Deletion at the nth node of a Circular Linked List in Java
Deletion at the nth node of a Circular Linked List using Java
In this article, we will focus on how to delete the nth node from a Circular Singly Linked List in Java.
Circular Linked List is a variation of the linked list where the last node points back to the head node, forming a circular structure. This data structure is particularly useful in applications that require continuous traversal, such as in multiplayer games, CPU scheduling, or real time systems.
We’ll cover:
- What it means to delete the nth node in a circular linked list and Step by step explanation
- Multiple approaches with complete Java code and Time/space complexity for each method
- Examples of input and output

- Circular Singly Linked List: Each node has a single pointer to the next node.
- Circular Doubly Linked List: Each node has two pointers (next and previous).
Problem Statement for Deletion at the nth Node of a Circular Linked List in Java
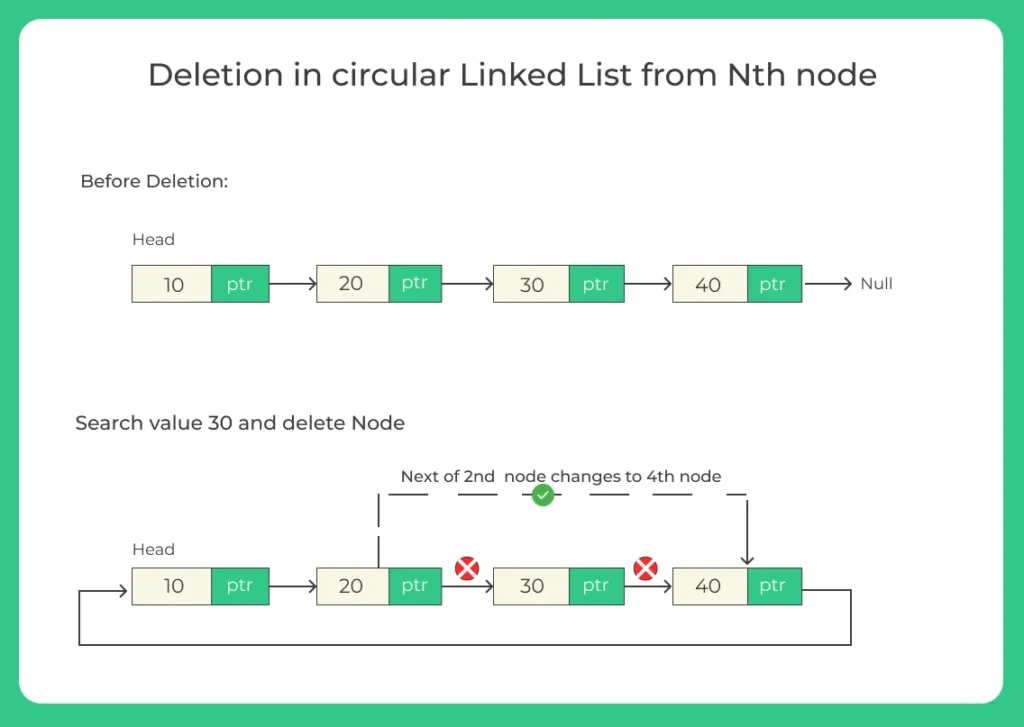
Given a Circular Singly Linked List and an integer n, your task is to delete the nth node in the list.
Input:
Circular List: 10 → 20 → 30 → 40 → 10 (back to head)
n = 3
Output:
New List: 10 → 20 → 40 → 10 (back to head)
Here, the 3rd node (30) has been deleted.

Approach to solve the problem
There are 2 main cases to handle:
- Deleting the head node (n = 1)
- Deleting any other node (n > 1)
We must also handle edge cases:
- Empty list
- n is greater than the length of the list
- List has only one node
Algorithm for Deletion at the nth node of a circular linked list
Let’s break it down simply:
Step 1: Check for Empty List
If head is null, there’s nothing to delete.
Step 2: Handle Deletion at Head (n == 1)
- Traverse the list to find the last node (tail).
- Point tail’s next to head.next.
- Set head = head.next.
Step 3: Deletion at Position n > 1
- Traverse to the (n-1)th node (previous node).
- Change prev.next to prev.next.next to bypass the nth node.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Java Code for Deletion at the nth node of a circular linked list
public class CircularLinkedListDeletion {
// Node structure
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
static Node head = null;
// Function to insert at the end of the circular linked list
public static void insert(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
return;
}
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != head) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
}
// Function to delete nth node
public static void deleteNthNode(int n) {
if (head == null || n <= 0) {
System.out.println("Invalid operation");
return;
}
// Case 1: Only one node in the list
if (head.next == head && n == 1) {
head = null;
return;
}
// Case 2: Deleting the head node
if (n == 1) {
Node last = head;
while (last.next != head) {
last = last.next;
}
head = head.next;
last.next = head;
return;
}
// Case 3: Deleting nth node (n > 1)
Node temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
if (temp == head) {
System.out.println("Position exceeds list length");
return;
}
}
// temp is (n-1)th node
if (temp.next == head) {
System.out.println("Position exceeds list length");
return;
}
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}
// Function to print the list
public static void printList() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node temp = head;
do {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
System.out.println();
}
// Main method with example
public static void main(String[] args) {
insert(10);
insert(20);
insert(30);
insert(40);
System.out.println("Original Circular Linked List:");
printList();
int position = 3;
deleteNthNode(position);
System.out.println("After deleting node at position " + position + ":");
printList();
}
}
Sample Output:
Original Circular Linked List: 10 20 30 40 After deleting node at position 3: 10 20 40
Space and Time complexity for Deletion at nth node of a circular linked list in Java
| Deletion Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Traversal to nth node | O(n) | O(1) |
| Deletion at head | O(n) (to find tail) | O(1) |
| Deletion at other nodes | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up….
Deleting the nth node from a Circular Singly Linked List in Java involves careful pointer manipulation, especially for the head node. With this article, you’ve learned how to:
- Handle edge cases (empty list, one-node list, invalid position)
- Delete head or internal nodes
- Maintain the circular structure
- Implement and test the logic with Jav
This knowledge is a key step in mastering linked list based data structures and improving your understanding of pointer based algorithms in Java.
FAQ's Related to Deletion at nth node of a Circular Linked List
Answer:
time complexity is O(n) in the worst case, because we may need to traverse the list to reach the (n-1)th node.
Answer:
Nothing will happen. The function should ideally handle this case by returning early or displaying a message.
Answer:
Yes but we must update the tail node’s pointer to the new head to maintain the circular structure.
Answer:
Algorithm detects this condition and avoids deletion, ensuring safety from null pointer exceptions.
Answer:
Technically yes, but iteration is more memory efficient for linked list operations like deletion.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment