Deletion in Circular Linked List in Java
Java Program to Delete a Node of a Circular Linked List
In this Deletion in Circular Linked List in Java Programming article, we will explore deletion operations in a circular singly linked list (CSLL) using Java. We’ll examine all possible deletion scenarios, analyze time and space complexity, provide complete code examples, and highlight important and interesting facts about circular linked lists.
Circular linked list is a variation of the linked list in which the last node points back to the head instead of null. This circular nature offers certain advantages, especially in applications where continuous traversal is desired, such as in scheduling algorithms, real time applications, and buffering data structures.

Types of Deletion in Circular Linked List
In a circular linked list, deletion can be categorized into the following types:
Structure of a Circular Linked List:
Each node in a singly circular linked list has:
- data: the value it stores
- next: a reference to the next node
In the last node, instead of next = null (as in a regular singly linked list), we set next = head, completing the circle.
From now on you will get to know about Deletion in Circular Linked using Java:
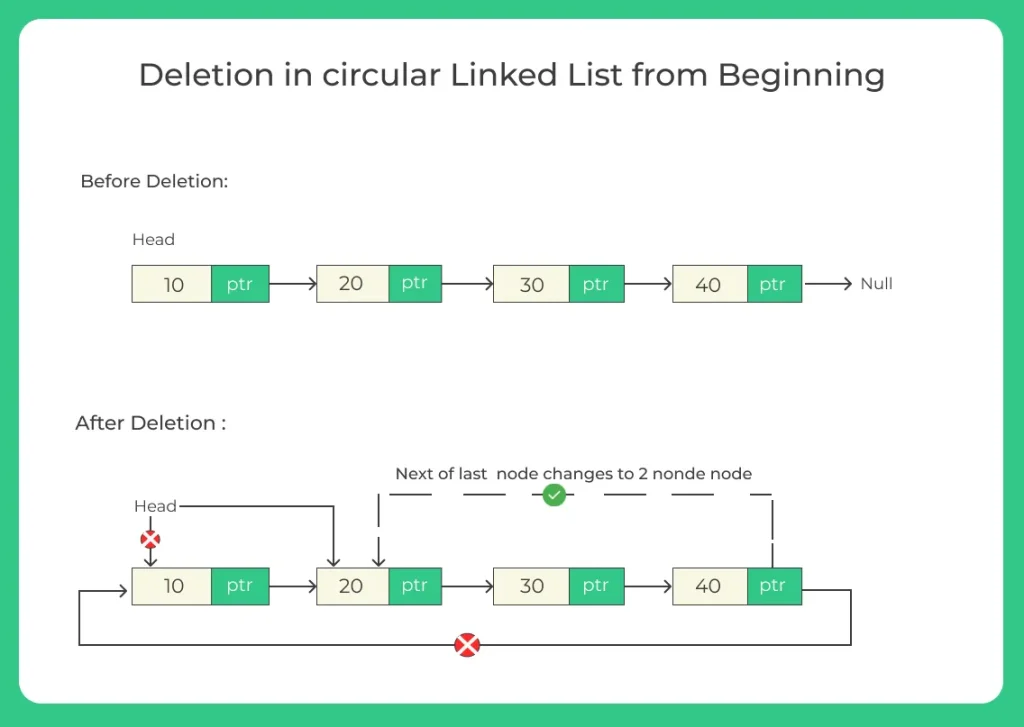
1. Deletion from beginning of a circular linked list
- The first node (head) is removed.
- We need to update the last node’s next pointer to the new head.
- Special case: Only one node? Just set head = null.
Use Cases:
- Removing the oldest or highest priority element.
- Rotating buffers or schedules.
Algorithm:
- deleteFirst()
- IF head == null
- return
- ELSE IF head != tail
- head = head -> next
- tail -> next = head
- ELSE
- head = tail = null
Time Complexity: O(n)
Code Snippet:
public void deleteFirst() {
if(head == null) {
return;
}
else {
if(head != tail ) {
head = head.next;
tail.next = head;
}
else {
head = tail = null;
}
}
}
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
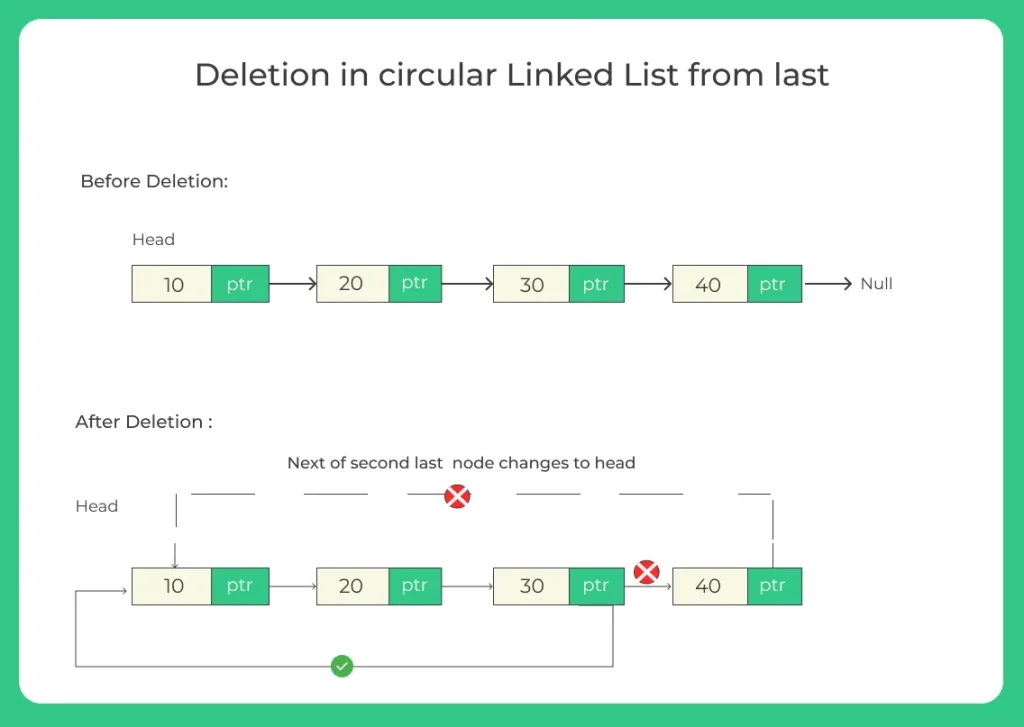
2. Deletion from last of a circular linked list
- Traverse the list to find the second last node.
- Change its next to point to the head.
- Special case: If there’s only one node, list becomes empty.
Use Cases:
Useful when removing the most recent entry in circular stacks or logs.
Algorithm:
- deleteLast()
- IF head == null
- return
- ELSE IF head != tail
- Node current = head
- WHILE current->next != tail
- current = current-> next
- tail = current;
- tail -> next = head
- ELSE
- head = tail = null
Time Complexity: O(n)
Code Snippet:
public void deleteLast() {
if(head == null) {
return;
}
else {
if(head != tail ) {
Node current = head;
while(current.next != tail) {
current = current.next;
}
tail = current;
tail.next = head;
}
else {
head = tail = null;
}
}
}
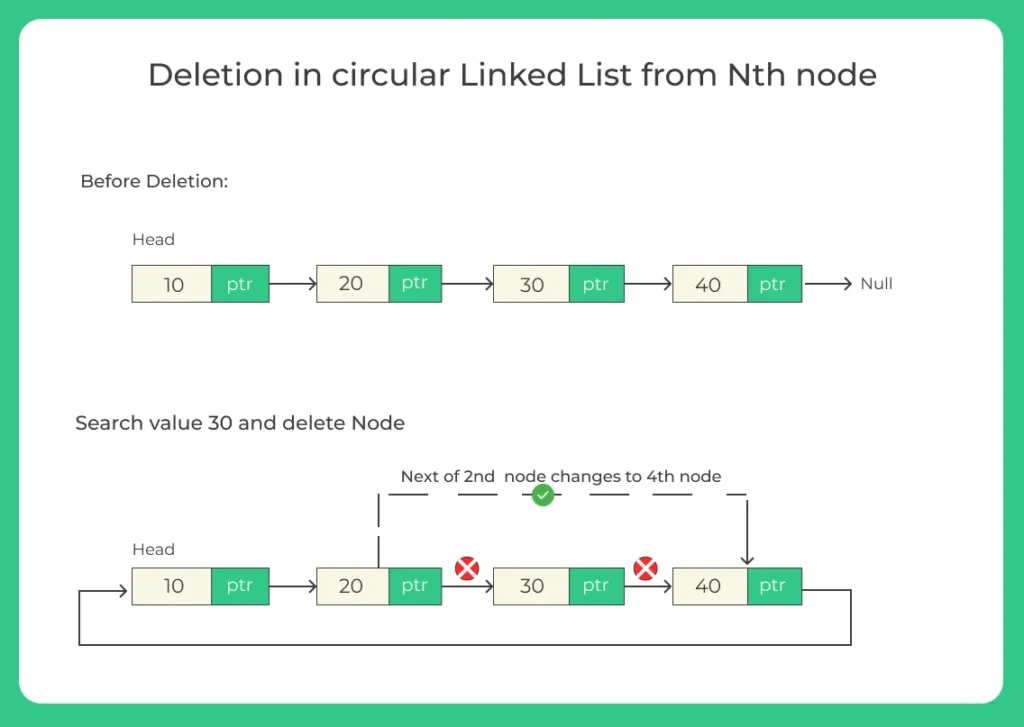
3. Deletion at a Given Position of a circular linked list
- Locate the node just before the target position.
- Adjust the pointer to skip the target node.
- Validate index boundaries.
Use Cases:
Random access deletion in non-linear data flows.
Optimized deletion in network packet queues.
Algorithm:
- deleteLast()
- IF head == null
- return
- ELSE
- WHILE (–n>0)
- previous = temp;
- temp = temp.next;
- previous.next = temp.next;
- WHILE (–n>0)
Time Complexity: O(n)
Code Snippet:
public void deleteAtPosition(int position) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
if (position == 1) {
deleteFirst();
return;
}
Node current = head;
Node previous = null;
int count = 1;
while (count < position && current.next != head) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
count++;
}
if (count != position) {
return;
}
if (current == tail) {
deleteLast();
return;
}
previous.next = current.next;
current.next = null;
}
So as you can observe that these were the Deletion in Circular Linked List in Java with the following Space and Time Complexity:
| Deletion in Circular Linked List | Space Complexity | Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Deletion at the beginning | O(1) | O(n) |
| Deletion at the end | O(1) | O(n) |
| Deletion after a specific node | O(1) | O(n) |
Code for deletion of a node in circular Linked List in Java
Code 1: Singly Circular Linked List
Method Types:
- deleteFirst()
Type: Deletion at the beginning (head)
List Type: Singly Circular Linked List - deleteLast()
Type: Deletion at the end (tail)
List Type: Singly Circular Linked List - deleteNthNode(int n)
Type: Deletion at a specific position (Nth node)
List Type: Singly Circular Linked List
Code 2: Doubly Circular Linked List
Method Types:
- deleteFirst()
Type: Deletion at the beginning (head)
List Type: Doubly Circular Linked List
(Although it doesn’t update head.prev explicitly, the structure supports doubly linked list behavior.) - deleteLast()
Type: Deletion at the end (tail)
List Type: Doubly Circular Linked List
(Includes head.prev = tail to maintain backward linkage.) - deletenth(int n)
Type: Deletion at a specific position (Nth node)
List Type: Doubly Circular Linked List
(Uses both prev and next pointers to unlink the node.)
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Obj = new Main();
Obj.add(10);
Obj.add(20);
Obj.add(30);
Obj.add(40);
Obj.add(50);
Obj.add(60);
System.out.println("List Before Deletion");
Obj.print();
System.out.println("List After Deleting first node");
Obj.deleteFirst();
Obj.print();
System.out.println("List After Deleting last node");
Obj.deleteLast();
Obj.print();
Obj.deleteNthNode(2);
System.out.println("List After Deleting 2nd node");
Obj.print();
}
public class Node{
int element;
Node next;
public Node(int element) {
this.element = element;
}
}
public Node head = null;
public Node tail = null;
public void print() {
Node temp = head;
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("null");
}
else {
do{
System.out.print(" "+ temp.element);
temp = temp.next;
}while(temp != head);
System.out.println();
}
}
public void add(int element){
Node newNode = new Node(element);
if(head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
}
else {
tail.next = newNode;
tail = newNode;
tail.next = head;
}
}
public void deleteFirst() {
if(head == null) {
return;
}
else {
if(head != tail ) {
head = head.next;
tail.next = head;
}
else {
head = tail = null;
}
}
}
public void deleteLast() {
if(head == null) {
return;
}
else {
if(head != tail ) {
Node current = head;
while(current.next != tail) {
current = current.next;
}
tail = current;
tail.next = head;
}
else {
head = tail = null;
}
}
}
public int calcLen(){
int len = 0;
Node temp=head;
while(temp!=tail){
temp = temp.next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
public void deleteNthNode(int n)
{
int len = calcLen();
// Can only insert after 1st position
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
if(n < 1 || n > len)
{
System.out.println("Can't delete\n");
}
else
{
if(n == 1)
{
head = head.next;
return;
}
// required to traverse
Node temp = head;
Node previous = null;
// traverse to the nth node
while(--n > 0) {
previous = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// assigned next node of the previous node to nth node's next
previous.next = temp.next;
System.out.println("Deleted: " + temp.element);
}
}
}Output
List Before Deletion 10 20 30 40 50 60 List After Deleting first node 20 30 40 50 60 List After Deleting last node 20 30 40 50 Deleted: 30 List After Deleting 2nd node 20 40 50
import java.lang.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Obj = new Main();
Obj.add(10);
Obj.add(20);
Obj.add(30);
Obj.add(40);
Obj.add(50);
Obj.add(60);
System.out.println("List Before Deletion");
Obj.print();
System.out.println("List After Deleting first node");
Obj.deleteFirst();
Obj.print();
System.out.println("List After Deleting last node");
Obj.deleteLast();
Obj.print();
Obj.deletenth(2);
System.out.println("List After Deleting 2nd node");
Obj.print();
}
public class Node{
int element;
Node next;
Node prev;
public Node(int element) {
this.element = element;
}
}
public Node head = null;
public Node tail = null;
public void print() {
Node temp = head;
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("null");
}
else {
do{
System.out.print(" "+ temp.element);
temp = temp.next;
}while(temp != head);
System.out.println();
}
}
public void add(int element){
Node newNode = new Node(element);
if(head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
newNode.prev=head;
}
else {
tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev=tail;
tail = newNode;
tail.next = head;
}
}
public int Length(Node head)
{
Node current = head;
int count = 0;
// if list is empty
// simply return length zero
if (head == null)
{
return 0;
}
// traverse forst to last node
else
{
do
{
current = current.next;
count++;
} while (current != head);
}
return count;
}
public void deleteFirst() {
if(head == null) {
return;
}
else {
if(head != tail ) {
head = head.next;
tail.next = head;
}
else {
head = tail = null;
}
}
}
public void deleteLast() {
if(head == null) {
return;
}
else {
if(head != tail ) {
Node current = head;
while(current.next != tail) {
current = current.next;
}
tail = current;
tail.next = head;
head.prev=tail;
}
else {
head = tail = null;
}
}
}
public void deletenth (int n)
{
if (head == null)
{
return;
}
else
{
Node current = head;
int pos = n;
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++)
{
current = current.next;
}
if (current == head)
{
head = current.next;
}
else if (current == null)
{
current = current.prev;
}
else
{
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
//Delete the middle node
current = null;
}
}
void printList ()
{
//Node current will point to head
Node curr = head;
if (head == null)
{
System.out.println ("List is empty");
return;
}
while (curr != null)
{
//Prints each node by increasing order of the pointer
System.out.print (curr.element + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println ();
}
}Output
List Before Deletion 10 20 30 40 50 60 List After Deleting first node 20 30 40 50 60 List After Deleting last node 20 30 40 50 List After Deleting 2nd node 20 40 50
Learn DSA
FAQ's Related to Circular Linked List
Answer:
- Circular linked list is a variation of a linked list in which the last node points back to the first node, forming a loop.
- It can be singly (only next pointers) or doubly (with both next and prev pointers).
Answer:
In a circular linked list, special care must be taken to maintain the circular reference (i.e., last node’s next should point to the head). In deletion, we must update links carefully to keep the circular structure intact.
Answer:
Singly Circular: Move
headtohead.nextand updatetail.next = head.Doubly Circular: Move
headtohead.next, updatetail.next = head, andhead.prev = tail.
Answer:
- Singly Circular: Traverse until the second-last node, make it the new tail, and set tail.next = head.
- Doubly Circular: Set tail = tail.prev, and update tail.next = head, head.prev = tail.
Answer:
Traverse to the required position and unlink the node by updating the next (and prev if doubly circular) pointers of the surrounding nodes.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment