Insertion at end in Circular Linked List in C++

How to insert at end in circular linked list in CPP?
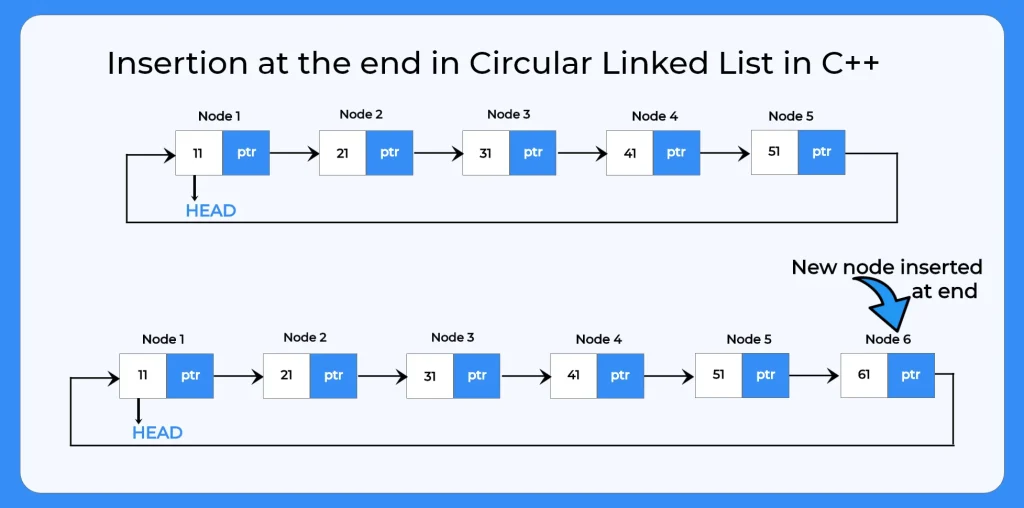
In single linked list, every node points to its next node in the list and the last node points NULL. But in circular linked list, every node points to its next node in the list but the tail node points to the head node in the list.
In this article, we will learn how code a program for insertion at end in circular linked list in C++ programming language.
Steps to write a C++ program for insertion at the end in circular linked list
- Create new node with the help of data given.
- If the circular linked list is empty make new node as head of the list.
- And if the list has already some data present in it then,struct a node pointer say p, and initialize with head.
- Traverse until the next of the pointer points the head.
- Set p → next = temp and temp → next = head, this will link newly inserted node with the previous head.
- Print the new list with the help of print function.
Syntax
class Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
}; 
Algorithm to write a C++ program for insertion at the end in circular linked list
- STRUCT NODE P
- INTEGER A=NUM1
- STRUCT NODE TEMP
- TEMP->NUM=A;
- P=HEAD
- WHILE(P->NEXT!-HEAD)
- P=P->NEXT
- END WHILE
- P->NEXT=TEMP
- TEMP->NEXT=HEAD
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C++ program for insertion at end in circular linked list
The C++ program for insertion at the end in a circular linked list adds a new node after the last node, ensuring the circular connection is maintained by linking the new node back to the head. This operation helps efficiently expand the list while preserving its circular structure.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int num;
struct Node *next;
} *head;
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data) //function to create linked list
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->num = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode; // assigning itself as head
(*head)->next = *head; // assigning itself as next node
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n"; return; } // if CLL already as >=1 node
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in CLL
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = newNode; // last node's next as this new node
newNode->next = *head; // new node's next as current head node
*head = newNode; // changing head node to this new node
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n"; // previous head node becomes 2nd node } void insertEnd (struct Node **head, int num1) //function to insert element at end { struct Node *p; struct Node *temp = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node)); temp->num = num1;
p = *head;
while (p->next != *head)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = temp;
temp->next = *head;
}
void display (struct Node *head)
{
cout << "\nCircular Linked List : " << endl;
// if circular linked list is empty currently
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node *temp = head;
// since we need to take care of circular nature of linked list
do
{
cout << temp->num << " "; temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
cout << endl;
}
int main () //main function
{
// first node will be null at creation
struct Node *head = NULL;
insertStart (&head, 1);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 3);
insertStart (&head, 4);
insertStart (&head, 5);
cout<<"Before insertion ";
display (head);
insertEnd (&head, 8);
cout<<"After insertion ";
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output:
1 Inserted 2 Inserted 3 Inserted 4 Inserted 5 Inserted Before Insertion Circular Linked List: 5 4 3 2 1 After Insertion Circular Linked List: 5 4 3 2 1 8
Explanation:
- The code defines a circular linked list where the last node connects back to the head, maintaining a circular structure.
- The insertStart() function inserts new nodes at the beginning, updating the head pointer each time.
- The insertEnd() function traverses the list and links a new node at the end while preserving the circular connection.
- The display() function uses a do-while loop to traverse and print all nodes since the list is circular.
- The program demonstrates insertion at both start and end positions and displays the list before and after the operation.
Time and space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at Start | O(n) | O(1) |
| Insertion at End | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
You’ve now learned how inserting a node at the end of a circular linked list works differently from a regular singly linked list. Instead of the last node pointing to NULL, it connects back to the head, maintaining the circular flow. With the C++ example explained, performing this operation becomes much easier to understand and implement.
Practicing this concept helps strengthen your grasp of pointer handling and traversal in circular structures. It’s a useful skill that often appears in interviews and coding tasks, preparing you to work efficiently with various linked list operations in C++.
FAQs
Insertion at the end in a circular linked list means adding a new node just before the head node, making the new node the last one that points back to the head.
In insertion at the end, the new node connects before the head, while in insertion at the beginning, it becomes the new head pointing to the old head.
The time complexity is O(n) for traversal when there’s no tail pointer and O(1) if a tail pointer is maintained.
If the list is empty, the new node points to itself, and that node becomes both the head and tail of the circular linked list.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment