Split Circular Linked List into two halves in Java
Java Program to Split a Circular Linked List into two equal halves
In this article, we will learn how to split a circular linked list into two halves in Java, step by step, using Java. Circular Linked List is a variation of a linked list where the last node does not point to null, but instead points back to the head node, forming a loop.
Splitting a circular linked list into two equal (or nearly equal) halves is a common interview question. It helps test knowledge of pointer manipulation, linked list traversal, and the fast slow pointer technique.

Program to Split a Circular Linked List in two halves
Problem Statement:
Given a Circular Singly Linked List split it into two circular linked lists such that:
- If the list has even number of nodes, both lists are equal in size
- If the list has odd number of nodes, the first half will contain one extra node
- Both resulting lists must remain circular.
Example:
Input:
10 → 20 → 30 → 40 → 50 → back to 10
Output:
List 1: 10 → 20 → 30 → back to 10 List 2: 40 → 50 → back to 40
Concepts used to Split a circular linked list:
| Concepts | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Slow & Fast Pointer | To find the midpoint in a single traversal |
| Circular Linking | Ensures both resulting lists remain circular |
| Node Class | Stores data and next reference |
Approach:
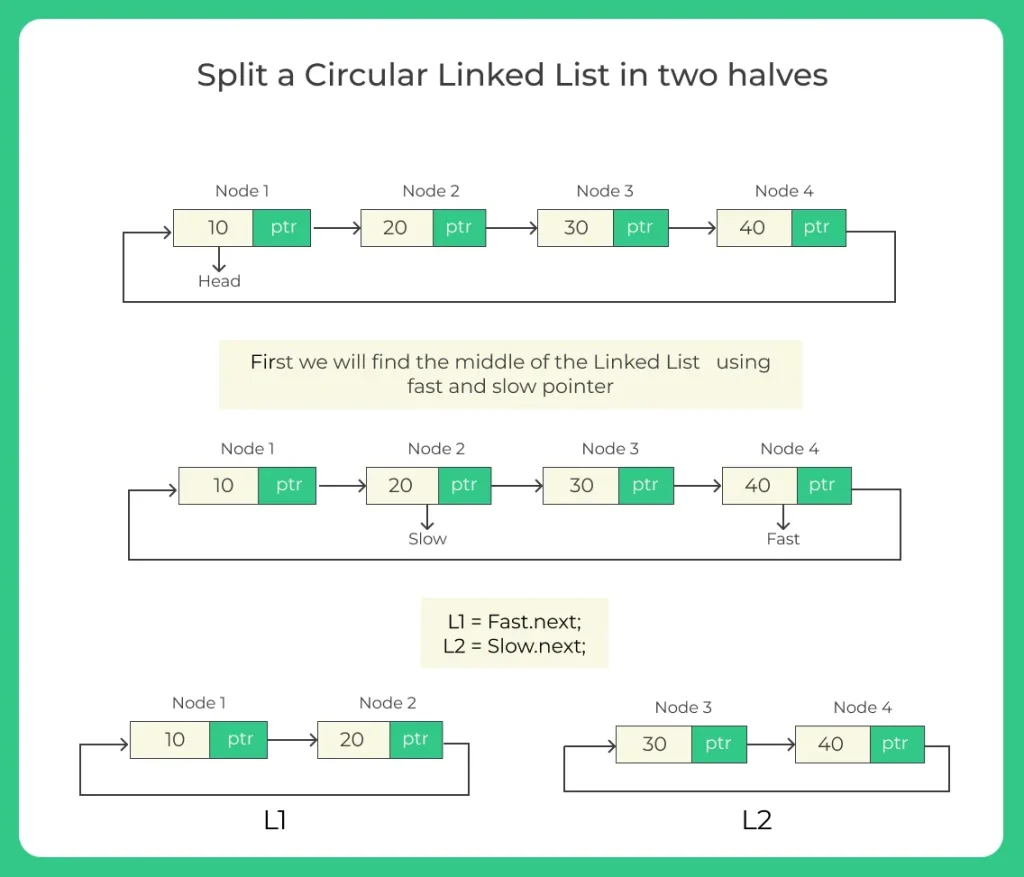
The most efficient method to split a circular linked list is the Slow and Fast Pointer Technique:
- slow moves one step at a time
- fast moves two steps at a time
- When fast reaches the last node (or one before last), slow will be at the midpoint
- Using slow and fast, we detach the list into two circular lists
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Algorithm to Split a Circular Linked List in Two Halves
Algorithm:
- Initialize two pointers:
- slow = head
- fast = head
- Traverse the circular linked list:
- WHILE (fast.next != head AND fast.next.next != head)
- slow = slow.next
- fast = fast.next.next
- WHILE (fast.next != head AND fast.next.next != head)
- If the list has odd number of nodes:
- IF (fast.next.next == head)
- fast = fast.next
- IF (fast.next.next == head)
- Now pointers are at split positions:
- head1 = head
- head2 = slow.next
- Make first list circular:
- slow.next = head1
- Make second list circular:
- fast.next = head2
- END
Java Program to Split a Circular Linked List in Two Halves
class CircularLinkedListSplit {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Node head;
// Function to split the circular linked list
void splitList() {
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head;
if (head == null || head.next == head) {
return; // No split possible
}
// Use slow and fast pointers to find mid
while (fast.next != head && fast.next.next != head) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// For odd number of nodes, move fast one step more
if (fast.next.next == head) {
fast = fast.next;
}
// First half head
Node head1 = head;
// Second half head
Node head2 = slow.next;
// Make first half circular
slow.next = head1;
// Make second half circular
fast.next = head2;
// Print both lists
System.out.println("First Circular Linked List:");
printCircularList(head1);
System.out.println("Second Circular Linked List:");
printCircularList(head2);
}
// Function to print circular list
void printCircularList(Node node) {
Node temp = node;
if (node != null) {
do {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != node);
}
System.out.println();
}
// Function to add node at end
void addNode(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != head) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircularLinkedListSplit list = new CircularLinkedListSplit();
list.addNode(10);
list.addNode(20);
list.addNode(30);
list.addNode(40);
list.addNode(50);
System.out.println("Original Circular Linked List:");
list.printCircularList(list.head);
list.splitList();
}
}
Output:
Original Circular Linked List: 10 20 30 40 50 First Circular Linked List: 10 20 30 Second Circular Linked List: 40 50
Space Complexity: O(1)
FAQ's Related to Program to Split Circular Linked List
Answer:
It allows you to divide the list into two independent circular lists, often used in scheduling, round robin algorithms, and interview problems.
Answer:
Operation involves dividing an original circular linked list into two distinct, smaller circular linked lists. The first resultant list contains the initial sequence of nodes up to the middle, and the second list contains the remaining nodes.
Answer:
Slow and Fast Pointer Method (also known as the Hare and Tortoise algorithm) is the most efficient way to find the middle in a single traversal.
- slow pointer moves one node at a time.
- fast pointer moves two nodes at a time.
When the fast pointer (or fast.next) reaches the last node or just before the head of the original list, the slow pointer will be at the correct middle point for the split.
Answer:
Slow and fast pointer approach is more efficient because it only requires a single traversal of the list, while the counting method requires two full traversals (one to count, one to split).
Answer:
- Standard approach is that if the original list has an even number of nodes, both resulting lists have an equal number of nodes (N/2 each).
- If the list has an odd number of nodes, the first half contains one extra node (Ex. list of 5 nodes results in lists of 3 and 2 nodes).
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment