Deletion in Circular Linked List in C

C Program for Circular Linked List Deletion
In the Deletion in Circular Linked List in C we can delete the node in the following ways :
- Deletion from the Beginning
- Deletion from the End
- Deletion from the specific Position
Deletion in Circular Linked List in C
In this topic we want to discuss about delete the any node in circular linked list So, In this scenario is also have three ways to delete the node in linked list like doubly or singly linked list.
- Deletion at beginning
- Deletion at middle
- Deletion at end
1. It is not easy to reverse the linked list.
2. If proper care is not taken, then the problem of infinite loop can occur.
3. If we are at a node, then we can go to any node. But in linear linked list it is not possible to go to previous node. Easy implementation of some operations is possible
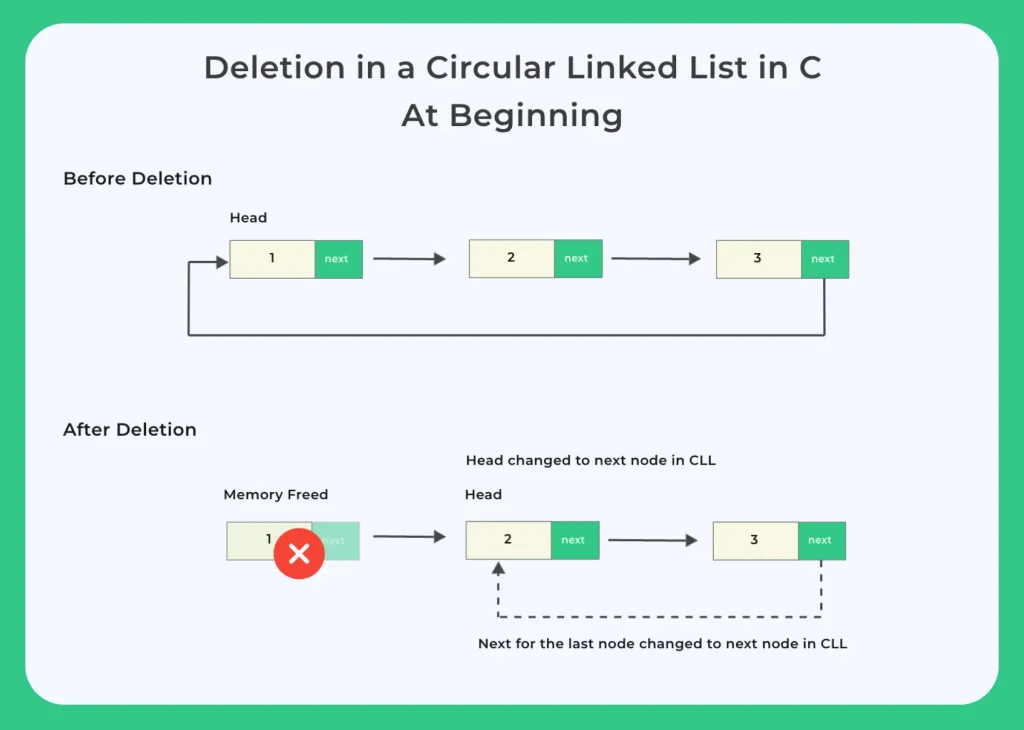
Deletion at beginning
Let’s have a look at the code for deletion at the beginning –void deleteBegin(struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// if only 1 node in CLL
if (temp->next == *head)
{
*head = NULL;
return;
}
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in CLL
while (curr->next != *head)
curr = curr->next;
// assign last node's next to 2nd node in CLL
curr->next = (*head)->next;
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
free (temp);
}

Deletion at end
Let’s have a look at the code for deletion at the end –void deleteEnd (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
struct Node *previous;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (temp->next == *head)
{
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// else traverse to the last node
while (temp->next != *head)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to head
previous->next = *head;
// delete the last node
free (temp);
// 2nd last now becomes the last node
}
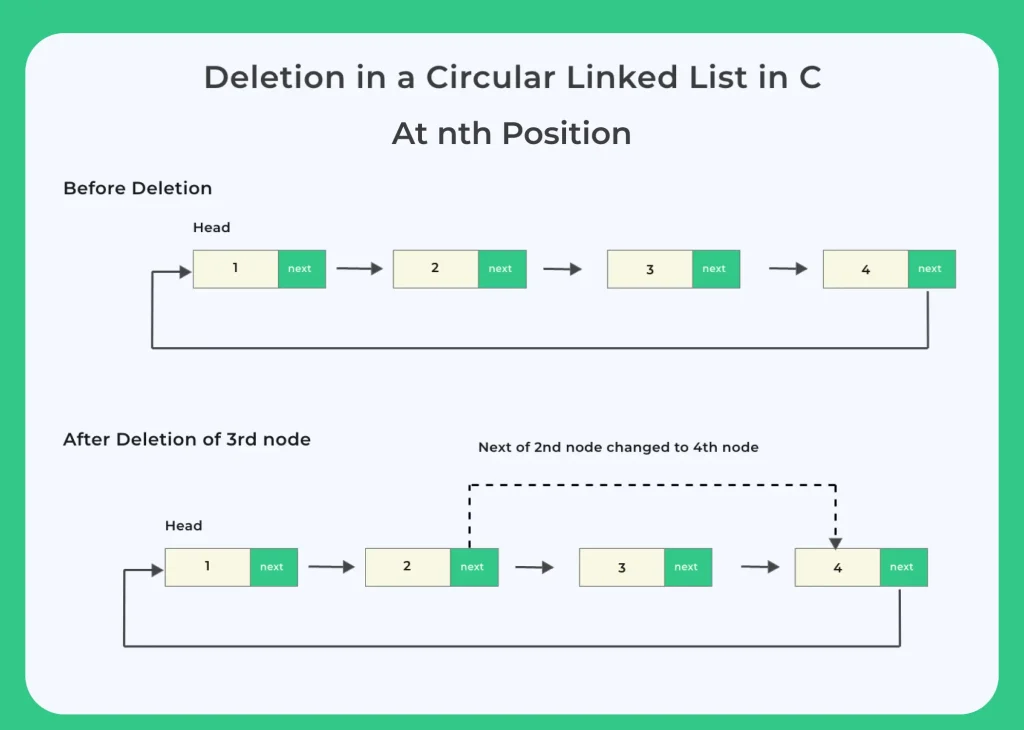
Deletion in between (After a given node)
Let’s have a look at the code for deletion after a given node –void deletePos (struct Node **head, int n)
{
int size = calcSize (*head);
if (n < 1 || size < n)
{
printf ("Can't delete, %d is not a valid position\n", n);
}
else if (n == 1)
deleteFront (head);
else if (n == size)
deleteEnd (head);
else
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
struct Node *previous;
// traverse to the nth node
while (--n)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// change previous node's next node to nth node's next node
previous->next = temp->next;
// delete this nth node
free (temp);
}
}
Code for Deletion in circular
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// structure for Circular Linked List
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
int calcSize (struct Node *head);
void deleteBegin(struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *tempNode = *head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// if only 1 node in CLL
if (tempNode->next == *head)
{
*head = NULL;
return;
}
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in CLL
while (curr->next != *head)
curr = curr->next;
// assign last node's next to 2nd node in CLL
curr->next = (*head)->next;
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
free (tempNode);
}
void deleteEnd (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *tempNode = *head;
struct Node *previous;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (tempNode->next == *head)
{
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// else traverse to the last node
while (tempNode->next != *head)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode->next;
}
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to head
previous->next = *head;
// delete the last node
free (tempNode);
// 2nd last now becomes the last node
}
void deletePos (struct Node **head, int n)
{
int size = calcSize (*head);
if (n < 1 || size < n)
{
printf ("Can't delete, %d is not a valid position\n", n);
}
else if (n == 1)
deleteBegin(head);
else if (n == size)
deleteEnd (head);
else
{
struct Node *tempNode = *head;
struct Node *previous;
// traverse to the nth node
while (--n)
{
// store previous link node as we need to change its next val
previous = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode->next;
}
// change previous node's next node to nth node's next node
previous->next = tempNode->next;
// delete this nth node
free (tempNode);
}
}
void insert (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
(*head)->next = *head;
return;
}
struct Node *curr = *head;
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = newNode;
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
int calcSize (struct Node *head)
{
int size = 0;
struct Node *temp = head;
if (temp == NULL)
return size;
do
{
size++;
temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
return size;
}
void display (struct Node *head)
{
// if there are no node in CLL
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node *temp = head;
//need to take care of circular structure of CLL
do
{
printf ("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
// first node will be null at creation
struct Node *head = NULL;
insert (&head, 10);
insert (&head, 11);
insert (&head, 12);
insert (&head, 13);
insert (&head, 14);
insert (&head, 15);
insert (&head, 16);
display (head);
deleteBegin(&head);
display (head);
deleteEnd (&head);
display (head);
deletePos (&head, 3);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 15 14 13 12 11 10 15 14 13 12 11 15 14 12 11
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment