Insertion at specific position in Circular Linked List in C++
How we can insert data at specific position in circular linked list?
Insertion at specific position in circular linked list in C++ is one the insertion operation that we can perform on the circular linked list. In this article we will be learning steps and algorithm to do the same. We can perform insertion at following places also:-
- Insertion at the beginning of the circular linked list.
- Insertion at the end of the circular linked list.
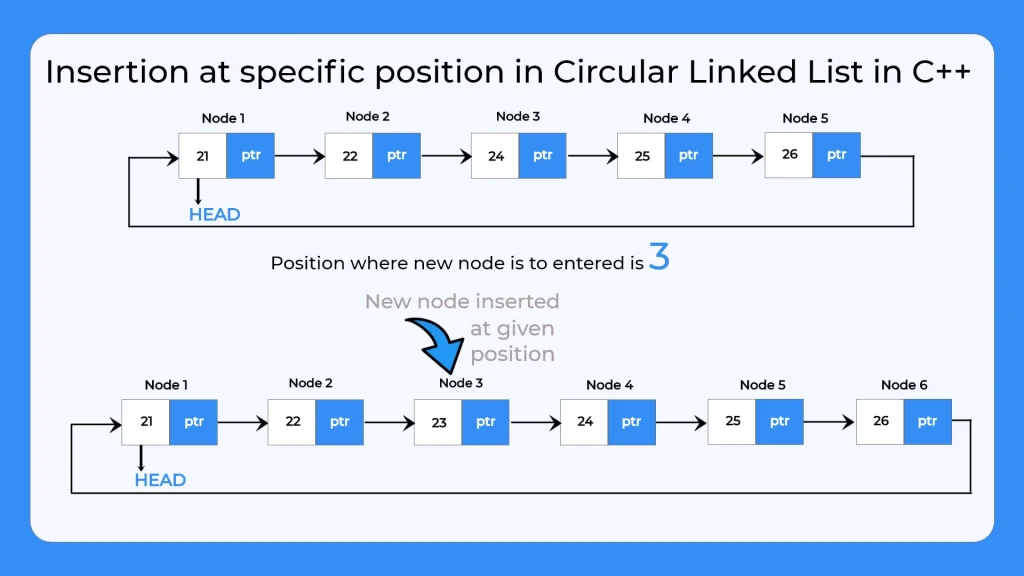
Steps to insert new node at specific position in circular linked list in CPP
- If the circular linked list is empty, terminate function.
- Else define two node pointers.
- Create new node and stor the data in the new node
- Now traverse till the specific position and insert this new node there.
- Link the pointer of this new node to the node present at this place previously.
- Print the new circular linked list to see the result.
Syntax
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
};
Algorithm to write a CPP program to insert at specific position in Circular Linked List
- STRUCT NEWNODE & CURNODE
- IF HEAD==NULL
- EXIT
- ELSE
- NEWNODE->NUM=NUM
- CURNODE=HEAD
- FOR I=0 TO POS-3
- CURRNODE=CURRNODE->NEXT
- END FOR
- NEWNODE->NEXT=CURNODE->NEXT
- CURNODE->NEXT=NEWNODE
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C++ program for insertion at specific position in circular linked list
In a circular linked list, insertion at a specific position allows you to add a new node anywhere within the list, maintaining its circular structure. This operation requires careful traversal and pointer adjustments to ensure smooth linking between nodes.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int num;
struct Node *next;
} *head;
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data) //function to create linked list
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->num = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode; // assigning itself as head
(*head)->next = *head; // assigning itself as next node
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n"; return; } // if CLL already as >=1 node
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in CLL
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = newNode; // last node's next as this new node
newNode->next = *head; // new node's next as current head node
*head = newNode; // changing head node to this new node
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n";
// previous head node becomes 2nd node
}
void insertSpecific(struct Node **head,int num, int pos)//function to insert element at specific position
{
struct Node *newnode, *curNode;
int i;
if(*head == NULL)
{
cout<<"List is empty"; } else { newnode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newnode->num = num;
curNode = *head;
for(i=0; i<=pos-3; i++) { curNode = curNode->next;
}
newnode->next = curNode->next;
curNode->next = newnode;
}
}
void display (struct Node *head)
{
cout << "\nCircular Linked List : " << endl;
// if circular linked list is empty currently
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node *temp = head;
// since we need to take care of circular nature of linked list
do
{
cout << temp->num << " "; temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
cout << endl;
}
int main () //main function
{
// first node will be null at creation
struct Node *head = NULL;
insertStart (&head, 1);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 3);
insertStart (&head, 4);
insertStart (&head, 5);
cout<<"Before insertion ";
display (head);
insertSpecific (&head,8,2);
cout<<"After insertion ";
display (head);
return 0;
}Output:
1 Inserted 2 Inserted 3 Inserted 4 Inserted 5 Inserted Before insertion Circular Linked List : 5 4 3 2 1 After insertion Circular Linked List : 5 8 4 3 2 1
Explanation:
- In this program, a circular linked list is implemented where the last node links back to the head, ensuring continuous traversal.
- The insertStart() function adds a new node at the beginning and correctly updates pointers to maintain the circular structure.
- The insertSpecific() function inserts a node at a user-defined position by traversing the list and adjusting links to include the new node.
- The display() function prints all nodes in the circular linked list, looping until it reaches the head again.
- The main function shows how nodes are inserted both at the start and at a specific position, followed by displaying the updated list.
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at Beginning | O(n) | O(1) |
| Insertion at Specific Position | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
Understanding insertion at a specific position in a circular linked list helps you manage node placement efficiently using C++. This concept builds a strong base for handling other linked list operations.
Keep practicing different cases like inserting at the start or end to strengthen your logic. For more in-depth learning and interview prep, explore PrepInsta’s coding courses.
FAQs
It means adding a new node at a desired location within the circular linked list by properly adjusting the links between existing nodes to maintain the circular structure.
You traverse the list using a loop and a counter until the specified position is reached, then adjust the pointers to insert the new node correctly.
If the given position exceeds the number of nodes, insertion cannot be done unless handled explicitly in code, often by displaying an error or adding the node at the end.
The time complexity is O(n), as traversal may be required through all nodes to reach the given position, while the space complexity remains O(1).
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment