Inheritance in C++
Inheritance
On this page we will discuss about inheritance in C++ .Inheritance is basically the ability for a class to be able to derive its properties from a different class. It is the most important feature of object oriented programming . So we will discuss inheritance in details along.
Inheritance in C++
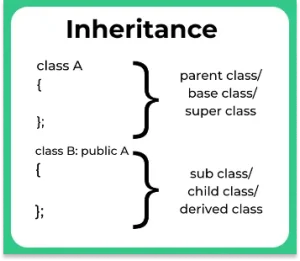
Inheritance is a process in which one object acquires all the properties and behaviour of it’s parent object automatically . It is the most important feature of object oriented programming and allows –
- High code re-use
- Lesser time to code
- Easier to maintain application and edit codes
- Re-use pre-defined properties and data
Syntax for Inheriting Declaration –
class NameOfDerivedClass : (Visibility mode) NameOfBaseClass // Data Members and functions } In terms of Parent and Child nomenclature -class NameOfChildClass : (Visibility mode) NameOfParentClass{ // Data Members and functions }
Different Modes of Inheritance in C++
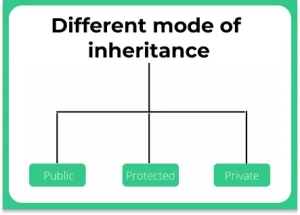
There are three different ways in which we can define relationship between base and derived class while defining inheritance –
- Public mode:
- Public members of base class become public in derived class
- Protected members of base class become Protected in derived class
- Private members are inaccessible in derived class
- Protected mode:
- Public members of base class become protected in derived class
- Protected members of base class become Protected in derived class
- Private members are inaccessible in derived class
- Private mode:
- Public members of base class become private in derived class
- Protected members of base class become private in derived class
- Private members are inaccessible in derived class
Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// base class
class Animal {
public:
void jump() {
cout << "I can jump!" << endl;
}
void sit() {
cout << "I can sit!" << endl;
}
};
// derived class
class Dog : public Animal {
public:
void bark() {
cout << "I can bark! Woof woof!!" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
// Create object of the Dog class
Dog doggy;
// Calling members of the base class
doggy.jump();
doggy.sit();
// Calling member of the derived class
doggy.bark();
return 0;
}
Output:
I can jump! I can sit! I can bark! Woof woof!!
Benefits of Inheritance
- This helps in reduce cost for projects
- Saves time in coding
- Decreases complexity of the program
- Increases reliability
Types of inheritance in C++
- Single Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Hybrid or Multipath Inheritance
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
OOPs Advanced - 1
- Inheritance
- Types of Inheritance in c++
- Polymorphism
- Upcasting and Downcasting in C++
- Operator Overloading (detailed)
- Input/Output Operators Overloading in C++
- Assignment Operators Overloading in C++
- Function Call Operator () Overloading in C++
- Class Member Access Operator (->) Overloading in C++
- Unary Operator Overloading in C++
- Binary Operator Overloading in C++
- Relational operator overloading in C++
- Overloading ++ and — increment and Decrement Operators in C++
- Constructor Overloading in C++






Login/Signup to comment