C Program for Insertion in circular linked list
Learn how to insert node in the circular linked list
In the following section we will learn how to write a code in C Program for insertion in circular linked list, insertion means add a new node in the empty or already existed linked list.
We can perform insertion at different positions such as:-
- Insertion at the beginning
- Insertion at the end
- Insertion at the nth node
Types of insertion in circular linked list :-
1. Insertion at beginning:-
Insertion at starting in circular linked list in which we have to insert a new node before the head of the linked list, then the new node will become the head of the linked list.
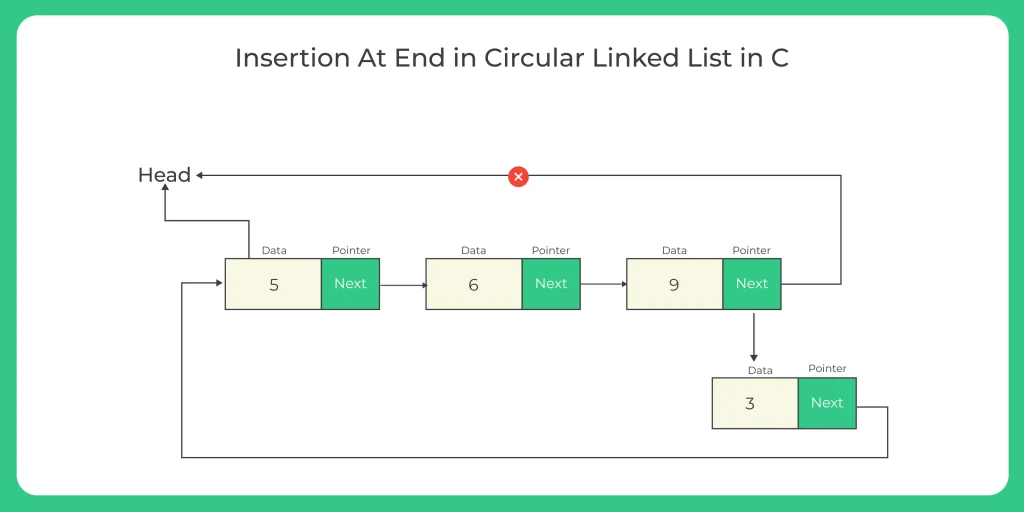
2. Insertion at end:-
Insertion at last in circular linked list in which we have to add a new node at the end of the list, then the new node will become the tail of the linked list.
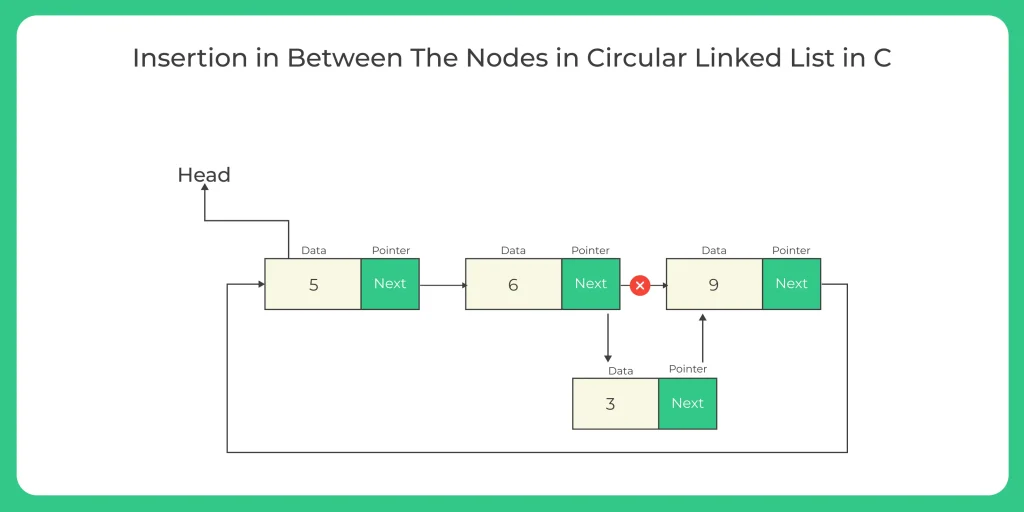
3. Insertion at nth node :-
Insertion at specific position means a new node is added according to the user wish in the linked list.
Insertion at beginning in linked list the steps are followed :-
- Make the linked list.
- Then we have to take an extra pointer which points to the end node of the circular linked list.
- Then we have a pointer that is pointing to the end node, then end node-> next will point to the first node.
- At last follow the algorithm for insertion at beginning in circular linked list given below.
Function for insertion at the beginning
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
(*head)->next = *head;
return;
}
// if LL already as >=1 node
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in LL
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
// assign LL's last node's next as this new node
curr->next = newNode;
// assign newNode's next as current head
newNode->next = *head;
// change head to this new node
*head = newNode;
} Insertion at end in linked list the steps are followed :-
- Make a new node.
- Assign the new node next to circular list.
- If the list is empty then return new node.
- Assign the new node next to the front of the list.
- Assign tail next to the new node.
- Return the end node of the circular linked list.
Function for insertion at the end
void insertLast (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
(*head)->next = *head;
return;
}
// if LL already as >=1 node
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in LL
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
// assign LL's current last node's next as this new node
curr->next = newNode;
// assign this new node's next as current head of LL
newNode->next = *head;
} 
Insertion in between the nodes in linked list the steps are followed :-
- Make a new node and set the data.
- Move to pos-1 position in the circular linked list.
- Now link the next pointer of new node with the node pointed by the next pointer of current(pos-1) node.
- After that join the next pointer of current node with the newly created node which means that the next pointer of current node will point to new node.
- Now print the linked list.
- Learn algorithm given below to understand better.
Function for insertion at the specific position
void insertPosition (int data, int pos, struct Node **head)
//function to insert element at specific position
{
struct Node *newnode, *curNode;
int i;
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("List is empty");
}
if (pos == 1)
{
insertStart (head, data);
return;
}
else
{
newnode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newnode->data = data;
curNode = *head;
while (--pos > 1)
{
curNode = curNode->next;
}
newnode->next = curNode->next;
curNode->next = newnode;
}
} 
Code For Insertion In Circular Linked List
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
(*head)->next = *head;
return;
}
// if LL already as >=1 node
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in LL
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
// assign LL's last node's next as this new node
curr->next = newNode;
// assign newNode's next as current head
newNode->next = *head;
// change head to this new node
*head = newNode;
}
void insertLast (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
(*head)->next = *head;
return;
}
// if LL already as >=1 node
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in LL
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
// assign LL's current last node's next as this new node
curr->next = newNode;
// assign this new node's next as current head of LL
newNode->next = *head;
}
void insertPosition (int data, int pos, struct Node **head)
//function to insert element at specific position
{
struct Node *newnode, *curNode;
int i;
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("List is empty");
}
if (pos == 1)
{
insertStart (head, data);
return;
}
else
{
newnode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newnode->data = data;
curNode = *head;
while (--pos > 1)
{
curNode = curNode->next;
}
newnode->next = curNode->next;
curNode->next = newnode;
}
}
void display (struct Node *head)
{
// if there are no node in LL
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node *temp = head;
//need to take care of circular structure of LL
do
{
printf ("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
printf("Insert at beginning: ");
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 1);
display (head);
printf("Insert at End: ");
insertLast (&head, 30);
insertLast (&head, 40);
display (head);
printf("Insert at Specific Position: ");
insertPosition (5, 3, &head);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Insert at beginning: 1 2 Insert at End: 1 2 30 40 Insert at Specific Position: 1 2 5 30 40
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment