Insertion in Circular Linked List in java
Performing Insertion in Circular Linked List in Java Programming
About Insertion in Circular Linked List in Java
In this Insertion in Circular Linked List in Java article, we will explore the different types of insertion operations and how to implement them effectively.
A circular linked list is a variation of a linked list where each node consists of two parts: data (which stores the value) and next (a pointer to the next node). The head points to the first node, and the tail also points to the first node, forming a continuous loop.

Insertion in Circular Linked List in Java
Circular Linked List is a type of linked list where the last node points back to the first node instead of null, forming a circular chain. This structure is particularly useful in applications requiring cyclic traversal.
We can perform 3 different types of insertion in circular linked list, these different types of insertion are:
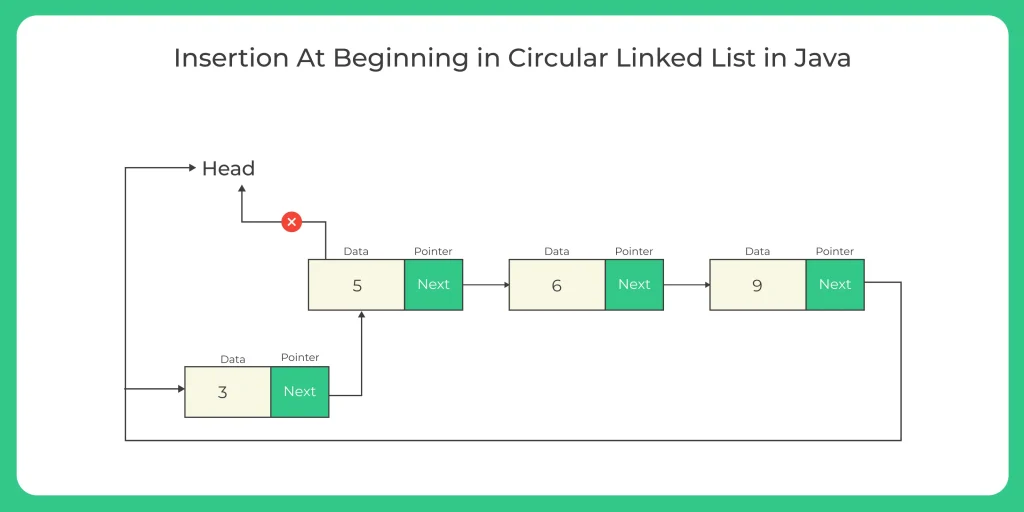
1. Insertion at the Beginning:
This involves inserting a new node before the first node. We need to adjust the last node’s next pointer to point to the new node.
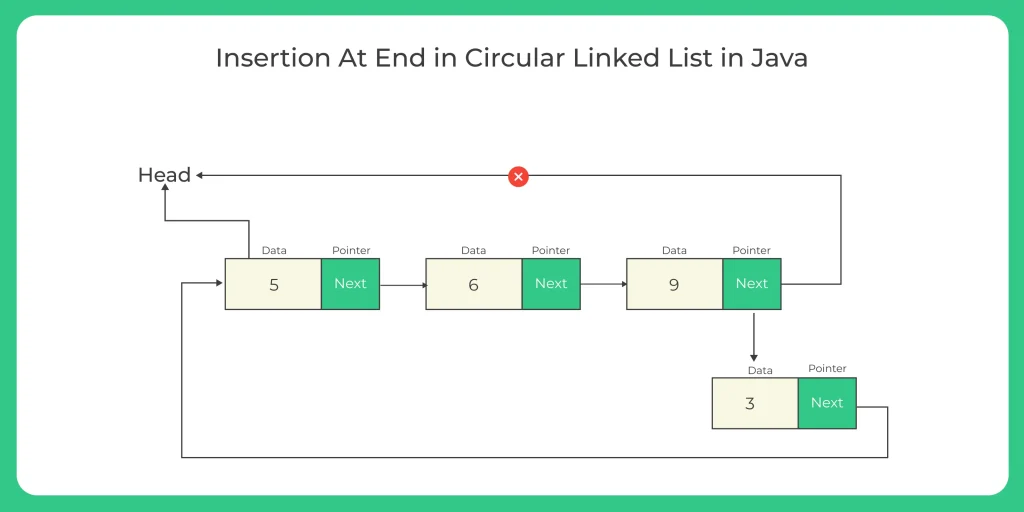
2. Insertion at the End:
Inserting a new node at the end involves adjusting the last node’s next pointer to point to the new node, and then pointing the new node’s next to the head node.
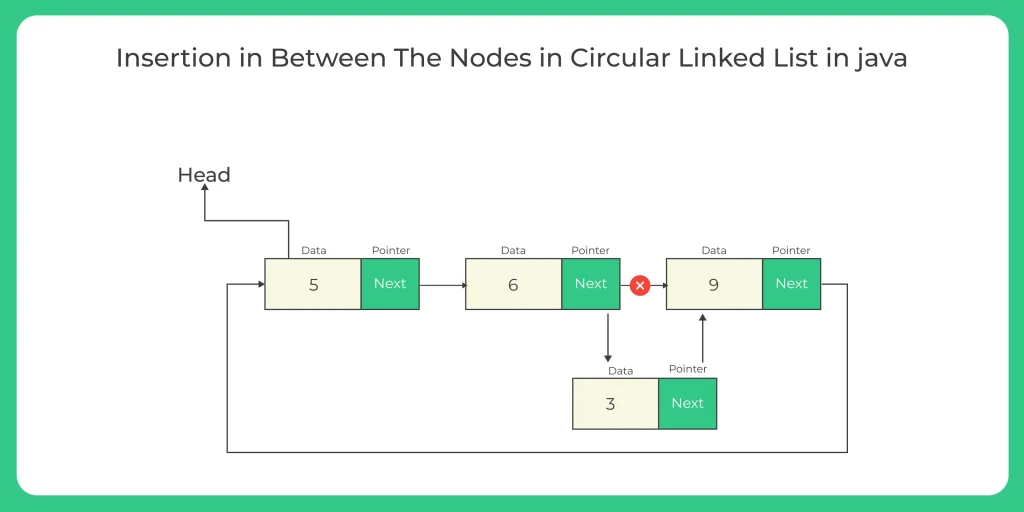
3. Insertion After a Specific Node:
In this case, we locate the target node and insert the new node right after it, adjusting the pointers accordingly.
1. Algorithm for Insertion at the Beginning of a Circular Linked List
- Node Class: Create a Node class representing a node in the list, containing two properties: data (the value of the node) and next (a reference to the next node).
- Circular LinkedList Class: Develop a separate class for the circular linked list, containing two nodes: head and tail.
This class will have two main methods: addAtStart() and show().
addAtStart() Method:
- If the list is empty (head is null), the new node becomes the head, and both head and tail will point to this node.
- And If the list is not empty, the new node is set as the new head, and its next property is set to the previous head.
Space Complexity: O(n) (storing 'n' nodes in the linked list)
Insertion at beginning Java code :
public void insertBegin(int element){
Node newEle = new Node(element);
if(head == null) {
head = newEle;
tail = newEle;
newEle.next = head;
newEle.prev=head;
}
else {
head.prev = newEle;
newEle.prev=tail;
newEle.next = head;
tail.next = newEle;
head=newEle;
}
size++;
} Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
2. Algorithm for Insertion at the End of a Circular Linked List
- Node Class: Define a Node class that represents a node in the list, consisting of two properties: data (the node’s value) and next (a reference to the next node).
- Circular LinkedList Class: Implement a separate class for the circular linked list, containing two nodes: head and tail.
This class includes two primary methods: addAtEnd() and show().
addAtEnd() Method:
- If the list is empty (head is null), the new node is added as the head, and both head and tail will reference this node.
- Where as If the list is not empty, the new node is set as the new tail, and the previous tail’s next property is updated to point to this new node.
- And the next property of the new tail is set to the head, maintaining the circular structure.
Space Complexity: O(n)
Insertion at End :
public void insertEnd(int element){
Node newEle=new Node(element);
if(head == null) {
head = newEle;
tail = newEle;
newEle.next = head;
newEle.prev=head;
}
else{
tail.next=newEle;
newEle.next=head;
newEle.prev=tail;
head.prev=newEle;
tail=newEle;
}
}
3. Algorithm for Insertion at the Nth Node in a Circular Linked List
- Node Class: Define a Node class representing a node in the list, containing two properties: data (the node’s value) and next (a reference to the next node).
- Circular Linked List Class: Create a separate class for the circular linked list with two nodes: head and tail.
This class includes two main methods: addAtNthPos() and show().
addAtNthPos() Method:
- If the list is empty (head is null), the new node is added as the head, and both head and tail will reference this node.
- And If the list is not empty, the new node is inserted at the specified position n. The new node’s next property is set to the current node at position n, and the previous node’s next is updated to point to the new node.
Space Complexity: O(n)
Insertion at specific position :
// Insert after a specific node
public void insertAfter(int data, int target) { if (last == null) return; Node newNode = new Node(data); Node temp = last.next; do { if (temp.data == target) { newNode.next = temp.next; temp.next = newNode; if (temp == last) { last = newNode; } return; } temp = temp.next; } while (temp != last.next); }
Java code for insertion in a circular Linked List
The two methods are:
- insertAfter(): This method is present in the first code and is used to insert a new node after the specified nth node in a Circular Singly Linked List.
- insertAfterPosition(): This method is present in the second code and is used to insert a new node after the specified nth node in a Circular Doubly Linked List.
import java.lang.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Obj = new Main();
Obj.insertBegin(11);
Obj.insertBegin(22);
Obj.insertEnd(33);
Obj.insertEnd(44);
Obj.insertAfter(2, 77);
Obj.print();
}
public class Node {
int element;
Node next;
public Node(int element) {
this.element = element;
}
}
public Node head = null;
public Node tail = null;
int size = 0;
public void insertBegin(int element) {
Node newEle = new Node(element);
if (head == null) {
head = newEle;
tail = newEle;
newEle.next = head;
} else {
newEle.next = head;
head = newEle;
tail.next = head;
}
size++;
}
public void insertEnd(int element) {
Node newEle = new Node(element);
if (head == null) {
head = newEle;
tail = newEle;
newEle.next = head;
} else {
tail.next = newEle;
newEle.next = head;
tail = newEle;
}
size++;
}
public void insertAfter(int n, int data) {
if (n < 1 || n > size) {
System.out.println("Invalid position: " + n);
return;
}
Node newNode = new Node(data);
Node temp = head;
// Traverse to the nth node
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
newNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
// If inserted after the last node, update the tail reference
if (temp == tail) {
tail = newNode;
}
size++;
}
public void print() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node current = head;
System.out.println("Nodes of the circular linked list:");
do {
System.out.print(current.element + " ");
current = current.next;
} while (current != head);
System.out.println();
}
}
Output
Insertion at Beginning : 22 11 Insertion at End : 22 11 33 44 Insertion after 2nd position 44 22 77 11 33
import java.lang.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main Obj = new Main();
Obj.insertBegin(11);
Obj.insertBegin(22);
System.out.println("Insertion at Beginning:");
Obj.print();
Obj.insertEnd(33);
Obj.insertEnd(44);
System.out.println("Insertion at End:");
Obj.print();
Obj.insertAfterPosition(2, 77);
System.out.println("Insertion after 2nd position:");
Obj.print();
}
public class Node {
int element;
Node next;
Node prev;
public Node(int element) {
this.element = element;
}
}
public Node head = null;
public Node tail = null;
int size = 0;
public void insertBegin(int element) {
Node newEle = new Node(element);
if (head == null) {
head = newEle;
tail = newEle;
newEle.next = newEle;
newEle.prev = newEle;
} else {
newEle.next = head;
newEle.prev = tail;
head.prev = newEle;
tail.next = newEle;
head = newEle;
}
size++;
}
public void insertEnd(int element) {
Node newEle = new Node(element);
if (head == null) {
head = newEle;
tail = newEle;
newEle.next = newEle;
newEle.prev = newEle;
} else {
newEle.next = head;
newEle.prev = tail;
tail.next = newEle;
head.prev = newEle;
tail = newEle;
}
size++;
}
public void insertAfterPosition(int n, int data) {
int len = getLength();
if (n < 1 || n > len) {
System.out.println("Invalid position: " + n);
return;
}
Node freshNode = new Node(data);
Node temp = head;
// Traverse to the nth node
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
Node nextNode = temp.next;
freshNode.next = nextNode;
freshNode.prev = temp;
temp.next = freshNode;
nextNode.prev = freshNode;
// Update the tail reference if the node is added at the end
if (temp == tail) {
tail = freshNode;
}
size++;
}
public int getLength() {
if (head == null) return 0;
int count = 1;
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != head) {
count++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return count;
}
public void print() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
Node current = head;
System.out.println("Nodes of the circular doubly linked list:");
do {
System.out.print(current.element + " ");
current = current.next;
} while (current != head);
System.out.println();
}
}
Output:
Insertion at Beginning : 22 11 Insertion at End : 22 11 33 44 Insertion after 2nd position 22 11 77 33 44
Learn DSA
Conclusion:
- Insertion operations in Circular Linked Lists can be performed at the beginning, end, or after a specific node.
- Each insertion method has its specific use case and time complexity implications.
- Understanding these operations provides a strong foundation for implementing more advanced data structures and algorithms.
By analyzing their Space and Time Complexity:
| Operation in Circular Linked List | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at the beginning | O(1) | O(n) |
| Insertion at the end | O(n) | O(n) |
| Insertion after a specific node | O(n) | O(n) |
FAQ's Related Insertion in Circular Linked List
Answer:
In Java, a node is typically defined as a class with three attributes: int data, Node next, and Node prev. This structure allows each node to store data and maintain links to both the next and previous nodes.
Answer:
- Create a new node with the given data.
- Set the new node’s next to the current head and prev to the tail.
- Update head.prev to the new node and tail.next to the new node.
- Update head to the new node.
Answer:
Both operations have a time complexity of O(1) because they involve a constant number of pointer updates without the need to traverse the entire list.
Answer:
- Traverse the list to locate the specified position.
- Create a new node and adjust its next and prev pointers to link it between the nodes at position and position + 1.
- Update the surrounding nodes’ pointers to maintain the circular structure.
Answer:
- Java handles null pointers by throwing a NullPointerException.
- To prevent this, checks are implemented before accessing node references.
For example, checking if (head == null) before accessing head.next ensures safe execution.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment