Insertion in circular linked list in C++
What is Insertion in circular linked list in C++ programming?
Insertion in a Circular Linked List in C++ can be simply understood as adding a new node to an existing circular linked list. It helps in maintaining the circular structure while adding new data.
There are three common ways to insert a node in a circular linked list:
- Insertion at beginning of the circular linked list.
- Insertion at specific position in circular linked list.
- Insertion at end in circular linked list.

Types of insertion in circular linked list
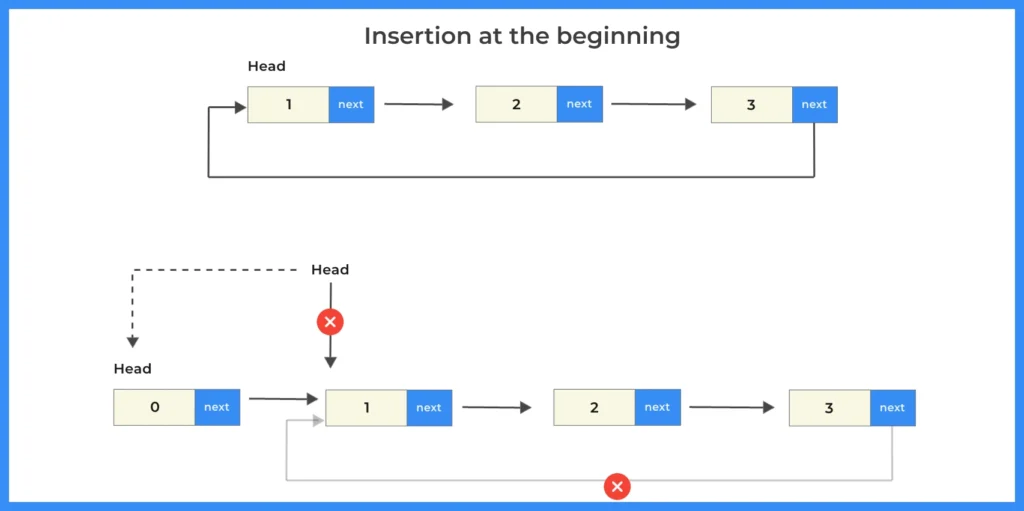
1. Insertion at beginning:
- In this type of insertion, a new node is added before the head node.
- The new node becomes the new head, and the last node’s
nextpointer is updated to point to this new head node, maintaining the circular structure.
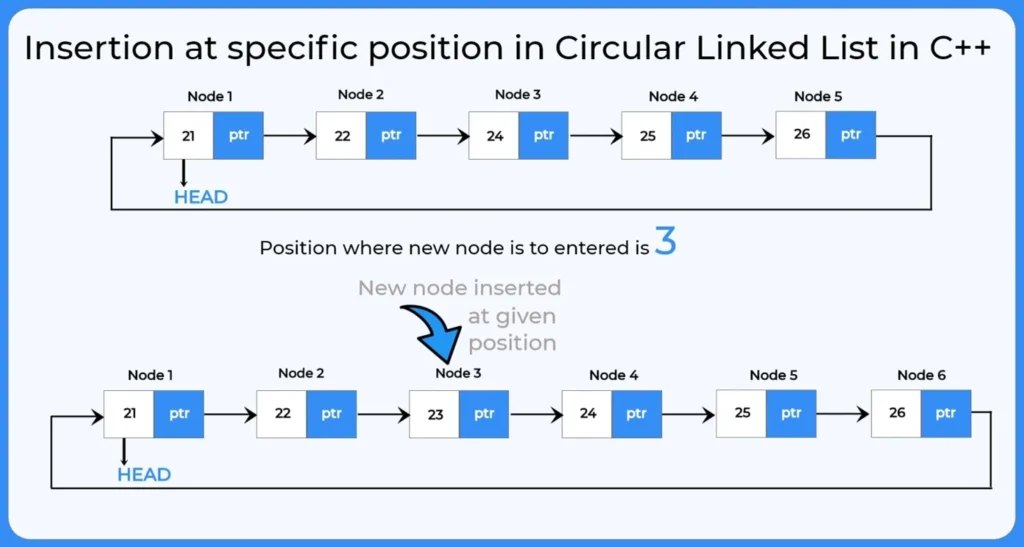
2. Insertion at specific position:
If we want to insert a new node at specific position then we need to traverse till that position and insert a new node there shifting the position of remaining nodes by one.
- A new node is added at a specified position in the list.
- The position can be before, after, or between any nodes.
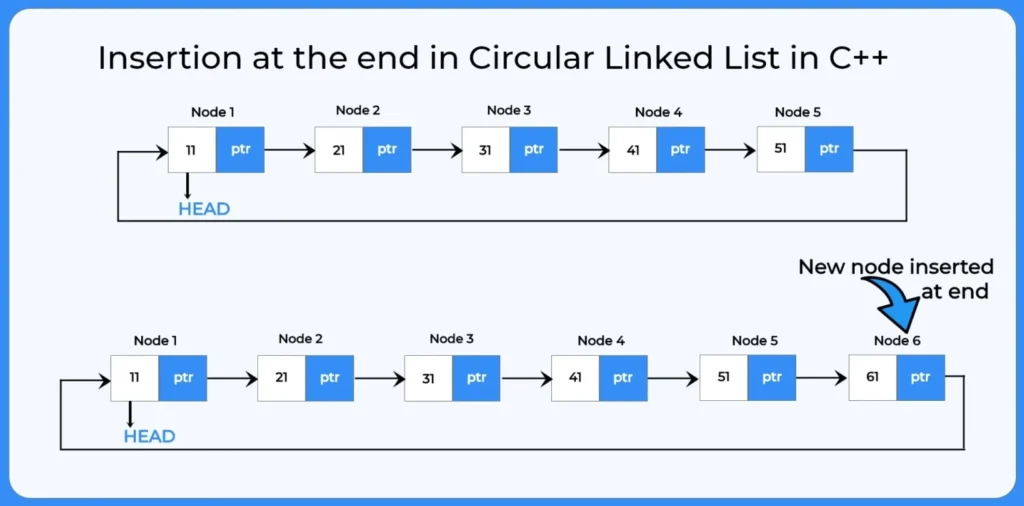
3. Insertion at end:
In this type of insertion in circular linked list a new node is added after the end node of the list, and this newly added node will now act as tail of the list.
- In this type, a new node is added after the last node.
- The
nextpointer of the new node is set to the head node to maintain the circular structure.
Insertion at Beginning of Circular Linked List
How to perform insertion at beginning in circular linked list?
To perform insertion at beginning in circular linked list we will use the following steps:
Create a new node and assign data.
Link the new node to the current head node.
Update the last node’s
nextpointer to point to the new node.Update the head pointer to the new node.
void insertBeginning(int num)
{
struct node *newnode, *curNode;
if(head == NULL)
{
cout<<"List is empty";
}
else
{
newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->num = num;
newnode->next = head;
curNode = head;
while(curNode->next != head)
{
curNode = curNode->next;
}
curNode->next = newnode;
head = newnode;
}
} Time Complexity = O(1)
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Insertion at Specific position of Circular Linked List
How to perform insertion at specific position in circular linked list?
To perform insertion at specific position in circular linked list we will use the following steps:
- Traverse the list to locate the specified position.
- Create a new node and assign data.
- Adjust the
nextpointers of the previous and new node to maintain the circular structure.
void insertSpecificPosition(int num, int pos)
{
struct node *newnode, *curNode;
int i;
if(head == NULL)
{
cout<<"List is empty";
}
else {
newnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->num = num;
curNode = head;
for(i=0; i<=pos-3; i++) { curNode = curNode->next;
}
newnode->next = curNode->next;
curNode->next = newnode;
}
} Time Complexity = O(1)
Insertion at the end of Circular Linked List
How to perform insertion at end in circular linked list?
To perform insertion at end in circular linked list we will use the following steps:
After creating a linked list with some data in it we will define:
Create a new node and assign data.
Traverse to the last node.
Set the last node’s next to the new node.
Update the new node’s next to point to the head node.
void insertEnd(int num1)
{
struct node *p;
int a;
a=num1;
struct node *temp=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->num=a;
p=head;
while(p->next!=head)
{
p=p->next;
}
p->next=temp;
temp->next=head;
} Time Complexity = O(1)
Practical Considerations and Optimizations
1. Maintaining a Tail Pointer:
- To optimize insertions at the beginning or end, maintain a tail pointer (pointer to the last node).
- This allows O(1) time insertion at both ends because you can directly update the tail’s next pointer without traversal.
2. Empty List Handling:
Always handle the empty list case separately: inserting the first node must point to itself.
3. Edge Cases:
- Validate insertion positions carefully to avoid corrupting the list.
- Positions less than 1 or greater than list length + 1 should be rejected or handled gracefully.
C++ Code Insertion in Circular Linked List
C++ code for insertion in a circular linked list demonstrates how to add new nodes at different positions such as the beginning, end, or a specific location. This program helps understand how pointers are adjusted to maintain the circular structure, ensuring the last node always points back to the head node.
#includeusing namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node* next; Node(int value) { data = value; next = nullptr; } }; class CircularLinkedList { private: Node* head; public: CircularLinkedList() : head(nullptr) {} void insertAtEnd(int value) { Node* newNode = new Node(value); if (head == nullptr) { head = newNode; newNode->next = head; return; } Node* temp = head; while (temp->next != head) temp = temp->next; temp->next = newNode; newNode->next = head; } void display() { if (head == nullptr) return; Node* temp = head; do { cout << temp->data << " "; temp = temp->next; } while (temp != head); cout << endl; } }; int main() { CircularLinkedList cll; cll.insertAtEnd(10); cll.insertAtEnd(20); cll.insertAtEnd(30); cll.insertAtEnd(40); cout << "Circular Linked List elements are: "; cll.display(); return 0; }
output:
Circular Linked List elements are: 10 20 30 40
Explanation:
- A Node class is used to store data and a pointer to the next node.
- The list is circular, meaning the last node points back to the head.
- If the list is empty, the new node becomes both the head and the tail.
- For insertion, we traverse to the last node and connect it to the new node.
- The display() function prints all elements until it loops back to the head node.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at End | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall | O(n) | O(1) |
Conclusion
- Insertion operations in circular linked lists require careful pointer management to maintain the circular structure.
- Whether inserting at the beginning, end, or a specific position, understanding the underlying steps and their complexity is vital for efficient and error free implementations.
- With proper handling and optimizations like maintaining a tail pointer, circular linked lists become powerful tools for numerous real world problems.
Learn DSA
FAQ's Related Circular Linked List
Answer:
A circular linked list is a linked list where the last node points back to the first node, forming a circle.
Answer:
The three types are insertion at the beginning, insertion at the end, and insertion at a specific position.
Answer:
A new node is created and placed before the current head, and the last node’s pointer is updated to the new node, which becomes the new head.
Answer:
Because you need to traverse the list to find the last node before inserting the new node.
Answer:
Yes, you can insert a node at any valid position by traversing to the correct place and updating pointers accordingly.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment