C++ program to insert in a sorted circular linked list
How to insert in a sorted circular linked list in C++?
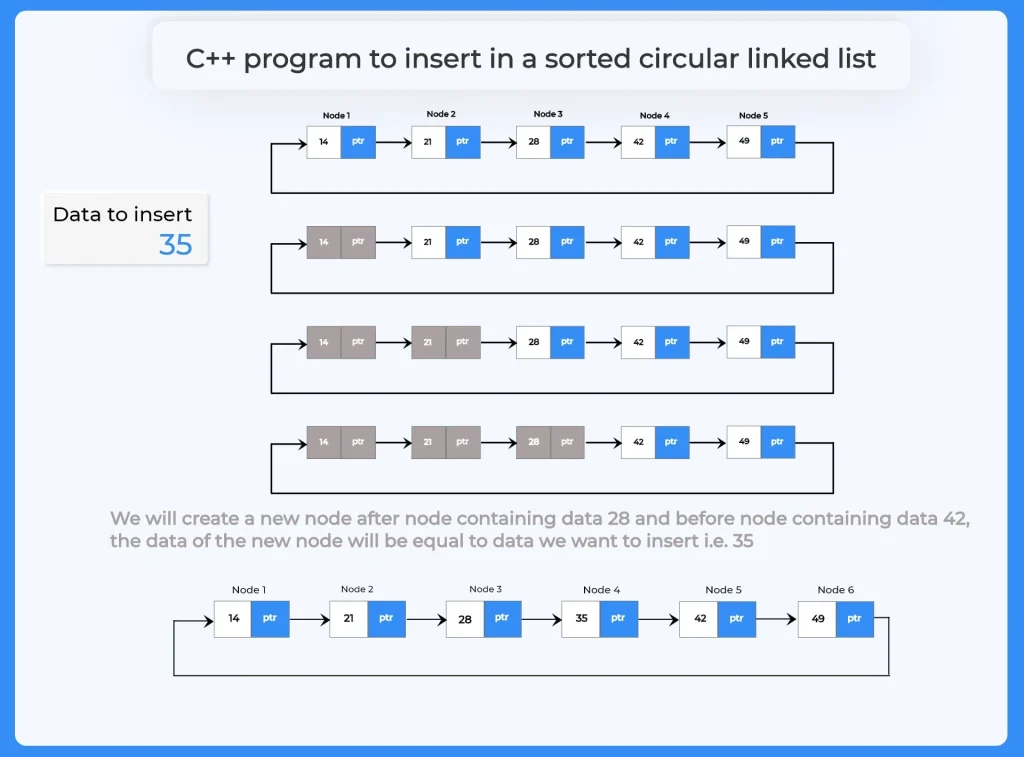
C++ program to insert in a sorted circular linked list means to insert the data in a circular linked list in a way that its logical order does not get disturbed. To do this first we need to ensure that the list we are working upon is already sorted else we will have to sort the given list before performing the operation.

Steps write a C++ program to insert in a sorted circular linked list
- Write set of codes to construct circular linked list.
- Create a function to build the circular linked list.
- Make a function to print the circular linked list data.
- Now create a function for insertion in a sorted list.
- If current node pointer is equal to head insert new node here.
- Else if data of current is greater then data of new node then insert new node before current node.
- Else insert new node after current node.
- Print the new list with newly inserted node.
struct Node { int num; struct Node *next; };
Algorithm to insert in a sorted circular linked list in C++
- IF(CURRENT == HEAD)
- NEW_NODE->NEXT=NEW_NODE
- HEAD_REF=NEW_NODE
- CURRENT->DATA>=NEW_NODE->DATA
- WHILE(CURRENT->NEXT!=HEAD_REF)
- CURRENT=CURRENT->NEXT
- CURRENT->NEXT=NEW_NODE
- NEW_NODE->NEXT=HEAD_REF
- HEAD_REF=NEW_NODE
- ELSE
- WHILE(CURRENT->NEXT!=HEAD_REF&&CURRENT->NEXT->DATA<NEW_NODE->DATA
- CURRENT=CURRENT->NEXT
- NEW_NODE->NEXT=CURRENT->NEXT
- CURRENT->NEXT=NEW_NODE
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C++ program for insertion in a sorted circular linked list
In a C++ program for insertion in a sorted circular linked list, elements are inserted in such a way that the list remains sorted at all times. It efficiently connects the new node in the proper place without breaking the circular flow of the list.
#include<iostream> //haeder files
using namespace std;
// create node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
} *head;
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data) //function to create linked list
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode; // assigning itself as head
(*head)->next = *head; // assigning itself as next node
cout << newNode->data << " Inserted\n"; return; } // if CLL already as >=1 node
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in CLL
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = newNode; // last node's next as this new node
newNode->next = *head; // new node's next as current head node
*head = newNode; // changing head node to this new node
cout << newNode->data << " Inserted\n"; // previous head node becomes 2nd node } // this function for insert the new node in linked list void sortedInsert (struct Node **head, int n) { struct Node *nextNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node)); nextNode->data = n;
struct Node *thisNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
thisNode = *head;
// Case 1 of the above algo
if (thisNode == NULL)
{
nextNode->next = nextNode;
*head = nextNode;
}
// Case 2 of the above algo
else if (thisNode->data >= nextNode->data)
{
/* If value is smaller than head's value then
we need to change next of last node */
while (thisNode->next != *head)
thisNode = thisNode->next;
thisNode->next = nextNode;
nextNode->next = *head;
*head = nextNode;
}
// Case 3 of the above algo
else
{
/* Locate the node before the point of insertion */
while (thisNode->next != *head && thisNode->next->data < nextNode->data)
thisNode = thisNode->next;
nextNode->next = thisNode->next;
thisNode->next = nextNode;
}
}
//this Function to print nodes in a given linked list
void display (struct Node *head)
{
cout << "\nCircular Linked List : " << endl;
// if circular linked list is empty currently
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node *temp = head;
// since we need to take care of circular nature of linked list
do
{
cout << temp->data << " "; temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
cout << endl;
}
// main method start
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
insertStart (&head, 50);
insertStart (&head, 40);
insertStart (&head, 30);
insertStart (&head, 20);
insertStart (&head, 10);
cout << "Before insertion ";
display (head);
sortedInsert (&head, 33);
cout << "After insertion ";
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output:
50 Inserted 40 Inserted 30 Inserted 20 Inserted 10 Inserted Before insertion Circular Linked List : 10 20 30 40 50 After insertion Circular Linked List : 10 20 30 33 40 50
Explanation:
- The program starts by defining a node structure containing data and a pointer for linking nodes in circular fashion.
- Insertion begins by creating nodes and connecting them to form a circular linked list where the last node points to the head.
- In the sortedInsert function, a new node is placed in its correct position so the list remains sorted even after insertion.
- The program handles all edge cases like inserting into an empty list, before the head, or between two nodes efficiently.
- Finally, the display function prints all elements, taking care to stop once it reaches the starting node again.
Time and Space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at Beginning | O(n) | O(1) |
| Sorted Insertion | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
In this article, you’ve learned how to insert a new node into a sorted circular linked list while maintaining its order.
Now you should be able to identify edge cases (empty list, inserting at head, inserting in-middle), implement the logic, and validate your code using the example provided.
FAQs
If the list is empty, you simply create a new node and point its next to itself, and that node becomes the head.
If the new value is ≤ head’s data, you traverse to the last node, link last’s next to the new node, then set new node’s next to head and update head to this new node.
Traverse from head until you find a node whose next’s data is ≥ new value (or you’ve looped), then insert the new node after the current node and adjust pointers accordingly.
In that case you traverse until you return to the head (since it’s circular), then insert the new node just before the head (i.e., after the largest node), with the new node’s next pointing to head.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment