Deletion in Circular Linked List in C++
What is deletion in circular linked in CPP programming?
Deletion in circular linked in C++ in general words can be understood as deleting a node from a predefined circular linked list. We can perform three different types of deletion in circular linked list, these different types of deletion are:-
- Deletion from beginning of the circular linked list.
- Deletion from specific position in circular linked list.
- Deletion from end in circular linked list.
Types of Deletion in Circular Linked List
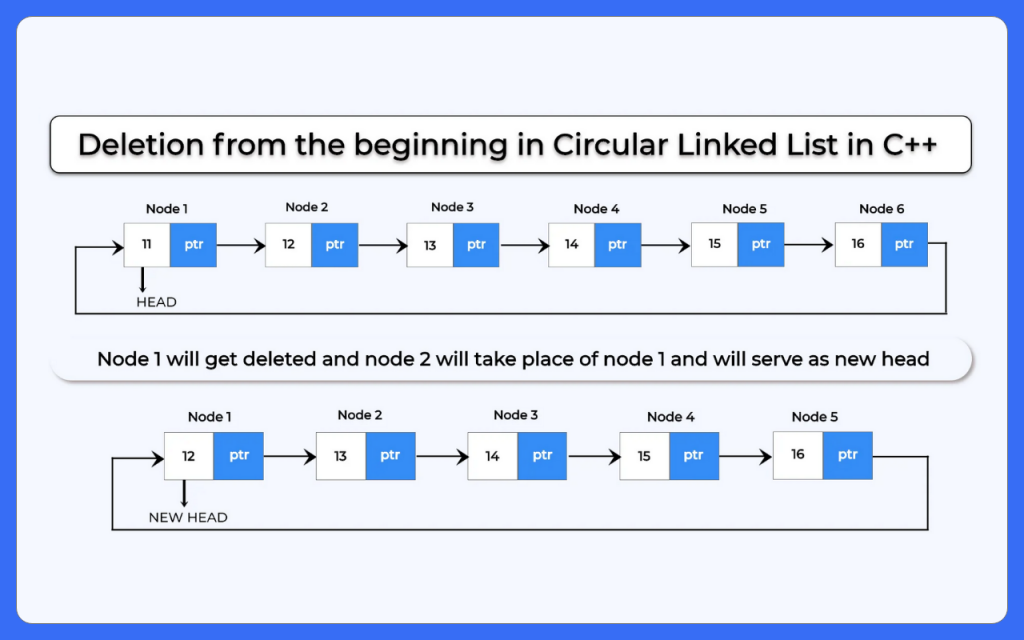
1.) Deletion from beginning:
In this type of deletion in circular linked list delete the head of the list and the second node of the list act as new head.
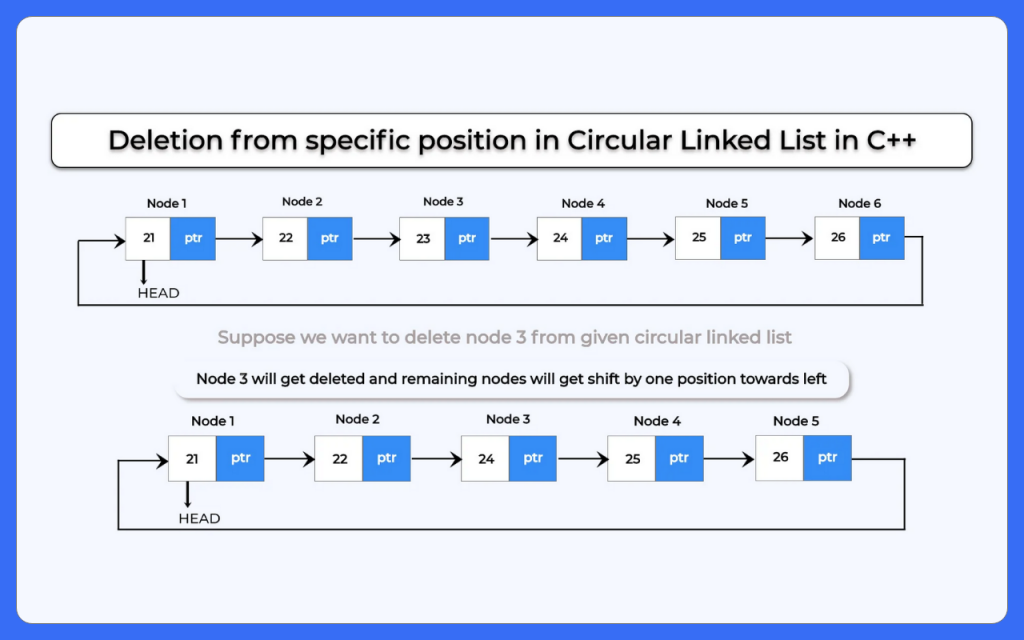
2.) Deletion from specific position:
If we want to delete a node from specific position then we need to traverse till that position and delete that node. After deleting the node we will decrease the position of nodes after that node by one.
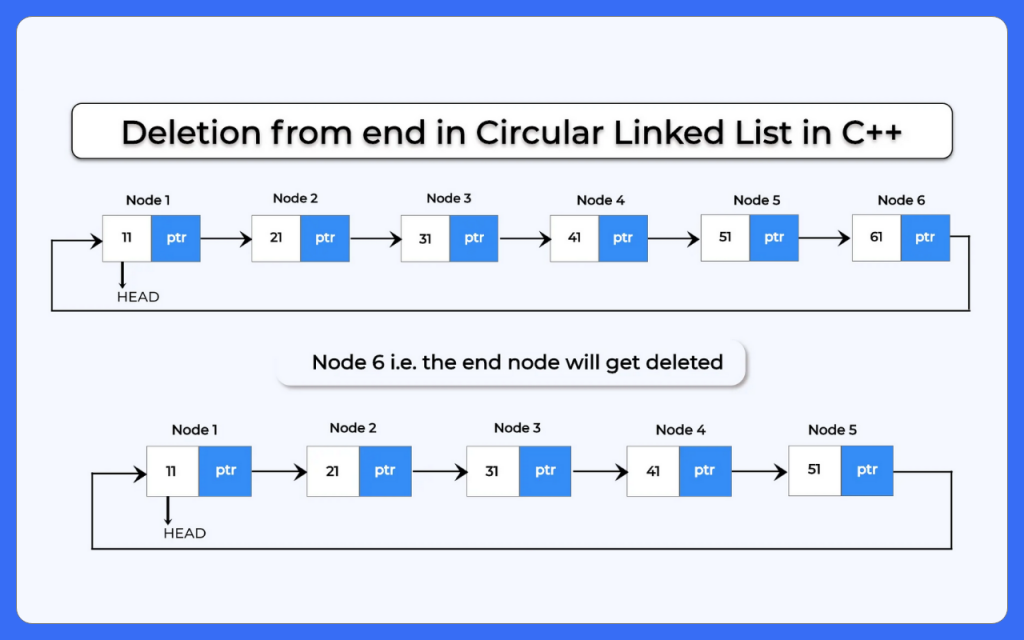
3.) Deletion from end:
In this of deletion in circular linked list we delete the tail of the list and after deleting the tail we will make last second node as the the new tail of the list

Case 1: Deletion from the Beginning
How to perform deletion from beginning in circular linked list?
To perform deletion from beginning in circular linked list we will use the following steps:-
- We will create a circular linked list with some data in it.
- We will define a node pointer and this node pointer as head of the list.
- Now we will traverse this node pointer till the end of the list and follow the algorithm for deletion from beginning in circular linked list below.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
};
void deleteHead(Node*& head) {
if (head == NULL) return;
if (head->next == head) {
delete head;
head = NULL;
return;
}
Node* temp = head;
Node* last = head;
while (last->next != head)
last = last->next;
last->next = head->next;
head = head->next;
delete temp;
}
void printList(Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return;
Node* temp = head;
do {
cout << temp->data << " "; temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != head);
cout << endl; } void insert(Node*& head, int data) { Node* newNode = new Node{data, NULL}; if (head == NULL) { head = newNode; head->next = head;
return;
}
Node* temp = head;
while (temp->next != head)
temp = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
newNode->next = head;
}
int main() {
Node* head = NULL;
insert(head, 10);
insert(head, 20);
insert(head, 30);
insert(head, 40);
cout << "Original List: ";
printList(head);
deleteHead(head);
cout << "After Deletion: ";
printList(head);
}
Output:
Original List: 10 20 30 40
After Deletion: 20 30 40
Explanation:
We find the last node, point it to the second node, and update head to head->next, then delete the old head.
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Case 2: Deletion at Specific Position in Circular Linked List
How to perform deletion from specific position in circular linked list?
To perform deletion from specific position in circular linked list we will use the following steps:-
- We will create a circular linked list.
- We will use a node pointer to traverse till the specific node.
- Using a second pointer we will store the node there temporary and will link the previous node to the next of this node.
- At last we will free the temporary pointer.
void deleteAtPos(Node*& head, int pos) {
if (head == NULL) return;
if (pos == 1) {
deleteHead(head);
return;
}
Node* temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i < pos - 1 && temp->next != head; i++)
temp = temp->next;
Node* toDelete = temp->next;
temp->next = toDelete->next;
delete toDelete;
}
Output:
Original List: 10 20 30 40
After Deletion at position 2: 10 30 40
Explanation:
We skip to one node before the target position and update its next pointer to bypass the node being deleted.
Case 3: Deletion at the end of Circular Linked List
How to perform deletion from end in circular linked list?
To perform deletion from end in circular linked list we will use the following steps:- After creating a linked list with some data in it we will define:-- We will define a node pointer this will initially point the head of the list and later will be used for traversing till the end of the list
- After traversing till the end of list we will store the last node in a temporary node.
- Now we will link the pointer of last second node to the head node.
- And at last we will free the node stored in a temporary node.
void deleteLast(Node*& head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == head) {
delete head;
head = NULL;
return;
}
Node* temp = head;
while (temp->next->next != head)
temp = temp->next;
Node* lastNode = temp->next;
temp->next = head;
delete lastNode;
}
Output:
Original List: 10 20 30 40 After Deletion: 10 20 30Explanation: We traverse to the second-last node and make it point to the head, removing the last node
Time and space Complexity:
| Operation | Time | Space |
|---|---|---|
| Insert | O(n) | O(1) |
| Delete Head | O(n) | O(1) |
| Delete at Position | O(n) | O(1) |
| Delete Last | O(n) | O(1) |
| Print List | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
Deleting nodes in a circular linked list might seem tricky at first, but once you understand how pointers connect and loop back, it becomes quite simple. This operation helps in efficiently managing data without breaking the circular flow of the list.
By practicing these deletion techniques in C++, you’ll gain better control over data structures and improve your ability to handle real-world programming problems. It’s a small but important step toward mastering linked lists.
FAQs - Deletion in Circular Linked List(Most Asked)
In a circular linked list, there’s no NULL to mark the end. The last node points back to the head, so while deleting, we must be extra careful to keep this loop intact. Missing one pointer update can break the list or cause an infinite loop.
If there’s only one node, deleting it means the list becomes empty. So, we simply delete that node and set the head to NULL.
Yes, but only in specific cases like deleting the head or by traversing and stopping one node before the target. You don’t always need a previous pointer, but you must carefully manage traversal logic.
The function may keep looping endlessly or crash if not handled properly. That’s why it’s important to validate the position first or use a safe traversal with a stop condition.
Yes, if you forget to update pointers correctly, the circular nature can break. After deletion, the last node must always point to the new head to keep the list circular.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java





Login/Signup to comment