Merge two sorted arrays in C++
Merge two sorted arrays in C++
Merge Two Sorted Array in C++ Problem – When working with arrays in C++, one common problem that often comes up is merging two sorted arrays into a single sorted array. This is a basic yet important concept in programming that helps you understand how data structures work and how to manage data efficiently.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through the step-by-step logic behind solving this problem using simple C++ code.

Merge two Sorted Arrays in C++
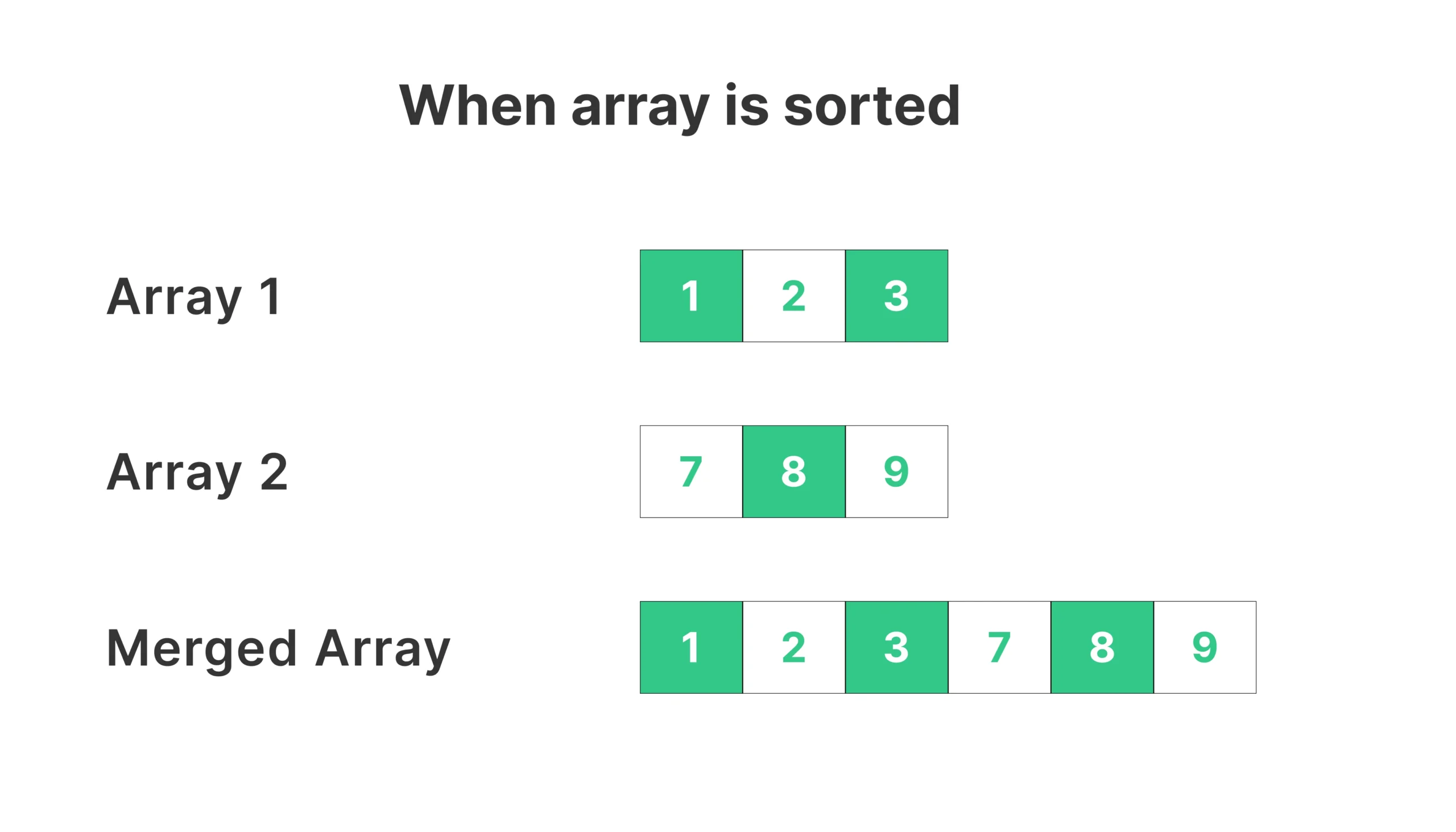
Given two sorted arrays, one array with size m+n and the other array with size n. We will merge the n sized array into m+n sized array and print the m+n sized merged array.
Example :
- Input : M[] = {1, 7, absent, absent, 124, 132, absent, 155, 200};
N[] = {2,4,152}; - Output : {1, 2, 4, 7, 124, 132, 152, 155, 200}
Algorithm
Let the arrays be M[] and N[]. Size of M[] be m+n and Size of N[] be n –
- First, move the non absent elements in M[] to the end and return the number of elements that are absent ie, store it in j
- Start from the jth element of the array M[] and 0th element of the array N[] and compare each value of the two arrays, and store the elements in M[] in ascending order.
Time Complexity for Merge two sorted array in C++
- O(m+n), where m and n are sizes of the arrays.
Method for Solving merge two sorted array in C++
List of Methods to Merge Two Sorted Arrays:
- Merge Using Two Pointers (With Extra Space)
- Merge In-Place (If One Array Has Extra Space)
- Merge and Then Sort
- Using STL std::merge() Function
- Min Heap (Priority Queue) Based Approach
- Merge K Sorted Arrays (Extension Problem)
- Using Map Method
Method 1: Merge Using Two Pointers (With Extra Space)
Algorithm:
- Initialize two pointers i and j at the beginning of both arrays.
- Compare the elements pointed by i and j, and append the smaller one to the result.
- Move the respective pointer forward.
- After the loop, add the remaining elements from either array to the result.
Time Complexity: O(n + m)
Space Complexity: O(n + m)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void mergeTwoPointers(int arr1[], int n, int arr2[], int m) {
vector result;
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
result.push_back(arr1[i++]);
else
result.push_back(arr2[j++]);
}
while (i < n) result.push_back(arr1[i++]);
while (j < m) result.push_back(arr2[j++]);
cout << "Merged Array (Two Pointers): ";
for (int num : result) cout << num << " ";
cout << endl;
}
Input:
Let’s assume the following arrays are passed to the function:
int arr1[] = {1, 3, 5, 7};
int arr2[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int n = 4, m = 4;
mergeTwoPointers(arr1, n, arr2, m);Output:
Merged Array (Two Pointers): 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Method 2: Merge In-Place (If One Array Has Extra Space)
Algorithm:
- Start from the end of both arrays.
- Compare elements and place the larger one at the end of the bigger array.
- Continue until all elements are merged.
Time Complexity: O(n + m)
Space Complexity: O(1) (in-place)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void mergeInPlace(int arr1[], int n, int arr2[], int m) {
int i = n - 1;
int j = m - 1;
int k = n + m - 1;
while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
if (arr1[i] > arr2[j])
arr1[k--] = arr1[i--];
else
arr1[k--] = arr2[j--];
}
while (j >= 0) {
arr1[k--] = arr2[j--];
}
cout << "Merged In-Place Array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n + m; i++) cout << arr1[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
Note – This code assumes that arr1 has enough space (of size n + m) to hold both arrays, but it does not show how the extra space is allocated. If arr1 is defined as int arr1[] = {1, 3, 5};, there’s no extra space.
Input:
To test the code correctly, you should define arr1 with n + m size and initialize only the first n elements:
int arr1[6] = {1, 3, 5}; // size = 6, initialized 3 elements
int arr2[] = {2, 4, 6};
int n = 3, m = 3;
mergeInPlace(arr1, n, arr2, m);Output:
Merged In-Place Array: 1 2 3 4 5 6
Method 3: Merge and Then Sort
Algorithm:
- Combine both arrays into a single vector.
- Sort the vector using built-in sort function.
Time Complexity: O((n + m) log(n + m))
Space Complexity: O(n + m)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void mergeAndSort(int arr1[], int n, int arr2[], int m) {
vector merged(arr1, arr1 + n);
merged.insert(merged.end(), arr2, arr2 + m);
sort(merged.begin(), merged.end());
cout << "Merged and Sorted Array: ";
for (int num : merged) cout << num << " ";
cout << endl;
}
Note –
The provided code does –
- Takes two arrays as input.
- Merges both into a single vector.
- Sorts the combined vector.
- Prints the merged and sorted array.
Input:
To see the output, you can run the function like this:
int main() {
int arr1[] = {5, 1, 9};
int arr2[] = {3, 6, 2};
int n = 3, m = 3;mergeAndSort(arr1, n, arr2, m);
return 0;
}
Output:
Merged and Sorted Array: 1 2 3 5 6 9
More Methods to Merge Sorted Array in C++
Method 4: Using STL std::merge() Function
Algorithm:
- Use the std::merge() function from the STL which merges two sorted ranges.
Time Complexity: O(n + m)
Space Complexity: O(n + m)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void mergeUsingSTL(int arr1[], int n, int arr2[], int m) {
vector result(n + m);
merge(arr1, arr1 + n, arr2, arr2 + m, result.begin());
cout << "Merged Using STL: ";
for (int num : result) cout << num << " ";
cout << endl;
}
Note –
The provided code does –
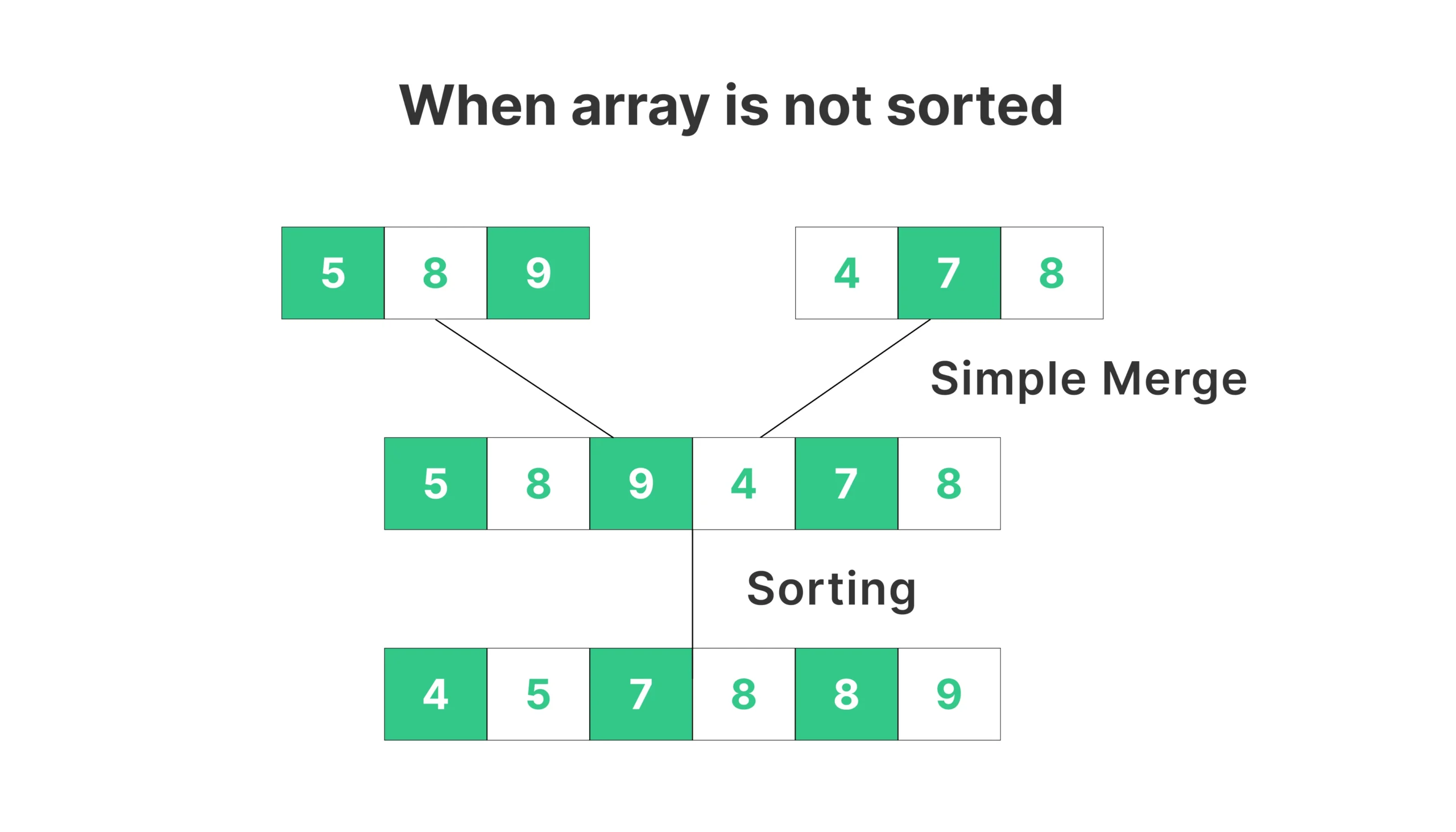
- Both input arrays (arr1 and arr2) must be sorted before using std::merge() from the C++ STL.
- If they are not sorted, std::merge() will not give a properly sorted output, as it assumes both input ranges are sorted.
Example Input (Sorted Arrays):
int main() {
int arr1[] = {1, 3, 5};
int arr2[] = {2, 4, 6};
int n = 3, m = 3;
mergeUsingSTL(arr1, n, arr2, m);
return 0;
}Output:
Merged Using STL: 1 2 3 4 5 6
If Input Is Not Sorted, If you use unsorted arrays like:
int arr1[] = {5, 1, 3};
int arr2[] = {4, 6, 2};Then std::merge() will give a wrong merge (not sorted properly):
Merged Using STL: 5 1 3 4 6 2
Method 5: Min Heap (Priority Queue) Based Approach
Algorithm:
- Push all elements into a min heap.
- Pop the heap to get sorted merged array.
Time Complexity: O((n + m) log(n + m))
Space Complexity: O(n + m)
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
void mergeUsingMinHeap(int arr1[], int n, int arr2[], int m) {
priority_queue<int, vector, greater> minHeap;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) minHeap.push(arr1[i]);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) minHeap.push(arr2[i]);
cout << "Merged Using Min Heap: ";
while (!minHeap.empty()) {
cout << minHeap.top() << " ";
minHeap.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
How It Works:
- Elements from both arrays (arr1 and arr2) are inserted into a min-heap (priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>>).
- A min-heap always keeps the smallest element at the top.
- As we pop elements from the heap, we get them in sorted ascending order.
Input:
To see the output, you can run the function like this:
int main() {
int arr1[] = {4, 1, 7};
int arr2[] = {3, 6, 2};
int n = 3, m = 3;
mergeUsingMinHeap(arr1, n, arr2, m);
return 0;
}Output:
Merged Using Min Heap: 1 2 3 4 6 7
Method 6: Merge K Sorted Arrays (Extension Problem)
Algorithm:
- Use a min heap to maintain the smallest element among the k arrays.
- Keep extracting and pushing the next element from the same array.
Time Complexity: O(N log K), where N is total elements, K is number of arrays
Space Complexity: O(K)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data, row, col;
Node(int d, int r, int c) : data(d), row(r), col(c) {}
};
struct compare {
bool operator()(Node const &a, Node const &b) {
return a.data > b.data;
}
};
void mergeKSortedArrays(vector<vector> &arr) {
priority_queue<Node, vector, compare> pq;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
if (!arr[i].empty()) {
pq.push(Node(arr[i][0], i, 0));
}
}
vector result;
while (!pq.empty()) {
Node current = pq.top(); pq.pop();
result.push_back(current.data);
if (current.col + 1 < arr[current.row].size()) {
pq.push(Node(arr[current.row][current.col + 1], current.row, current.col + 1));
}
}
cout << "Merged K Sorted Arrays: ";
for (int num : result) cout << num << " ";
cout << endl;
}
How It Works:
- A custom Node structure holds:
- data: actual element
- row: which array it’s from
- col: index within that array
- The priority queue (min-heap) always gives the smallest element at the top.
- Each time we extract the smallest element, we insert the next element from the same array (if any).
Input:
- Add this to the main() function:
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> arr = {
{1, 4, 7},
{2, 5, 8},
{3, 6, 9}
};
mergeKSortedArrays(arr);
return 0;
}Output:
Merged K Sorted Arrays: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Method 7: Using Map Method for Merging two Sorted Array
Using a map method ensures that the merged array is sorted and duplicate-free (if that’s desired), because:
- A map in C++ stores unique keys in sorted order by default.
- If duplicate elements need to be preserved, you can use a multimap.
When to Use Map Method
#include<iostream> #include<vector>
Output:
Merged Sorted Array (No Duplicates): 1 2 3 5 6 7 8
Summary of All Possible Methods to Merge Two Sorted Arrays in C++
| Method | Description | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Two Pointer Approach | Compare elements one by one using two pointers and merge into a new array. | O(n + m) | O(n + m) |
| In-Place Merge | Merge arrays in-place when one has enough extra space. | O(n + m) | O(1) |
| Merge and Sort | Concatenate both arrays and sort the result. | O((n + m) log(n + m)) | O(n + m) |
| Using std::merge() (STL) | Use STL’s merge() to combine two sorted ranges. | O(n + m) | O(n + m) |
| Using Min Heap (Priority Queue) | Push all elements into a min heap and extract in sorted order. | O((n + m) log(n + m)) | O(n + m) |
| Using std::map | Insert all elements as keys into a map to auto-sort and remove duplicates. | O((n + m) log(n + m)) | O(n + m) |
| Merge K Sorted Arrays | Generalization: Merge k sorted arrays using a min heap. | O(N log K), N = total elements | O(k) |
To wrap it up
Merging two sorted arrays in C++ is a useful skill that helps you combine data efficiently while keeping everything in order. By comparing elements from both arrays one by one, you can create a new sorted array without much hassle.
This technique is not only simple but also forms the basis for more advanced algorithms like merge sort. With a clear understanding and a bit of practice, you can easily implement this in your own programs and improve your coding skills. Keep experimenting, and soon merging arrays will become second nature.
First Nature is always – Learning New Things.
FAQs
Yes, for large datasets that exceed the available RAM, external sorting and multi-way merge algorithms are used. Data is divided into manageable chunks, each chunk is sorted and stored on disk, and then all sorted chunks are merged using a k-way merge algorithm—often with the help of a min-heap. This approach is commonly used in big data systems and databases to handle large-scale merges efficiently.
Each method has different costs.
- Two-pointer or std::merge: O(n + m) time and O(n + m) space.
- Gap method or in-place: O((n + m) log(n + m)) time and O(1) space.
- Min-heap method: Around O(n log m + m log n) time.
Map or sorting: Around O((n + m) log(n + m)) time and O(n + m) space. - K sorted arrays: O(N log k) time where N is the total number of elements.
Use the two-pointer method when you want speed and your arrays are already sorted. Use in-place methods when memory usage is critical. Use heap-based merging when you’re dealing with multiple arrays. Use map/sort-based approaches when implementation simplicity matters more than performance.
No, you can’t directly use these methods unless the arrays are sorted. First, sort each array or combine and sort them together. After that, you can use any of the merging methods.
Most merging techniques preserve duplicates. If you want only unique values, use sets. If one array is empty, the result is just the other array. Always make sure not to go out of bounds with your array indices during the merge.
Merging sorted arrays is used in external sorting, databases (merge-joins), search engines (index merging), and log file processing. For large datasets, techniques like k-way merge, parallel merging, and external memory algorithms help in optimizing performance.




Login/Signup to comment