Deletion from specific position in circular linked list in C++
How to delete from specific position in circular linked list?
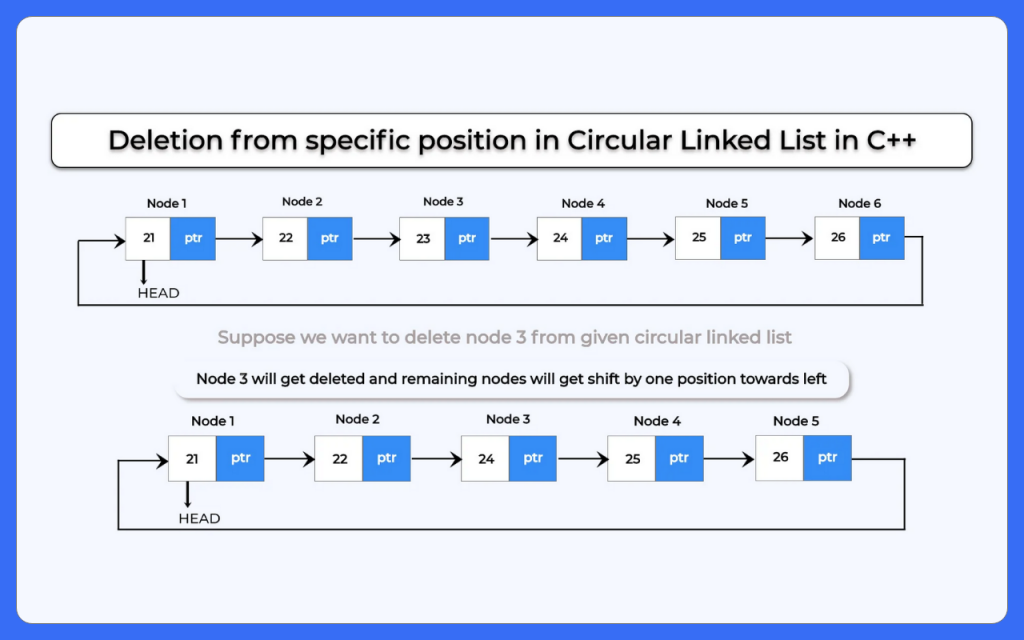
Deletion from nth position in a circular linked list is one of the variation of deletion operation that we usually perform on Circular Linked List. For performing deletion from a specific location we make use of pointers for traversing the circular linked list. Let’s see a C++ Program for deletion from nth position in a circular linked list

Steps to delete from specific position in circular linked list in CPP
- Initialize two node pointers p and q
- Initialize a variable k that will act as counter variable.
- Initialize del with pos-1.
- Now run a loop until k does not equal to del.
- In this loop make q=p and p=p->next
- Increase value of k by one on every successful iteration.
- Now make next of q equal to next of p.
- Delete node pointed by node pointer p.
struct node { int num; struct node * next; }
Algorithm in CPP programming to delete from specific position in Circular Linked List
- STRUCT NODE P & Q
- K = 0
- DEL = POS-1
- P = HEAD
- WHILE (K != DEL)
- Q = P
- P = P -> NEXT
- K++
- Q -> NEXT = P -> NEXT
- FREE P
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C++ program for deletion from specific position in circular linked list
A C++ program for deletion from a specific position in a circular linked list allows you to remove a node from any given location efficiently. It involves traversing the list to the desired position, updating the pointers, and maintaining the circular connection between nodes. This operation helps manage dynamic data structures effectively without breaking the circular nature of the list.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int num;
struct Node *next;
};
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data) //function to create linked list
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->num = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode; // assigning itself as head
(*head)->next = *head; // assigning itself as next node
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n"; return; } // if CLL already as >=1 node
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in CLL
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = newNode; // last node's next as this new node
newNode->next = *head; // new node's next as current head node
*head = newNode; // changing head node to this new node
cout << newNode->num << " Inserted\n"; // previous head node becomes 2nd node } void deleteBegin (struct Node **head) //function to delete beginning node from the circular linked list { struct Node *p, *temp; p = *head; while (p->next != (*head))
{
p = p->next;
}
temp = *head;
p->next = (*head)->next;
*head = (*head)->next;
free (temp);
}
void deleteSpecific (struct Node **head, int pos) //function to delete any node from the list
{
if (pos < 1)
{
cout << "Invalid position entered"; } else if (pos == 1) { deleteBegin (head); } else { struct Node *p, *q; int del, k = 0; del = pos - 1; p = *head; while (k != del) { q = p; p = p->next;
k++;
}
q->next = p->next;
free (p); //deleting specific node
} //deleting specific node
}
void display (struct Node *head)
{
cout << "\nCircular Linked List : " << endl;
// if circular linked list is empty currently
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node *temp = head;
// since we need to take care of circular nature of linked list
do
{
cout << temp->num << " "; temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
cout << endl;
}
int main () //main function
{
// first node will be null at creation
struct Node *head = NULL;
insertStart (&head, 1);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 3);
insertStart (&head, 4);
insertStart (&head, 5);
cout << "Before deletion ";
display (head);
deleteSpecific (&head, 5);
cout << "After deletion ";
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output:
1 Inserted 2 Inserted 3 Inserted 4 Inserted 5 Inserted Before deletion Circular Linked List : 5 4 3 2 1 After deletion Circular Linked List : 5 4 3 2
Explanation:
- This program demonstrates how to work with a Circular Linked List (CLL) where the last node connects back to the head, forming a loop.
- In the insertStart() function, a new node is created and added before the head; links are adjusted so the new node becomes the head while maintaining the circular structure.
- Through the deleteBegin() function, the first node of the list is removed by finding the last node, reconnecting it to the next node, and freeing the deleted node’s memory.
- The deleteSpecific() function locates a node at a given position, updates the previous node’s pointer to bypass it, and deletes the targeted node safely.
- Using the display() function, the list is printed in a circular manner with a do-while loop, ensuring all elements are shown once before looping back to the head.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insert Node at Beginning | O(n) | O(1) |
| Delete Node from Beginning | O(n) | O(1) |
| Delete Node from Specific Position | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
To wrap it up:
In this article, we’ve walked through how to remove a node from a specific position in a circular linked list using C++. You’ve seen the step-by-step logic from traversing the list with two pointers to updating links and freeing the targeted node providing you with a clear, runnable algorithm.
Whether you’re prepping for interviews or enhancing your data structures toolkit, understanding how deletion works in a circular list adds a valuable skill. With practice, you’ll be able to adapt and implement this logic efficiently in your own code.
FAQs
The main challenge is maintaining the circular structure after deletion. You must carefully adjust the previous node’s pointer to ensure the list remains connected and circular.
If the head is to be deleted, the last node’s pointer must be updated to point to the new head, and then the old head node is freed from memory.
In such a case, the program should handle it gracefully by displaying an error or ignoring the operation to prevent accessing invalid memory.
The time complexity is O(n) since we may need to traverse the list to reach the node before deletion, while the space complexity remains O(1).
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java




Login/Signup to comment