Insertion at the nth node in Circular Linked List in Java
Java Program for Insertion at the nth node in Circular Linked List
Insertion at the nth node in Circular Linked List in Java is an important operation that allows you to insert a new node at any specific position in the list.
Whether you’re inserting at the beginning, middle, or end, you must ensure the circular nature of the list is preserved, the last node must always point back to the head.
Insertion at the nth node in Circular Linked List in Java
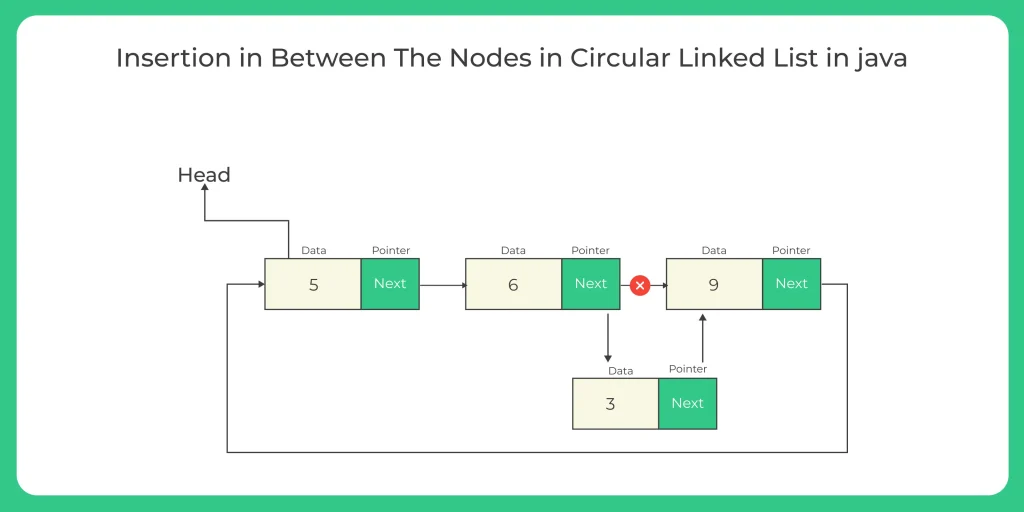
Insertion at the nth node means adding a new node after the (n-1)th node in the circular linked list.
For Example:
If you have a circular linked list:
10 → 20 → 30 → 40 → (back to 10)
and you insert 25 at position 3, the new list becomes:
10 → 20 → 25 → 30 → 40 → (back to 10)
Steps to be followed:
- Insert at the beginning (n = 1):
- New node becomes the new head.
- Last node’s next pointer must be updated to point to this new head.
- Insert at the end (n > length of list)
- Insert after the last node, update the tail.
- Insert at any middle position (1 < n ≤ length):
- Traverse until the (n−1)th node.
- Insert new node between (n−1)th and nth node.
Node Structure:
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
Methods for Insertion at the nth node in Circular Linked List in Java
We can perform Insertion at the nth node in Circular Linked List using 2 methods mentioned as follows:
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Method for Insertion at the nth node in Circular Linked List in Java
Method 1: Using Traversal Method
Algorithm for Insertion at the nth node:
Create a new node newNode with the given data.
If the list is empty:
Make newNode.next = newNode.
Set head = newNode.
Return.
- If inserting at position 1:
Traverse to the last node.
Set newNode.next = head.
Set last.next = newNode.
Update head = newNode.
Return.
- Otherwise:
Traverse the list to reach the (n−1)th node.
Insert newNode after it by adjusting pointers.
If inserted at the end, update the tail reference.
Java Code:
// Insertion at Nth Node in Circular Linked List using Traversal
class CircularLinkedList {
Node head;
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Insert at the Nth position
public void insertAtPosition(int data, int position) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// Case 1: Empty list
if (head == null) {
newNode.next = newNode;
head = newNode;
return;
}
// Case 2: Insert at beginning (position = 1)
if (position == 1) {
Node last = head;
while (last.next != head) {
last = last.next;
}
newNode.next = head;
last.next = newNode;
head = newNode;
return;
}
// Case 3: Insert at given position (middle or end)
Node temp = head;
int count = 1;
while (count < position - 1 && temp.next != head) {
temp = temp.next;
count++;
}
newNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
// If inserted at the end, update tail
if (temp == head && position != 1)
newNode.next = head;
}
// Display list
public void display() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node temp = head;
do {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircularLinkedList cll = new CircularLinkedList();
cll.insertAtPosition(10, 1);
cll.insertAtPosition(20, 2);
cll.insertAtPosition(30, 3);
cll.insertAtPosition(25, 3); // Insert 25 at position 3
System.out.println("Circular Linked List after inserting 25 at 3rd position:");
cll.display();
}
}
Output:
Circular Linked List after inserting 25 at 3rd position: 10 20 25 30
Space Complexity: O(1)
Method for Insertion at the nth node in Circular Linked List in Java
Method 2: Using Tail Pointer
Algorithm for Insertion at the nth node:
Maintain a tail pointer pointing to the last node.
Create a new node with the given data.
If the list is empty, make newNode.next = newNode, set both head and tail to newNode.
If inserting at position 1:
Point newNode.next = head
Update tail.next = newNode
Update head = newNode
- Otherwise:
Traverse from head to the (n−1)th node (or stop if temp == tail).
Insert the new node by adjusting pointers.
If inserted after the last node, update tail = newNode.
Java Code:
// Insertion at Nth Node in Circular Linked List using Tail Pointer
class CircularLinkedListWithTail {
Node head, tail;
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// Insert node at given position
public void insertAtPosition(int data, int position) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// Case 1: Empty list
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
return;
}
// Case 2: Insert at beginning
if (position == 1) {
newNode.next = head;
tail.next = newNode;
head = newNode;
return;
}
// Case 3: Insert at nth position
Node temp = head;
int count = 1;
while (count < position - 1 && temp.next != head) {
temp = temp.next;
count++;
}
newNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
// Update tail if inserted at end
if (temp == tail) {
tail = newNode;
}
}
// Display list
public void display() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node temp = head;
do {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircularLinkedListWithTail cll = new CircularLinkedListWithTail();
cll.insertAtPosition(10, 1);
cll.insertAtPosition(20, 2);
cll.insertAtPosition(30, 3);
cll.insertAtPosition(40, 4);
cll.insertAtPosition(25, 3);
System.out.println("Circular Linked List after inserting 25 at 3rd position:");
cll.display();
}
}
Output:
Circular Linked List after inserting 25 at 3rd position: 10 20 25 30 40
Space Complexity: O(1)
Comparison between Methods
Method / Approach | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Important Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traversal Based Insertion at Nth Node | O(n) | O(1) | Must traverse up to (n−1)th node; pointer adjustments take constant space. |
| Tail Pointer Based Insertion at Nth Node | O(n) (general nth position) | O(1) | Tail gives O(1) only for insertion at end; but nth node still needs traversal unless n = last. |
Insertion at the nth node in a Circular Linked List in Java is a fundamental operation that enhances the flexibility of linked list manipulation.
By understanding how to manage head, tail, and traversal pointers, you can efficiently insert nodes at any position while preserving the circular structure. For performance critical applications with frequent insertions at the end, maintaining a tail pointer is the best approach.
Frequently Asked Questions
Answer:
It means adding a new node at a specific position, where the new node comes after the (n−1)th node.
Answer:
If the list is empty, the new node should point to itself and become both the head and tail.
Answer:
In such cases, the new node is usually inserted at the end of the circular list, and the circular property is maintained.
Answer:
Yes, by maintaining a tail pointer, you can directly insert the new node after the tail in constant time.
Answer:
Because in a circular linked list, the tail must always point to the head to keep the circular connection intact.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java







Login/Signup to comment