Deletion from end in circular linked list in C++
How to delete from end in circular linked list?
Deletion from end in circular linked list in C++ is one of the deletion operation that we can perform on the circular sequenced list. The other deletion operations that we can perform are:-
- Deletion from beginning i.e. to delete the head node of the list.
- Deletion from any specific position i.e. to delete any node from the list.
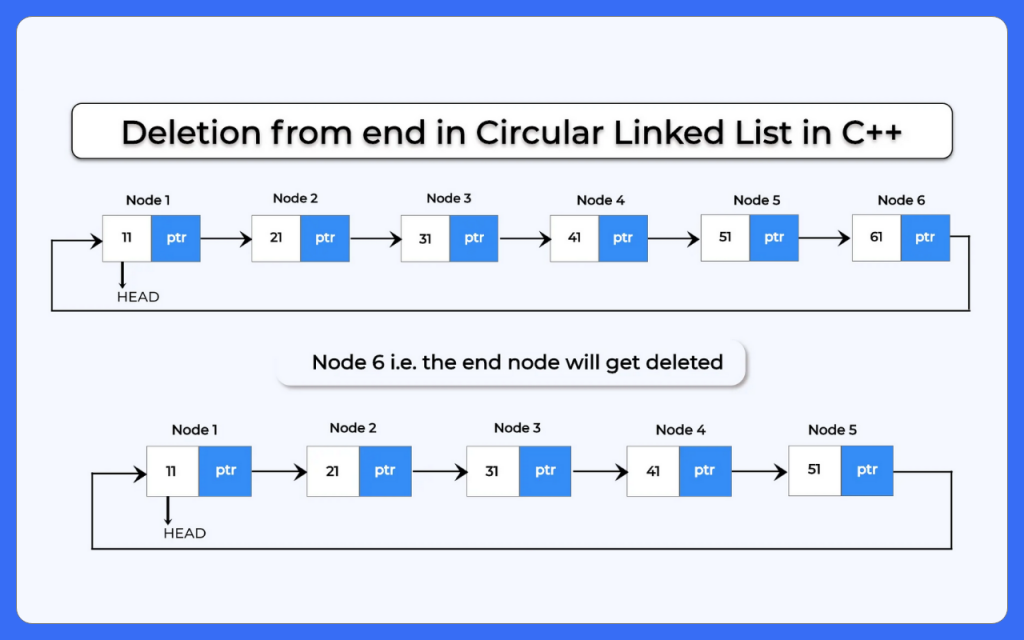
Steps to delete from end in circular linked list in CPP
- Print deletion not possible if list is empty.
- Else define two node pointers cur and prev
- Initialize cur pointer with head
- Change prev pointer to current and cur to cur->next until next of the current does not equal to head.
- Now link last second node that is the node pointed by prev node pointer to head.
- Free cur as it stores the last node of the list.
struct Node { int num; struct Node *next; };
Algorithm to write a CPP program to delete from end in Circular Linked List
- STRUCT CUR & PREV
- CUR=HEAD
- WHILE(CUR->NEXT!=HEAD)
- PREV=CUR
- CUR=CUR->NEXT
- END WHILE
- PREV->NEXT=HEAD
- FREE(CUR)
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C++ program for deletion from end in circular linked list
A C++ program for deletion from the end in a circular linked list removes the last node while maintaining the circular connection between nodes. It carefully traverses the list to find the node before the last one and updates its pointer to the head, ensuring the list remains intact after deletion.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int num;
struct Node *next;
} *head;
void insertStart(struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = new Node;
newNode->num = data;
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
newNode->next = *head;
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n"; } else { struct Node *curr = *head; while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = newNode;
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n";
}
}
void deleteEnd(struct Node **head)
{
if (*head == NULL)
{
cout << "List is empty. Nothing to delete." << endl; return; } struct Node *cur = *head, *prev = nullptr; while (cur->next != *head)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
prev->next = cur->next;
if (cur == *head)
{
*head = prev->next;
}
free(cur);
}
void display(struct Node *head)
{
cout << "Circular Linked List: ";
if (head == NULL)
{
cout << "Empty" << endl;
return;
}
struct Node *temp = head;
do
{
cout << temp->num << " "; temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != head);
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
insertStart(&head, 1);
insertStart(&head, 2);
insertStart(&head, 3);
insertStart(&head, 4);
insertStart(&head, 5);
cout << "Before deletion: ";
display(head);
deleteEnd(&head);
cout << "After deletion: ";
display(head);
return 0;
}
Output:
1 Inserted 2 Inserted 3 Inserted 4 Inserted 5 Inserted Before deletion: Circular Linked List: 5 4 3 2 1 After deletion: Circular Linked List: 5 4 3 2
Explanation:
- To represent the circular linked list, a Node structure is created containing data and a pointer that loops back to the head, forming a continuous circle.
- When inserting at the start using insertStart(), if the list is empty, the new node points to itself; otherwise, the function locates the last node and connects it to the new head.
- During deletion in deleteEnd(), the program moves through the list to reach the final node, disconnects it, and adjusts the previous node’s pointer to maintain the circular connection.
- For displaying the list, the display() function begins at the head node and prints all elements until it loops back to the starting node, ensuring every value appears once.
- In the main function, several nodes are inserted first, then one node is removed from the end, allowing the before-and-after output to demonstrate how deletion affects the list.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insert at Beginning | O(n) | O(1) |
| Delete from End | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
After exploring the steps and seeing the C++ implementation in detail, you now have a clear method for removing the last node in a circular linked list. You’ve understood how to handle the special cases empty list, single node and learned how to traverse to the penultimate node, redirect its pointer, and free the last node safely.
Keep in mind that mastering operations on circular linked lists builds your confidence with pointer handling, dynamic memory, and list invariants skills that are essential in data structures and interview scenarios. For a deeper grasp and more practice, don’t forget to check out the additional courses and examples at PrepInsta to sharpen your coding and concept clarity.
FAQs
If the list is empty, no deletion can occur because there are no nodes to remove. The program should first check if head == NULL before proceeding.
When only one node exists, deleting it makes the list empty, so the head pointer is set to NULL after freeing the node.
Since each node only points to the next, reaching the second last node allows us to modify its next pointer to the head, effectively removing the last node.
The time complexity is O(n) because we must traverse the entire list to locate the second last node, while the space complexity remains O(1).
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment