Sorting of elements by frequency in Java
Java Program for Sorting of elements by frequency
In this article, we will explore how to perform Sorting of elements by frequency in Java using two different approaches: the naive method and the hash map + sorting method.
In many real world applications like log analysis, vote counting, or recommendation systems, we often need to sort elements based on their frequency of occurrence. Java provides us with the tools and data structures needed to solve this efficiently.

Sorting of elements by frequency in Java
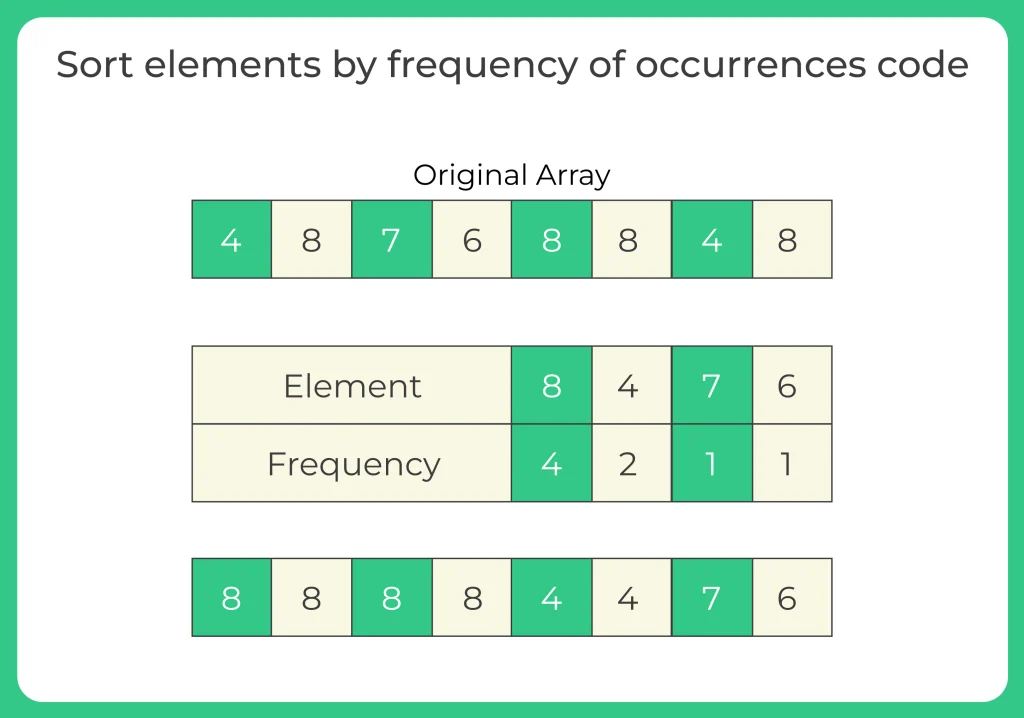
Example:
Input:
arr = [4, 8, 7, 6, 8, 8, 4, 8]
Step 1: Frequency Count
- 8 → 4 times
- 4 → 2 times
- 7, 6 → 1 time each
Step 2: Sort by frequency
- 8 appears 4 times
- 4 appears 2 times
- 7 and 6 appear once, so retain original order between them
Output:
[8, 8, 8, 8, 4, 4, 7, 6]
Methods to sort elements by their frequency using Java
Now we will learn about 2 methods to sort elements by frequency using Java:
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods for Sorting of elements by frequency in Java
Method 1: Naive Approach
Algorithm:
- Create a visited array to track processed elements.
- For each element in the array:
Count its frequency by iterating through the rest of the array.
Mark duplicates as visited.
Store elements with their frequency in a list.
Sort the list based on frequency.
Print elements based on their frequency.
Space Complexity: O(n)
Java Code:
import java.util.*;
public class FrequencySortNaive {
public static void sortByFrequency(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (visited[i])
continue;
int count = 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[i] == arr[j]) {
visited[j] = true;
count++;
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < count; k++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2, 3, 2, 4, 5, 12, 2, 3, 3, 12};
sortByFrequency(arr);
}
}
Output:
2 2 2 3 3 3 4 5 12 12
Method 2: Using HashMap + Sorting (Efficient)
Algorithm:
Traverse the array and store frequency of each element using a HashMap.
Store array elements and their original order using a LinkedHashMap or array index.
Convert the map into a list of entries.
Sort the list using a custom comparator:
Sort by frequency (descending)
If frequency matches, retain order based on index of first occurrence.
Build the result by repeating each element based on its frequency.
Space Complexity: O(n)
Java Code:
import java.util.*;
public class FrequencySortEfficient {
public static void sortByFrequency(int[] arr) {
Map freqMap = new HashMap<>();
Map firstIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
freqMap.put(arr[i], freqMap.getOrDefault(arr[i], 0) + 1);
if (!firstIndexMap.containsKey(arr[i])) {
firstIndexMap.put(arr[i], i); // preserve order of first occurrence
}
}
List uniqueElements = new ArrayList<>(freqMap.keySet());
// Sort based on frequency, then first occurrence
uniqueElements.sort((a, b) -> {
int freqCompare = Integer.compare(freqMap.get(b), freqMap.get(a));
if (freqCompare == 0) {
return Integer.compare(firstIndexMap.get(a), firstIndexMap.get(b));
}
return freqCompare;
});
// Print result
for (int num : uniqueElements) {
int freq = freqMap.get(num);
for (int i = 0; i < freq; i++) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2, 3, 2, 4, 5, 12, 2, 3, 3, 12};
sortByFrequency(arr);
}
}
Output:
2 2 2 3 3 3 12 12 4 5
Comparison Table: Time and Space Complexity
| Method | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Naive Approach | O(n²) | O(n) | Easy to implement, slow for large arrays |
| HashMap + Sorting | O(n log n) | O(n) | Efficient and scalable |
To wrap it up with….
Sorting elements by frequency is a common problem that tests your understanding of maps, sorting, and custom comparators.
While the naive approach is simple, the HashMap + sorting approach is the go to method for optimal performance.
By mastering both, you’ll not only improve your coding skills but also prepare yourself for interviews and real world Java problems.
FAQ's related to Sorting of elements by frequency in Java
Answer:
Using a HashMap to count frequencies followed by sorting using a comparator is the most efficient and recommended approach.
Answer:
In case of a tie, the element that appeared first in the original array should come first. This can be handled by tracking the first index of each element.
Answer:
TreeMap maintains elements in sorted key order, which is not suitable when we want to sort by frequency. So HashMap (for counting) with List (for sorting) is preferred.
Answer:
The approach works the same way since it uses HashMap. Negative numbers and large inputs are fully supported.
Answer:
It is useful for learning or small datasets, but not recommended for performance sensitive scenarios.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment