Selection Sort in C++
What is Selection Sort in C++?
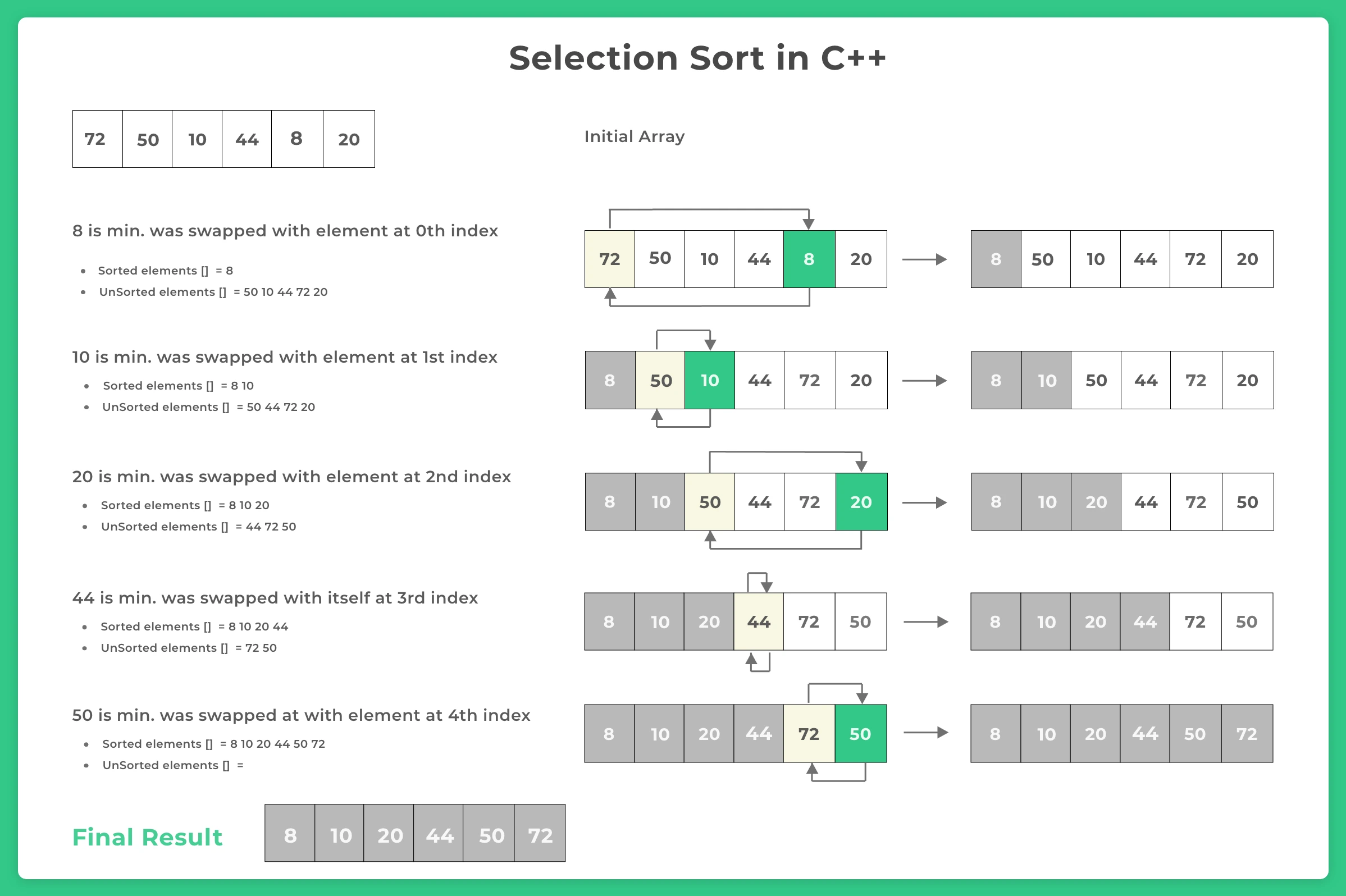
Selection sort is another algorithm that is used for sorting i.e. arranging the given data in logical order. This sorting algorithm, iterates through the list and finds the smallest element in the list and swaps it with the first element. And this process is repeated until the list is sorted. In this article, we will learn more about selection sort in C++. This article also contains steps, algorithm and implementation details for the same.
| Time Complexity (Best) | Ω(n2) |
| Time Complexity (Avg) | Θ(n2) |
| Time Complexity (Worst) | O(n2) |
| Space Complexity | O(1) |

Steps for Selection Sort in C++
There are the following Steps of the selection sort algorithm in C++.
- From the given list find the smallest element.
- Swap first element in the list with smallest element from the the list.
- Now exclude the first element and select the smallest element from the remaining list.
- Now repeat above steps till the list is sorted.
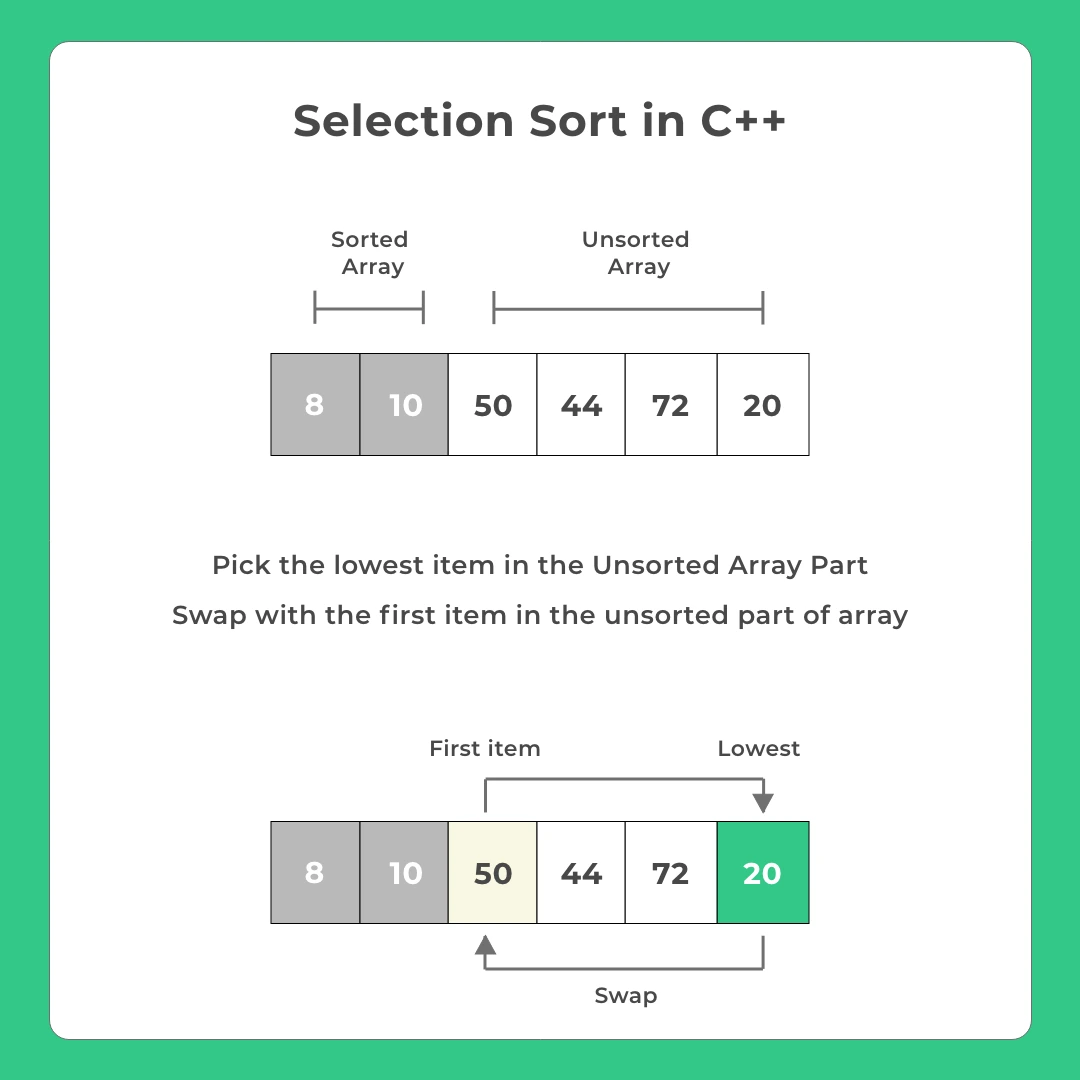

An alternate way of looking at the same algorithm
At any given point during the selection sort algorithm. The array will be divided into one sorted part and another unsorted part.
- Pick the smallest element from the unsorted part
- Swap with the first item in the unsorted part of the array
- Now we will have one more item in sorted part and one lesser item in unsorted part of the array
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C++ programming code for selection sort
This code implements Selection Sort in C++.
- Prints the array before sorting.
- Uses selection sort to sort the array in ascending order.
- Finds the smallest element in the unsorted part.
- Swaps it with the current position.
- Prints the sorted array after all passes.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//Display function to print values.
void display(int array[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << array[i] << "\t";
cout << "\n";
}
//The main function to drive other functions.
int main()
{
int array[] = {5, 3, 1, 9, 8, 2, 4, 7};
int size = sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]);
cout << "Before sorting: \n";
display(array, size);
int i, j, min_idx,temp;
//Loop to iterate elements of array.
for (i = 0; i < size-1; i++)
{
//Here we try to find the min element in array.
min_idx = i;
for (j = i+1; j < size; j++){
if (array[j] < array[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
}
// Here we interchange the min element with first one.
temp = array[min_idx];
array[min_idx] = array[i];
array[i] = temp;
}
cout << "After sorting: \n";
display(array, size); //Using dispaly function to print sorted array.
return 0;
}Output
Before sorting: 5 3 1 9 8 2 4 7 After sorting: 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 9
Explanation:
- The program includes the <iostream> library and uses std namespace for input/output operations.
- The display function prints all elements of an array separated by tabs.
- In main(), an integer array is initialized, and its size is calculated using sizeof.
- The program prints the array before sorting using the display function.
- It implements Selection Sort: for each element, it finds the minimum in the unsorted part and swaps it with the current element.
- After sorting, the program prints the sorted array using the same display function.
Advantages
- It gives the same time complexity regardless of arrangements of items in the array or data set
- Since number of operations(swapping, size – 1) are less, so its favorable to use when swapping operations are costly in system
Disadvantages
- The time complexity is quiet high i.e. O(n2) thus not good
To wrap it up:
Selection Sort in C++ is a simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly selects the smallest element from the unsorted part and places it in the correct position. It is easy to understand and implement, making it suitable for small datasets or when memory usage is a concern.
However, its time complexity is consistently high (O(n²)) regardless of input, which makes it inefficient for large datasets. While it minimizes swaps, it is generally slower than other advanced sorting algorithms like Quick Sort or Merge Sort.
FAQs
Selection Sort is a simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly finds the minimum element and places it at the correct position in the array.
Its time complexity is O(n²) for all cases, as it always scans the remaining elements to find the minimum.
Selection Sort is unstable because it may change the relative order of equal elements during swapping.
It is preferred for small arrays or when memory write operations are costly, as it performs fewer swaps than other simple sorts.
Sorting
Sorting algorithms are easy to learn but are really important for college semester exams and companies offering package between 3 – 6 LPA would ask direct searching questions in online test/ interviews.

Sorting
Sorting algorithms are easy to learn but are really important for college semester exams and companies offering package between 3 – 6 LPA would ask direct searching questions in online test/ interviews.

Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment