C++ program to count nodes in circular linked list
How to count nodes in circular linked list in C++?
To write a C++ program to count nodes in circular linked list, we need to initialize a node pointer and a variable that will store the count of nodes.
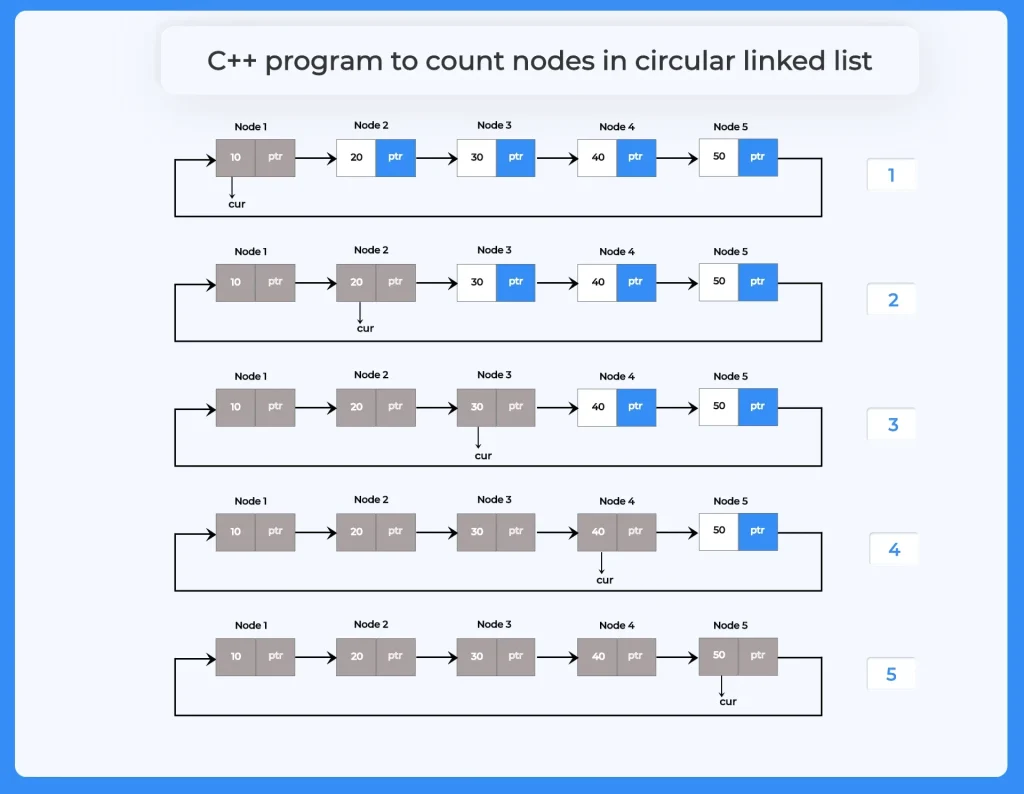
Use the node pointer to point each node of the list and increase the count of the counter variable by one on every successful iteration. Stop the iteration when node pointer points the head.
Steps write a C++ program to count nodes in circular linked list
- Write set of codes to construct circular linked list.
- Create a function to build the circular linked list.
- Make a function to print the circular linked list data.
- Create a function to count the number of nodes present in circular linked list.
- In this function initialize a variable to count the number of nodes.
- Initialize a pointer that will point to each node on every successful iteration.
- Stop the iteration when pointer points the head again.
- Return the count of nodes.
- Now call these functions in the main function and print the total count of nodes.
struct Node { int num; struct Node *next; };
Algorithm to count nodes in circular linked list in C++
- INT CNT=0
- STRUCT NODE CUR = HEAD
- DO
- CUR = CUR -> NEXT
- CNT++
- WHILE (CUR != HEAD)
- RETURN CNT
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C++ program for counting nodes in circular linked list
In a C++ program for counting nodes in a circular linked list, the logic involves traversing the list once while maintaining a counter to record each node visited. Since the list is circular, the traversal stops when it loops back to the head node. This method provides an efficient way to find the total number of nodes in the list.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int num;
struct Node *next;
} *head;
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data) //function to create linked list
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->num = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode; // assigning itself as head
(*head)->next = *head; // assigning itself as next node
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n"; return; } // if CLL already as >=1 node
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in CLL
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = newNode; // last node's next as this new node
newNode->next = *head; // new node's next as current head node
*head = newNode; // changing head node to this new node
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n";
// previous head node becomes 2nd node
}
void display (struct Node *head)
{
//cout << "\nCircular Linked List : " << endl;
// if circular linked list is empty currently
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node *temp = head;
// since we need to take care of circular nature of linked list
do
{
cout << temp->num << " "; temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
cout << endl; } int count (struct Node *head) //function to count number of nodes { int cnt = 0; struct Node *cur = head; //Iterating till end of list do { cur = cur->next;
cnt++;
}
while (cur != head);
return cnt;
}
int main () //main function
{
head = NULL;
insertStart (&head, 1);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 3);
insertStart (&head, 4);
insertStart (&head, 5);
struct Node *head1 = NULL;
struct Node *head2 = NULL;
cout << "\nCircular linked list data:\n";
display (head);
cout << "\nTotal number of nodes are: " << count (head);
}
Output: 1 Inserted 2 Inserted 3 Inserted 4 Inserted 5 Inserted Circular linked list data: 5 4 3 2 1 Total number of nodes are: 5
Explanation:
- The code begins by defining a Node structure that holds an integer data field and a pointer to the next node, enabling the creation of a circular linked list where the last node connects back to the head.
- In the insertStart() function, each new node is inserted at the beginning of the circular linked list. The function carefully updates the links so that the new node becomes the new head while maintaining the circular connection.
- When inserting the very first node, it is made to point to itself, ensuring the circular property is maintained even for a single-node list.
- The display() function iterates through the circular linked list using a do-while loop to print each node’s value, making sure the loop stops only when it reaches the head node again.
- The count() function traverses the circular linked list, incrementing a counter for each node until it loops back to the head, giving the total number of nodes present in the list.
Time and Space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at Start | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
| Count Nodes | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
Counting the nodes in a circular linked list becomes straightforward when you treat the list’s head as the stopping point. Traverse from the head, increment a counter each time you move to the next node, and halt when you return to the head.
This technique ensures you correctly account for all nodes even in a circular structure, avoiding infinite loops and missed nodes. Implementing it cleanly in C++ reinforces your understanding of both linked-list dynamics and circular traversal logic.
FAQs
You can use a while loop with a boolean flag to track the first traversal, ensuring you stop when the pointer revisits the head node.
In that case, the head node points to itself, so the count should return 1, ensuring the loop condition checks for temp->next != head.
Yes, recursion can be used by passing the head and current node as parameters, stopping when the current node revisits the head.
First detect the loop using Floyd’s Cycle Detection, then count nodes in the loop by iterating until the pointer revisits the same node.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment