Virtusa Power Coding Challenge Questions
Sample Virtusa Power Coding Challenge Questions
Here on this page we have shared some sample Virtusa Power Coding Challenge Questions with Solution to provide you proper idea how DSA based Advanced level questions are given to solve after Coding Challenge to secure the Job Role of Virtusa Power Coder Profile with salary of Rs. 6.5 LPA.
Go through this page to get clear understanding of Sample Question we have shared to practice effectively. All the best!!!

Virtusa is offering Software Developer and Software Tester job profile for 2025 batch.
Last Date to Apply: 3 October 2025
You can checkout about Virtusa Neural Hackathon 2025 below….
Challenge Details:
- No. of Questions: 4 coding questions
- Time: 50 minutes
- Difficulty Level: Moderate
- Topics Covered: Arrays, Strings, Searching, Sorting, Basic Algorithms, etc.
- Goal: To check your logic-building ability, syntax knowledge, and problem-solving skills.
Challenge Details:
- No. of Questions: 3 complex coding questions
- Time: 80 minutes
- Difficulty Level: Hard
- Topics Covered: Advanced Algorithms, Trees, Graphs, Dynamic Programming, etc.
- Goal: To identify top coders who can solve real world, complex problems efficiently.
From here, you will get sample Virtusa Power Coding Challenge Questions with Solution to practice properly including Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Concepts…..
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Sample Virtusa Power Coding Challenge Questions
Problem 1: Serializing and Deserializing Binary Tree
Create an algorithm to convert a binary tree into a string (serialization) and then reconstruct the same binary tree from that string (deserialization).
Goal is to ensure that the binary tree can be serialized into a string and later de serialized back to its original structure without any loss of information. There are no specific rules for how you should implement this; the approach is up to you.
Example 1:
- Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
- Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
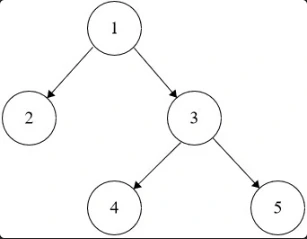

Constraints:
- 0 <= The number of nodes in the tree <= 1000.
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Note: Try to solve the problem with O(n) time and O(n) space, where n is the total number of nodes in the binary tree.
Solving by Breadth First Search Method
In the BFS approach, the binary tree is serialized level by level using a queue to store node values. During deserialization, the data is processed sequentially to rebuild the tree by connecting child nodes level-wise.
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(n)
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Codec {
public:
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return "N";
string res;
queue<TreeNode*> queue;
queue.push(root);
while (!queue.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = queue.front();
queue.pop();
if (!node) {
res += "N,";
} else {
res += to_string(node->val) + ",";
queue.push(node->left);
queue.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
stringstream ss(data);
string val;
getline(ss, val, ',');
if (val == "N") return nullptr;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
queue<TreeNode*> queue;
queue.push(root);
while (getline(ss, val, ',')) {
TreeNode* node = queue.front();
queue.pop();
if (val != "N") {
node->left = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
queue.push(node->left);
}
if (!getline(ss, val, ',')) break;
if (val != "N") {
node->right = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
queue.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
import java.util.*;
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
public class Codec {
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return "N";
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node == null) {
res.append("N,");
} else {
res.append(node.val).append(",");
queue.add(node.left);
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
return res.toString();
}
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] vals = data.split(",");
if (vals[0].equals("N")) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[0]));
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int index = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty() && index < vals.length) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (!vals[index].equals("N")) {
node.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[index]));
queue.add(node.left);
}
index++;
if (index < vals.length && !vals[index].equals("N")) {
node.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[index]));
queue.add(node.right);
}
index++;
}
return root;
}
}
from collections import deque
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
if not root:
return "N"
res = []
queue = deque([root])
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if not node:
res.append("N")
else:
res.append(str(node.val))
queue.append(node.left)
queue.append(node.right)
return ",".join(res)
def deserialize(self, data):
vals = data.split(",")
if vals[0] == "N":
return None
root = TreeNode(int(vals[0]))
queue = deque([root])
index = 1
while queue and index < len(vals):
node = queue.popleft()
if vals[index] != "N":
node.left = TreeNode(int(vals[index]))
queue.append(node.left)
index += 1
if index < len(vals) and vals[index] != "N":
node.right = TreeNode(int(vals[index]))
queue.append(node.right)
index += 1
return root
Problem 2: Detect Square
You are given a stream of 2D points with x-y coordinates, and you can perform the following operations:
- Add – Add new points to a data structure. Duplicate points are allowed and treated independently.
- Query – For a given query point, count how many ways you can select three additional points from the data structure to form a square. The square must have sides parallel to the x-axis and y-axis, and all sides must be of equal length (no diagonal squares).
Constraints:
- point.length == 2
- 0 <= x, y <= 1000
Example:
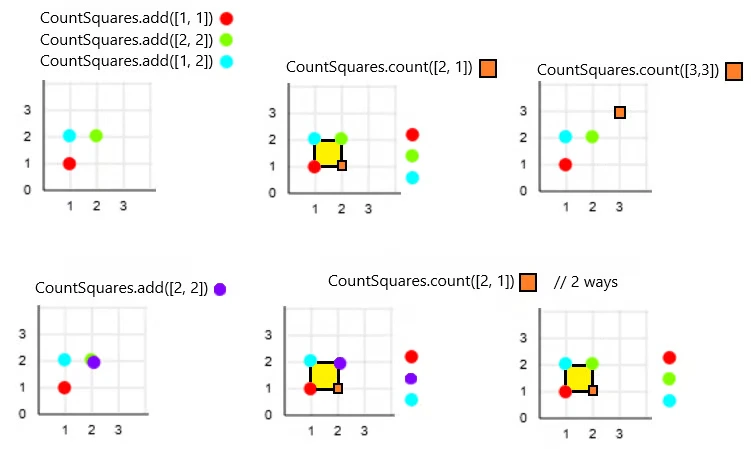

"add", [[1, 2]], "count", [[2, 1]], "count", [[3, 3]],
"add", [[2, 2]], "count", [[2, 1]]]
Output: [null, null, null, null, 1, 0, null, 2]
countSquares.add([1, 1]);
countSquares.add([2, 2]);
countSquares.add([1, 2]);
countSquares.count([2, 1]); // return 1.
countSquares.count([3, 3]); // return 0.
countSquares.add([2, 2]); // Duplicate points are allowed.
countSquares.count([2, 1]); // return 2.
Solving Hash Map method:
Use a hash map to store the frequency of each point added. To detect squares, iterate over all possible diagonal points for the query point, and calculate the frequencies of the other two required points to form a square.
- Time complexity: O(1) for add(), O(n) for count()
- Space complexity: O(n)
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class CountSquares {
private:
unordered_map<long, int> ptsCount;
vector<vector> pts;
long getKey(int x, int y) {
return (static_cast(x) << 32) | static_cast(y);
}
public:
CountSquares() {}
void add(vector point) {
long key = getKey(point[0], point[1]);
ptsCount[key]++;
pts.push_back(point);
}
int count(vector point) {
int res = 0;
int px = point[0], py = point[1];
for (const auto& pt : pts) {
int x = pt[0], y = pt[1];
if (abs(px - x) != abs(py - y) || px == x || py == y) continue;
res += ptsCount[getKey(x, py)] * ptsCount[getKey(px, y)];
}
return res;
}
};
import java.util.*;
public class CountSquares {
private Map<List, Integer> ptsCount;
private List<List> pts;
public CountSquares() {
ptsCount = new HashMap<>();
pts = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void add(int[] point) {
List p = Arrays.asList(point[0], point[1]);
ptsCount.put(p, ptsCount.getOrDefault(p, 0) + 1);
pts.add(p);
}
public int count(int[] point) {
int res = 0;
int px = point[0], py = point[1];
for (List pt : pts) {
int x = pt.get(0), y = pt.get(1);
if (Math.abs(px - x) != Math.abs(py - y) || px == x || py == y) continue;
res += ptsCount.getOrDefault(Arrays.asList(x, py), 0) *
ptsCount.getOrDefault(Arrays.asList(px, y), 0);
}
return res;
}
}
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import List
class CountSquares:
def __init__(self):
self.ptsCount = defaultdict(int)
self.pts = []
def add(self, point: List[int]) -> None:
self.ptsCount[tuple(point)] += 1
self.pts.append(point)
def count(self, point: List[int]) -> int:
res = 0
px, py = point
for x, y in self.pts:
if abs(px - x) != abs(py - y) or px == x or py == y:
continue
res += self.ptsCount[(x, py)] * self.ptsCount[(px, y)]
return res
Problem 3: What is N-Queen Problem?
N-queens puzzle is about placing n queens on an n x n chessboard so that no two queens can attack each other.
Queens can attack in three ways: horizontally, vertically, and diagonally.
Problem Statement:
- Your task is to find all possible ways to place the queens on the board, ensuring no two queens attack each other.
- Each solution will show a unique board arrangement where ‘Q’ represents a queen and ‘.’ represents an empty square. The solutions can be returned in any order.
- Input: n = 4
- Output: [[“.Q..”,”…Q”,”Q…”,”..Q.”],<br>[“..Q.”,”Q…”,”…Q”,”.Q..”]]
Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 8
Example:
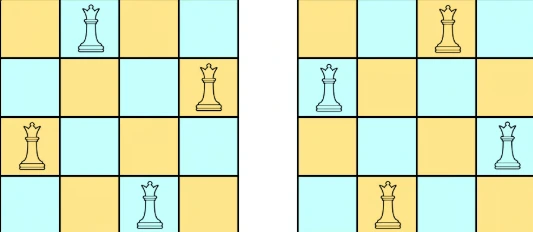
Solving by Backtracking(Bit Mask) Method
This optimized approach uses bit masking to track columns and diagonals, making it extremely space-efficient. By representing occupied columns and diagonals as bits in integers, we can quickly check and update states during recursion, making it suitable for larger board sizes.
- Time complexity: O(n!)
- Space complexity: O(n^2)
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int col = 0, posDiag = 0, negDiag = 0;
vector board;
vector<vector> res;
vector<vector> solveNQueens(int n) {
board.resize(n, string(n, '.'));
backtrack(0, n);
return res;
}
void backtrack(int r, int n) {
if (r == n) {
res.push_back(board);
return;
}
for (int c = 0; c < n; ++c) {
if ((col & (1 << c)) || (posDiag & (1 << (r + c))) || (negDiag & (1 << (r - c + n)))) {
continue;
}
col ^= (1 << c);
posDiag ^= (1 << (r + c));
negDiag ^= (1 << (r - c + n));
board[r][c] = 'Q';
backtrack(r + 1, n);
col ^= (1 << c);
posDiag ^= (1 << (r + c));
negDiag ^= (1 << (r - c + n));
board[r][c] = '.';
}
}
};
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
int col = 0, posDiag = 0, negDiag = 0;
List<List> res;
char[][] board;
public List<List> solveNQueens(int n) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
board = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(board[i], '.');
}
backtrack(0, n);
return res;
}
private void backtrack(int r, int n) {
if (r == n) {
List copy = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] row : board) {
copy.add(new String(row));
}
res.add(copy);
return;
}
for (int c = 0; c < n; c++) {
if ((col & (1 << c)) > 0 || (posDiag & (1 << (r + c))) > 0 || (negDiag & (1 << (r - c + n))) > 0) {
continue;
}
col ^= (1 << c);
posDiag ^= (1 << (r + c));
negDiag ^= (1 << (r - c + n));
board[r][c] = 'Q';
backtrack(r + 1, n);
col ^= (1 << c);
posDiag ^= (1 << (r + c));
negDiag ^= (1 << (r - c + n));
board[r][c] = '.';
}
}
}
class Solution:
def solveNQueens(self, n: int):
col = 0
posDiag = 0
negDiag = 0
res = []
board = [["."] * n for _ in range(n)]
def backtrack(r):
nonlocal col, posDiag, negDiag
if r == n:
res.append(["".join(row) for row in board])
return
for c in range(n):
if (col & (1 << c)) or (posDiag & (1 << (r + c))) or (negDiag & (1 << (r - c + n))):
continue
col ^= (1 << c)
posDiag ^= (1 << (r + c))
negDiag ^= (1 << (r - c + n))
board[r][c] = "Q"
backtrack(r + 1)
col ^= (1 << c)
posDiag ^= (1 << (r + c))
negDiag ^= (1 << (r - c + n))
board[r][c] = "."
backtrack(0)
return res
Virtusa Power Coding Challenge Questions
Problem 4: Word Search II
Statement: You are given a 2D grid of letters (board) and a list of words. Your goal is to find all the words from the list that can be formed by following a continuous path on the grid.
- Word is considered valid if its letters can be connected using adjacent cells in the grid, either horizontally or vertically.
- However, you cannot use the same cell more than once while forming a word. Return all the words from the list that meet these conditions.
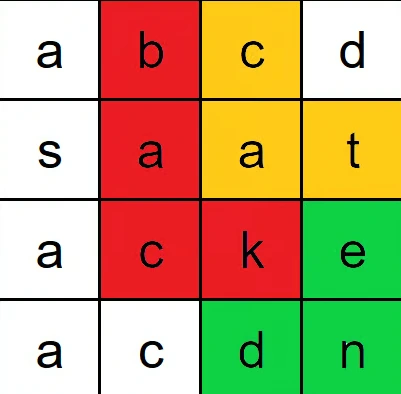

Constraints:
- 1 <= board.length, board[i].length <= 10
- board[i] consists only of lowercase English letter.
- 1 <= words.length <= 100
- 1 <= words[i].length <= 10
- words[i] consists only of lowercase English letters.
- All strings within words are distinct.
board = [
["a","b","c","d"],
["s","a","a","t"],
["a","c","k","e"],
["a","c","d","n"]
],
words = ["bat","cat","back","backend","stack"]
Output: ["cat","back","backend"]
Solving by Backtracking(Trie + Hash Set) Method
Use a Trie to store words and a Hash Set to track found words. Backtracking checks characters in the Trie, adding valid words to the result set to improve efficiency.
- Time complexity: O\left ( m\times n \times 4 \times 3^{t-1} + s\right ).
- Space complexity: O(s)
:: where m is the number of rows, n is the number of columns, t is the maximum length of any word in the array words and s is the sum of the lengths of all the words.
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class TrieNode {
public:
unordered_map<char, TrieNode*> children;
bool isWord;
TrieNode() : isWord(false) {}
void addWord(const string& word) {
TrieNode* cur = this;
for (char c : word) {
if (!cur->children.count(c)) {
cur->children[c] = new TrieNode();
}
cur = cur->children[c];
}
cur->isWord = true;
}
};
class Solution {
unordered_set res;
vector<vector> visit;
public:
vector findWords(vector<vector>& board, vector& words) {
TrieNode* root = new TrieNode();
for (const string& word : words) {
root->addWord(word);
}
int ROWS = board.size(), COLS = board[0].size();
visit.assign(ROWS, vector(COLS, false));
for (int r = 0; r < ROWS; ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c < COLS; ++c) {
dfs(board, r, c, root, "");
}
}
return vector(res.begin(), res.end());
}
private:
void dfs(vector<vector>& board, int r, int c, TrieNode* node, string word) {
int ROWS = board.size(), COLS = board[0].size();
if (r < 0 || c < 0 || r >= ROWS || c >= COLS || visit[r][c] || !node->children.count(board[r][c])) {
return;
}
visit[r][c] = true;
node = node->children[board[r][c]];
word += board[r][c];
if (node->isWord) {
res.insert(word);
}
dfs(board, r + 1, c, node, word);
dfs(board, r - 1, c, node, word);
dfs(board, r, c + 1, node, word);
dfs(board, r, c - 1, node, word);
visit[r][c] = false;
}
};
import java.util.*;
class TrieNode {
Map<Character, TrieNode> children;
boolean isWord;
public TrieNode() {
children = new HashMap<>();
isWord = false;
}
public void addWord(String word) {
TrieNode cur = this;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
cur.children.putIfAbsent(c, new TrieNode());
cur = cur.children.get(c);
}
cur.isWord = true;
}
}
public class Solution {
private Set res;
private boolean[][] visit;
public List findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
TrieNode root = new TrieNode();
for (String word : words) {
root.addWord(word);
}
int ROWS = board.length, COLS = board[0].length;
res = new HashSet<>();
visit = new boolean[ROWS][COLS];
for (int r = 0; r < ROWS; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < COLS; c++) {
dfs(board, r, c, root, "");
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(res);
}
private void dfs(char[][] board, int r, int c, TrieNode node, String word) {
int ROWS = board.length, COLS = board[0].length;
if (r < 0 || c < 0 || r >= ROWS || c >= COLS || visit[r][c] || !node.children.containsKey(board[r][c])) {
return;
}
visit[r][c] = true;
node = node.children.get(board[r][c]);
word += board[r][c];
if (node.isWord) {
res.add(word);
}
dfs(board, r + 1, c, node, word);
dfs(board, r - 1, c, node, word);
dfs(board, r, c + 1, node, word);
dfs(board, r, c - 1, node, word);
visit[r][c] = false;
}
}
from typing import List
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self):
self.children = {}
self.isWord = False
def addWord(self, word: str):
cur = self
for c in word:
if c not in cur.children:
cur.children[c] = TrieNode()
cur = cur.children[c]
cur.isWord = True
class Solution:
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
root = TrieNode()
for word in words:
root.addWord(word)
ROWS, COLS = len(board), len(board[0])
res, visit = set(), set()
def dfs(r, c, node, word):
if (r < 0 or c < 0 or r >= ROWS or c >= COLS or
(r, c) in visit or board[r][c] not in node.children):
return
visit.add((r, c))
node = node.children[board[r][c]]
word += board[r][c]
if node.isWord:
res.add(word)
dfs(r + 1, c, node, word)
dfs(r - 1, c, node, word)
dfs(r, c + 1, node, word)
dfs(r, c - 1, node, word)
visit.remove((r, c))
for r in range(ROWS):
for c in range(COLS):
dfs(r, c, root, "")
return list(res)
Problem 5: Target Sum – A Problem of Possibilities
Programming challenges often push us to think outside the box, and the Target Sum Problem is no exception. It presents an intriguing scenario that combines arithmetic operations with logical reasoning.
Problem Description:
You are given an array of integers nums and an integer target.
For each number in the array, you can choose to either add or subtract it to a total sum.
For example, if nums = [1, 2], one possible sum would be “+1-2=-1”.
If nums=[1,1], there are two different ways to sum the input numbers to get a sum of 0: “+1-1” and “-1+1“.
Return the number of different ways that you can build the expression such that the total sum equals target.
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 20
- 0 <= nums[i] <= 1000
- -1000 <= target <= 1000
Explanation:
Explanation: There are 3 different ways to sum the input numbers to get a sum of 2.
+2 +2 -2 = 2
+2 -2 +2 = 2
-2 +2 +2 = 2
Solving using Recursion method:
- Time complexity: O(2n)
- Space complexity: O(n)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int findTargetSumWays(vector& nums, int target) {
return backtrack(0, 0, nums, target);
}
private:
int backtrack(int i, int total, vector& nums, int target) {
if (i == nums.size()) {
return total == target ? 1 : 0;
}
return backtrack(i + 1, total + nums[i], nums, target) +
backtrack(i + 1, total - nums[i], nums, target);
}
};
public class Solution {
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int target) {
return backtrack(0, 0, nums, target);
}
private int backtrack(int i, int total, int[] nums, int target) {
if (i == nums.length) {
return total == target ? 1 : 0;
}
return backtrack(i + 1, total + nums[i], nums, target) +
backtrack(i + 1, total - nums[i], nums, target);
}
}
from typing import List
class Solution:
def findTargetSumWays(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
def backtrack(i: int, total: int) -> int:
if i == len(nums):
return 1 if total == target else 0
return backtrack(i + 1, total + nums[i]) + backtrack(i + 1, total - nums[i])
return backtrack(0, 0)
These were some sample Virtusa Power Coding Challenge Questions and Answers, go through them properly and prepare effectively.
If you want to prepare questions like this for Virtusa Power Coding Challenge checkout our Coding Dashboard.
FAQ's related Virtusa Power Coding Challenge
Answer:
The Virtusa recruitment process mainly includes 4 rounds:
Round 1: Online Assessment (Aptitude, Logical Reasoning, Verbal, Pseudocode, CS Fundamentals and Coding)
Round 2: Technical Interview
Round 3: Group Discussion or Managerial Round
Round 4: HR Interview
Answer:
- Coder Profile: Includes 4 moderate-level coding questions to be solved in 50 minutes.
- Power Coder Profile: Includes 3 high difficulty coding questions with 80 minutes to solve. It is designed for candidates aiming for advanced roles or higher packages.
Answer:
The Virtusa assessment includes the following sections:
- Quantitative Aptitude and Logical Reasoning
- Verbal Ability
- Pseudocode and Programming Fundamentals
- Computer Science Fundamentals (OS, DBMS, Data Structures)
- Coding (for Coder/Power Coder tracks)
Answer:
No. While Virtusa hires extensively through campus placements, it also conducts off-campus drives and open hiring challenges like Talent Titan or Power Programmer Challenges through platforms like HirePro, TalentTitan, and Superset.
Answer:
To be eligible for Virtusa On campus hiring, candidates must meet the following criteria:
- Must be from the B.E./B.Tech (CSE, IT, ECE, EEE, EIE) or MCA/M.Tech background.
- Should belong to the 2025 passing out batch.
- Must have 60% or above in 10th, 12th, and graduation (or equivalent CGPA).
- Should not have more than 1 active backlog at the time of applying.
- Must not have a gap of more than 1 year in education.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others

 Apply For Jobs
Apply For Jobs Get Hiring Updates
Get Hiring Updates
