
// Function to count nodes in a circular linked list
public int countNodes() {
if (head == null)
return 0;
int count = 1;
Node current = head.next;
while (current != head) {
count++;
current = current.next;
}
return count;
}
// Function to display the list - for verification
public void display() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node temp = head;
do {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
System.out.println();
}
// Main method for testing
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircularLinkedList cll = new CircularLinkedList();
cll.addNode(10);
cll.addNode(20);
cll.addNode(30);
cll.addNode(40);
System.out.print("Circular Linked List: ");
cll.display();
int totalNodes = cll.countNodes();
System.out.println("Total number of nodes: " + totalNodes);
}
}
Output:
Circular Linked List: 10 20 30 40
Total number of nodes: 4
Time Complexity: O(n)
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Code to Count Total Nodes in Circular Linked List in Java
1. Code to Count Total Nodes in Singly Circular Linked List
- It implements a singly circular linked list, where each node contains an element and a next pointer that links to the next node, and the last node connects back to the head.
- It supports adding nodes at the end and traversing the list in a single direction. The countNodes() method uses the next pointer to loop through nodes until it reaches the head again and counts the total number of nodes.
- This structure is memory efficient and suitable for simple circular list operations.
Specifications:
Node:
element,nextCircularity: Single link (last node → head)
Memory: Less usage
Traversal: Forward only
prevpointer: Not present
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Obj = new Main();
Obj.add(10);
Obj.add(20);
Obj.add(30);
Obj.add(40);
Obj.add(50);
Obj.add(60);
Obj.print();
Obj.countNodes();
}
public class Node{
int element;
Node next;
public Node(int element) {
this.element = element;
}
}
int cnt;
static Node list1, list2;
public Node head = null;
public Node tail = null;
public void print() {
Node current = head;
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("Empty List");
}
else {
System.out.println("Circular Linked List is");
do{
//Prints each node by incrementing pointer.
System.out.print(" "+ current.element);
current = current.next;
}while(current != head);
System.out.println();
}
}
public void print(Node head) {
Node current = head;
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("Empty List");
}
else {
System.out.println("Circular Linked List is");
do{
//Prints each node by incrementing pointer.
System.out.print(" "+ current.element);
current = current.next;
}while(current != head);
System.out.println();
}
}
public void add(int element){
Node newNode = new Node(element);
if(head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
}
else {
tail.next = newNode;
tail = newNode;
tail.next = head;
}
}
public void countNodes() {
Node temp = head;
do{
cnt++;
temp = temp.next;
}while(temp != head);
System.out.println("Number of Nodes in the list is "+cnt);
}
}Output
Circular Linked List is 10 20 30 40 50 60 Number of Nodes in the list is 6
2. Code to Count Total Nodes in Doubley Circular Linked List
- It implements a doubly circular linked list, where each node contains an element, a next pointer to the next node, and a prev pointer to the previous node.
- Like Code 1, it adds nodes to the end and connects the last node back to the head, but also links nodes backward.
- However, the prev pointer is initialized but not utilized in traversal or other operations.
- The list is capable of bi directional traversal and easier deletion operations if extended.
Specifications:
Node:
element,next,prevCircularity: Double link (last node → head, head → last node)
Memory: More usage (due to
prev)Traversal: Forward (only implemented), reverse possible
prevpointer: Present but unused
Code:
import java.lang.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Obj = new Main();
Obj.add(10);
Obj.add(20);
Obj.add(30);
Obj.add(40);
Obj.add(50);
Obj.add(60);
System.out.println("Original List");
Obj.print();
Obj.countNodes();
}
public class Node{
int element;
Node next;
Node prev;
public Node(int element) {
this.element = element;
}
}
int cnt;
static Node list1, list2;
public Node head = null;
public Node tail = null;
public void print() {
Node temp = head;
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("null");
}
else {
do{
System.out.print(" "+ temp.element);
temp = temp.next;
}while(temp != head);
System.out.println();
}
}
public void add(int element){
Node newNode = new Node(element);
if(head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
newNode.prev=head;
}
else {
tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev=tail;
tail = newNode;
tail.next = head;
}
}
public void print(Node head) {
Node current = head;
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("Empty List");
}
else {
System.out.println("Circular Linked List is");
do{
//Prints each node by incrementing pointer.
System.out.print(" "+ current.element);
current = current.next;
}while(current != head);
System.out.println();
}
}
public void countNodes() {
Node temp = head;
do{
cnt++;
temp = temp.next;
}while(temp != head);
System.out.println("Number of Nodes in the list is "+cnt);
}
}
Output
Original List 10 20 30 40 50 60 Number of Nodes in the list is 6
Conclusion
- Counting the total number of nodes in a circular linked list involves careful traversal to detect when we loop back to the starting node.
- The key difference from linear linked list traversal is the stopping condition.
- This concept is fundamental when working with circular data structures in areas like memory management, scheduling, and real time systems.
Learn DSA
FAQ's related to Segregate 0s and 1s in an array
Answer:
To count nodes in a circular linked list in Java, start at the head node and use a loop to traverse using the next pointer. Increment a counter at each step, and stop when you reach the head again.
A do while loop is recommended to ensure at least one iteration even if the list contains a single node.
Answer:
- do while loop is preferred because in a circular linked list, the last node connects back to the head, and we must process the head before checking the condition.
- while loop might skip the only node in a single node list if not carefully written.
Answer:
- Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes
- Space Complexity: O(1), since no additional data structures are used
Answer:
Yes, the counter (e.g., cnt) should be reset to 0 at the beginning of the countNodes() method. If not reset, calling the method multiple times will result in an incorrect count due to accumulation from previous executions.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment