Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List
How to insert in a sorted circular linked list in C?
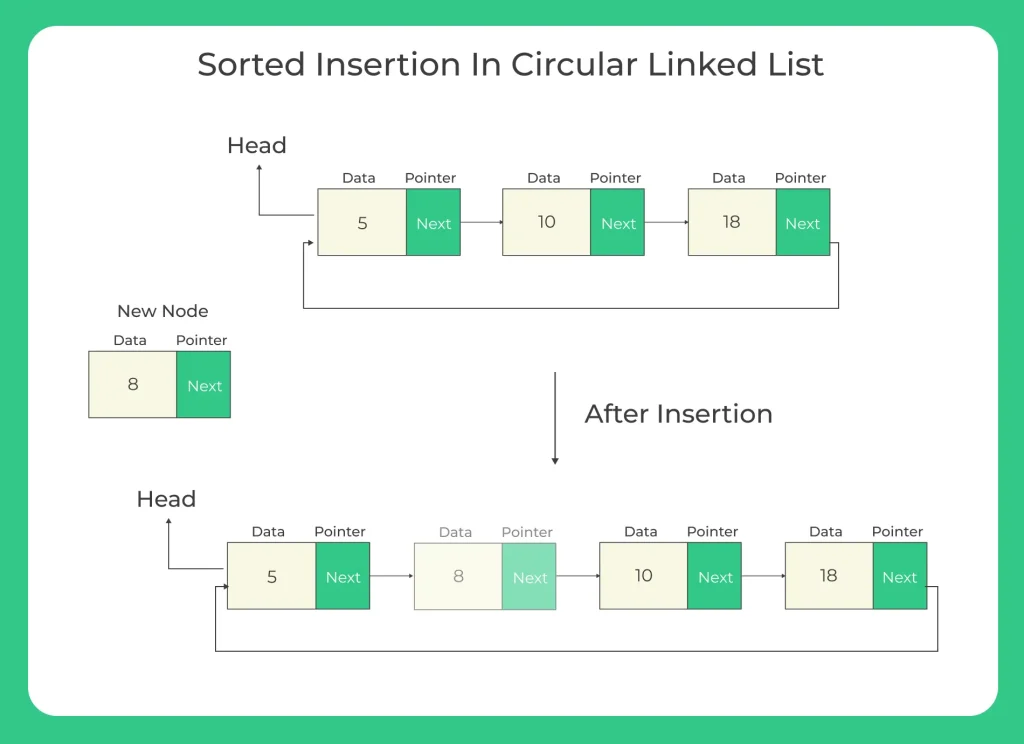
C program to insert in a sorted circular linked list means to insert the data in a circular linked list in a way that its logical order does not get disturbed. To do this first we need to ensure that the list we are working upon is already sorted else we will have to sort the given list before performing the operation.
Let us learn how to write a program for sorted insert in circular linked using the steps and algorithm discussed in this article.

Sorted insert in circular linked list
In this topic we will discuss about the how to insert the node in the sorted circular linked list.
first of all we will do allocated the memory for newly inserted node and put data in the newly allocated node.Let the pointer to the new node to be new_node.
After memory allocation we have three ways for insert the data is following –
- First one is if linked list is empty then since new_node is only node in circular linked list, make a self loop.and change the head pointer to the new_node pointer.
- Second case is new node insert in starting or before the head node.
- Find out the last node using a loop.
While(present->!=*head_ref)
present=present->next; - Change the next of last node;
present->next=new-node; - Change next of new node to point to head.
new_node->next=*head_ref; -
D- Change the head pointer to point to new node.
*head_ref=new_node;
- Find out the last node using a loop.
- Third case is when we insert the new node after the head in any position,then
-
Locate the node after which new node is to be inserted.
while(present->next!= *head_ref &&
present->next->data data) { present = present->next; } - Make next of new_node as next of the located pointer
new_node->next = present->next; - Change the next of the located pointer present->next = new_node;
-
Locate the node after which new node is to be inserted.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void sortedInsert (struct Node **head_ref, struct Node *new_node)
{
struct Node *present = *head_ref;
// Case 1 when list is empty
if (present == NULL)
{
new_node->next = new_node;
*head_ref = new_node;
}
// Case 2 when the node insert before the head
else if (present->data >= new_node->data)
{
//when value is smaller than head's value
while (present->next != *head_ref)
present = present->next;
present->next = new_node;
new_node->next = *head_ref;
*head_ref = new_node;
}
// Case 3 when node insert in after head in somewhere
else
{
//Locate the node before the point of insertion
while (present->next != *head_ref
&& present->next->data < new_node->data)
present = present->next;
new_node->next = present->next;
present->next = new_node;
}
}
void display (struct Node *head)
{
// if there are no node in LL
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node *temp = head;
//need to take care of circular structure of LL
do
{
printf ("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
printf ("\n");
}
int main () //main function
{
int arr[] = { 12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90 };
// start with empty linked list
struct Node *head = NULL;
struct Node *temp;
// Create linked list from the array arr[].
// Created linked list will be 1->2->11->12->56->90
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
temp = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
temp->data = arr[i];
sortedInsert (&head, temp);
}
printf ("Sorted Linked List is: ");
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
sorted Linked List is: 1 2 11 12 56 90
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment