Circular Linked List Insertion in the middle in C++
Program in C++ for Circular Linked List insertion in the middle
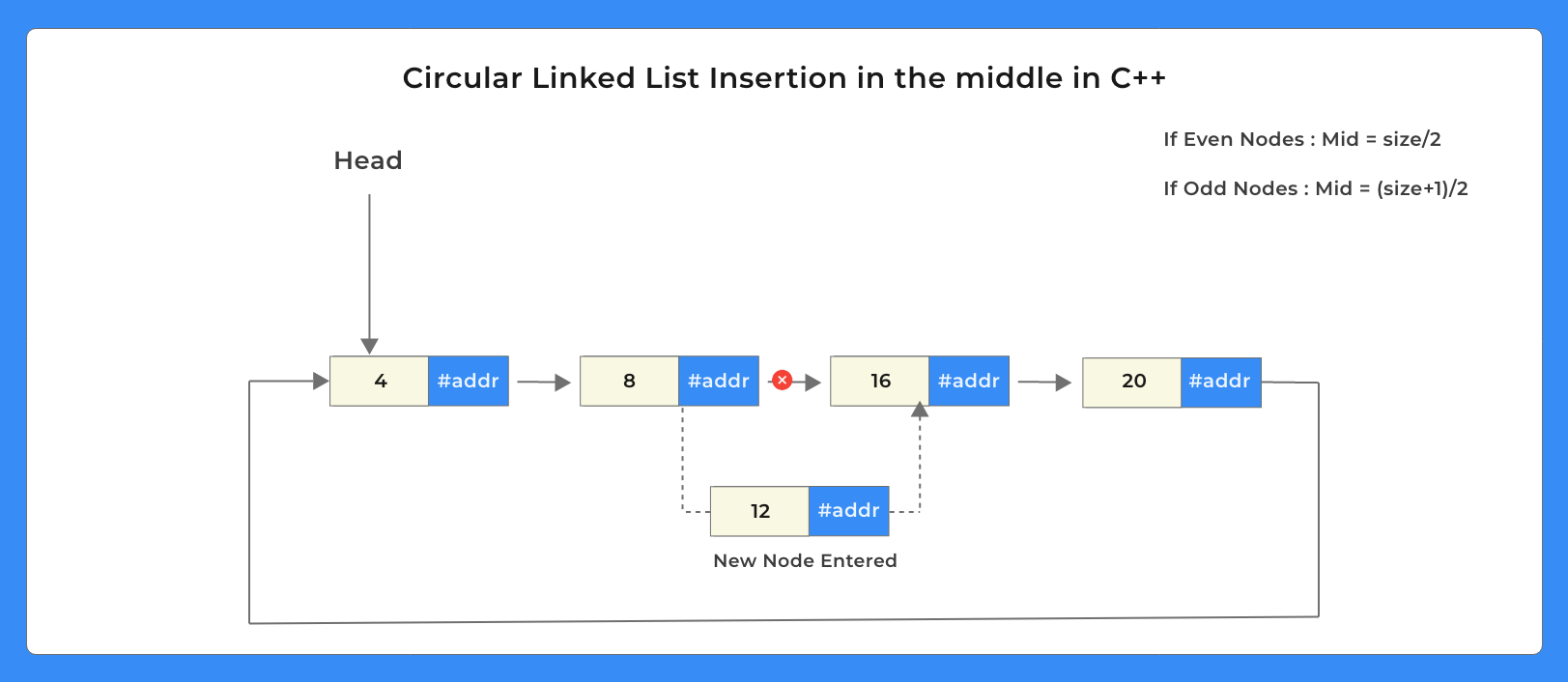
On this blog we will explore different codes to do Insertion in a Circular Linked List in the middle in C++
Method 1
Method 2
Method 1
Run
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
int getSize(Node* head);
void insert(Node** head, int data) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = data;
// If it's the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL) {
*head = newNode;
(*head)->next = *head;
return;
}
// If the Circular Linked List has >= 1 node
Node* curr = *head;
// Traverse till the last node in Circular Linked List
while (curr->next != *head) {
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = newNode;
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
int getSize(Node* head) {
int size = 0;
if (head == NULL) {
return size;
}
Node* node = head;
do {
node = node->next;
size++;
} while (node != head);
return size;
}
void insertMiddle(Node** head, int data) {
int size = getSize(*head);
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = data;
// If the CLL was empty
if (*head == NULL) {
// Use the insert function to insert
insert(head, data);
return;
}
// Otherwise
Node* temp = *head;
// Find the correct insertion position for the middle
int mid = (size % 2 == 0) ? (size / 2) : (size + 1) / 2;
// Unique case when there is only one node in CLL
if (mid == size) {
newNode->next = *head;
(*head)->next = newNode;
return;
}
// Traverse to the current mid position
while (--mid) {
temp = temp->next;
}
newNode->next = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
}
void display(Node* head) {
// If there are no nodes in LL
if (head == NULL)
return;
cout << "Linked List: ";
Node* temp = head;
// Need to take care of the circular structure of LL
do {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
} while (temp != head);
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
Node* head = NULL;
insert(&head, 20);
insert(&head, 4);
display(head);
insertMiddle(&head, 8);
display(head);
insertMiddle(&head, 16);
display(head);
insertMiddle(&head, 12);
display(head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List: 4 20 Linked List: 4 8 20 Linked List: 4 8 16 20 Linked List: 4 8 12 16 20
Method 2
Run
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
int getSize(Node* node);
void insert(Node** head, int data){
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if(*head == NULL){
*head = newNode;
(*head)->next = *head;
return;
}
// if Circular Linked List had >=1 node
Node* curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in Circular Linked List
while(curr->next != *head){
curr = curr->next;
}
curr->next = newNode;
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
void insertMiddle(Node** head, int data){
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = data;
// if the LL was empty
if(*head == NULL){
// use insert function to insert
insert(head, data);
return;
}
// otherwise
Node* temp = *head;
int size = getSize(*head);
// find correct insertion position for middle
int mid = (size % 2 == 0) ? (size/2) : (size+1)/2;
// Unique case when there is only one node in CLL
// we will be inserting at the last,
// inserting 2nd node at the last
// Example size = 1 will result in mid = 1 so entering after 1st node
// where size itself is 1 so entering last node
if(mid == size){
newNode->next = *head;
(*head)->next = newNode;
return;
}
// traverse to current mid position
while(--mid){
temp = temp->next;
}
newNode->next = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
}
int getSize(Node* head){
int size = 0;
Node* node = head;
do{
node = node->next;
size++;
}while(node!=head);
return size;
}
void display(Node* head){
// if there are no node in LL
if(head == NULL)
return;
cout << "Linked List: ";
Node* temp = head;
//need to take care of circular structure of LL
do{
cout << temp->data << " "; temp = temp->next;
}while(temp!=head);
cout << "\n" << endl;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
insert(&head,20);
insert(&head,4);
display(head);
insertMiddle(&head, 8);
display(head);
insertMiddle(&head, 16);
display(head);
insertMiddle(&head, 12);
display(head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List: 4 20 Linked List: 4 8 20 Linked List: 4 8 16 20 Linked List: 4 8 12 16 20
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment