C++ program to split a circular linked list into two halves

How to split a circular liked list into two halves in C++?
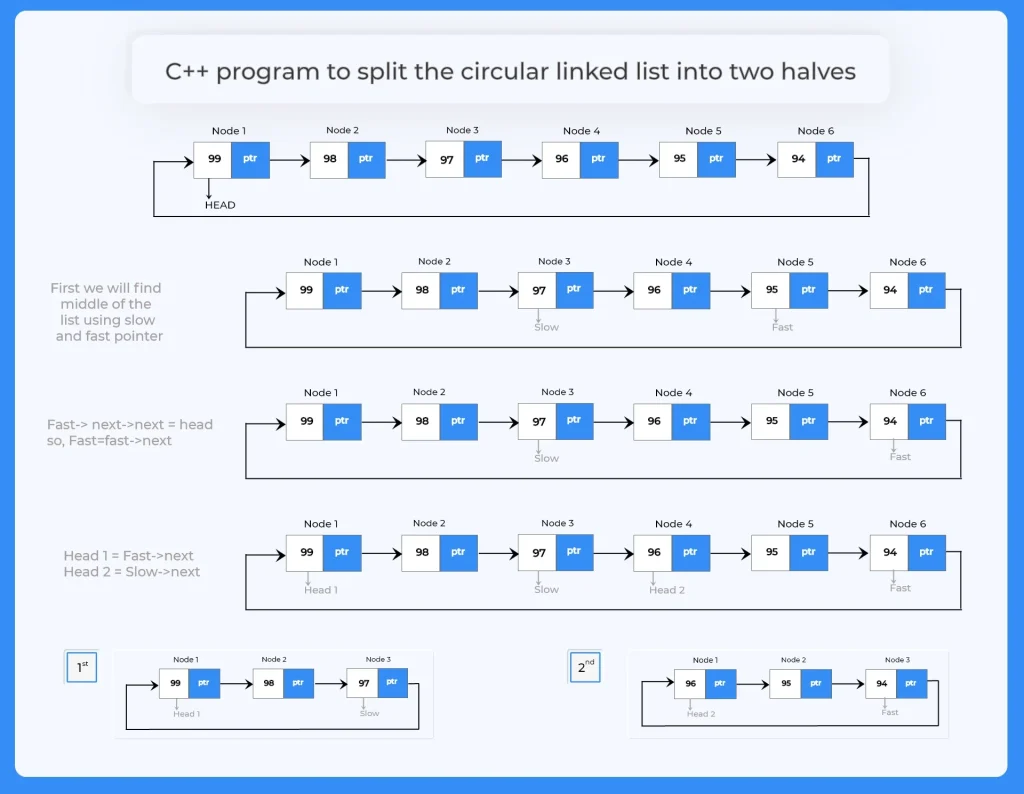
To write a C++ program to split a circular linked list into two halves, we will be finding the middle of the given list first. In order to find the middle of the list we will use the slow and fast pointer trick. And after finding the middle of the list we will make two heads in the list as each part of the list will have its own head.
Further in this article we will discuss steps and algorithm two find the middle of the list and make two heads and divide the list into two halves.
Steps to split a circular linked list into two halves in CPP
- Define the circular linked list in your program.
- Create some basic functions like to build and display the circular liked list.
- Now create a function to split the list into two halves.
- In this function find the middle of the list using the slow and fast pointer trick.
- Now when list will be divided into two halves there will be two heads.
- So, make the node pointed by fast pointer as first head.
- Make the node pointed by slow pointer as second head.
- Display both the halves to the user.
struct node { int num; struct node * next; }
Algorithm to split circular linked list into two halves in C++
- STRUCT NODE SLOW = HEAD
- STRUCT NODE FAST = HEAD
- IF HEAD==NULL
- RETURN
- WHILE(FAST->NEXT !=HEAD&&FAST->NEXT->NEXT!= HEAD)
- FAST=FAST->NEXT->NEXT
- SLOW=SLOW->NEXT
- END WHILE
- IF FAST->NEXT->NEXT==HEAD
- FAST=FAST->NEXT
- HEAD1 = HEAD
- IF FAST->NEXT != HEAD
- HEAD2=SLOW->NEXT
- FAST->NEXT=SLOW->NEXT
- SLOW->NEXT=HEAD
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C++ program for splitting the circular linked list into two halves
A C++ program for splitting a circular linked list into two halves helps divide the list into two equal parts, maintaining their circular structure. This process is useful for optimizing operations like parallel processing or balanced data handling. It ensures that each half can be independently traversed without losing connectivity.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int num;
struct Node *next;
} *head;
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data) //function to create linked list
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->num = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode; // assigning itself as head
(*head)->next = *head; // assigning itself as next node
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n"; return; } // if CLL already as >=1 node
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in CLL
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = newNode; // last node's next as this new node
newNode->next = *head; // new node's next as current head node
*head = newNode; // changing head node to this new node
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n";
// previous head node becomes 2nd node
}
void display (struct Node *head)
{
//cout << "\nCircular Linked List : " << endl;
// if circular linked list is empty currently
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node *temp = head;
// since we need to take care of circular nature of linked list
do
{
cout << temp->num << " "; temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
cout << endl; } void splitList (struct Node **head1, struct Node **head2) //function to split list into two halves { struct Node *slow = head; struct Node *fast = head; if (head == NULL) return; while (fast->next != head && fast->next->next != head) //finding middle of the list
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
if (fast->next->next == head)
fast = fast->next;
*head1 = head;
if (head->next != head)
*head2 = slow->next;
fast->next = slow->next;
slow->next = head;
}
int main () //main function
{
head = NULL;
insertStart (&head, 1);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 3);
insertStart (&head, 4);
insertStart (&head, 5);
struct Node *head1 = NULL;
struct Node *head2 = NULL;
cout << "\nCircular linked list data:\n";
display (head);
splitList (&head1, &head2);
cout << "\nFirst half data: ";
display (head1);
cout << "\nSecond half data: ";
display (head2);
return 0;
}
Output:
1 Inserted 2 Inserted 3 Inserted 4 Inserted 5 Inserted Circular linked list data: 5 4 3 2 1 First half data: 5 4 3 Second half data: 2 1
Explanation:
- Each node in this program is created using a structure that stores data and a pointer to the next node, helping to maintain the circular connection among all nodes.
- During insertion, a new node is dynamically allocated and linked properly so that it becomes the new head of the list while preserving the circular linkage among all existing nodes.
- When displaying the list, the traversal continues until the pointer reaches the head again, ensuring that every element of the circular linked list is printed exactly once.
- To divide the list, the algorithm moves two pointers one fast and one slow through the nodes, allowing it to identify the middle point efficiently without extra memory.
- After locating the middle, the circular list is separated into two smaller circular lists by updating the next pointers of the middle and last nodes, completing the split process.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insert Node at Start | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
| Split Circular List | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
In this article, we covered how to split a circular linked list into two halves by first locating the midpoint using the classic slow-and-fast pointer approach, and then restructuring the pointers so each half forms its own circular list. This method offers a clean and efficient way to divide the structure without breaking its circular nature.
By implementing the sample C++ code and following the algorithmic steps, you’ll be able to handle edge cases (like lists with even or odd numbers of nodes) and ensure both halves remain circular. Mastering this technique strengthens your grasp of pointer handling and linked list manipulations skills that frequently appear in coding interviews.
FAQs
Using the slow (moves one node at a time) and fast (moves two nodes at a time) pointer technique allows you to efficiently find the middle of the list in a single traversal. Once fast reaches the end (or loops around), slow will be at or near the middle, which is ideal for splitting the list into two halves.
For an odd-numbered list, the first half ends up with one extra node than the second half; for an even number, both halves end up equal. The algorithm handles this by checking if fast->next->next == head before finalizing the halves, ensuring that the pointers adjust correctly.
To maintain the circular property, the algorithm reassigns the next pointer of the last node of each half back to the head of that half. Specifically, fast->next is set to slow->next (for the second half) and slow->next is set to the original head (for the first half), preserving the circular nature in both lists.
If the head is NULL (empty list) or the list has just a single node (where head->next == head), the splitting operation simply returns without changes. In these cases, splitting doesn’t make sense (or the single node itself forms both halves logically), so the algorithm safely handles these edge conditions.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment