Introduction to Circular linked list
Circular Linked Lists
Circular linked lists are just like singly linked lists but all of its nodes are connected to form a circle.
The last node of the linked list will point to the head/first node of the linked list.
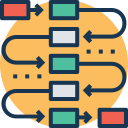
Circular linked list Advantages
The circular linked list is also two types.
- Singly linked list
- Doubly linked list
In a singly circular linked list, the address of the last node’s next pointer rather than being NULL is pointed towards the address of the head node.
Similarly, in a doubly linked list, in addition to the address of the last node’s next pointer being the address of head node. The previous pointer of the head node is provided to the address of the last node.
Advantages
- Any node can be starting point and we can still traverse the whole list
- It can also deem to be useful for implementation as queues as rather than maintaining the Front and Rear, we can use a circular linked list and just maintain the pointer to the first inserted node and it can simply be the next node to the last node.
- Circular linked lists are commonly used in OS’es for the task that requires repeatedly to be executed by OS.
Disadvantages
- Doubly Linked List is faster in getting previous node information due to previous pointer.
- Doubly Linked List can traverse in both forward and backward direction.
- Finding end of list and loop control is harder (no NULL to mark beginning and end).
- The entire list can be traversed starting from any node (traverse means visit every node just once).
So, when we want to traverse the node in a circular linked list so we will traverse in a singly circular linked list so, it is just like the singly linked list where tail nodes hold the address of head node so traversal can be done circularly in only one direction.
And the Traversal in a doubly linked list can be done circularly in both directions.
Creation of Circular Linked Lists
Defining struct for Circular Linked List (Singly)
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
//last node will have the address of the head class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
//last node will have the address of the head class LinkedList {
Node head; // head
// Linked list Node
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// constructor to initialize
Node(int d) {
data = d;
}
}
}
//last node will have the address of the head # Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data # Assign data
self.next = None # Initialize # next as null
# Linked List class
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize the Linked
# List object
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
//last node will have the address of the head Defining struct for Circular Linked List (Doubly)
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next , prev;
};
//last node will have the address of the head class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next , prev;
};
//last node will have the address of the head class LinkedList {
Node head; // head
// Linked list Node
class Node {
int data;
Node next , prev;
// constructor to initialize
Node(int d) {
data = d;
}
}
}
//last node will have the address of the head # Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data # Assign data
self.next = None # Initialize # next as null
self.prev = None # Initialize # next as null
# Linked List class
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize the Linked
# List object
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
//last node will have the address of the head // Linked List in C Implementation code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
// if its the first node being entered
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
(*head)->next = *head;
return;
}
// if LL already as >=1 node
struct Node *curr = *head;
// traverse till last node in LL
while (curr->next != *head)
{
curr = curr->next;
}
// assign LL's last node's next as this new node
curr->next = newNode;
// assign newNode's next as current head
newNode->next = *head;
// change head to this new node
*head = newNode;
}
void display (struct Node *head)
{
// if there are no node in LL
if (head == NULL)
return;
struct Node *temp = head;
//need to take care of circular structure of LL
do
{
printf ("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != head);
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
printf ("Linked List: ");
insertStart (&head, 6);
insertStart (&head, 5);
insertStart (&head, 4);
insertStart (&head, 3);
insertStart (&head, 2);
insertStart (&head, 1);
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output 10 20 30 40
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
// Pointer pointing towards next node
};
void insertFront (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// dynamically create memory for this newNode
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
// assign data value
newNode->data = data;
// change the next node of this newNode
// to current head of Linked List
newNode->next = *head;
//re-assign head to this newNode
*head = newNode;
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
cout << "\n";
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next;
}
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
// Need '&' i.e. address as we need to change head
insertFront (&head, 6);
insertFront (&head, 12);
insertFront (&head, 18);
insertFront (&head, 24);
insertFront (&head, 30);
cout << "the linked list is" << endl;
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
30 24 18 12 6
import java.lang.*;
class LinkedList {
Node head;
// not using parameterized constructor would by default
// force head instance to become null
// Node head = null; // can also do this, but not required
// Node Class
class Node{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
public Node insert(int data)
{
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// assigning this newNode's next as current head node
newNode.next = head;
// re-assigning head to this newNode
head = newNode;
return head;
}
public void display()
{
Node node = head;
//as linked list will end when Node reaches Null
while(node!=null)
{
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList ll = new LinkedList();
ll.insert(6);
ll.insert(5);
ll.insert(3);
ll.insert(4);
ll.insert(2);
ll.insert(1);
ll.display();
}
}
Output
1 2 4 3 5 6
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
Click Here - Circular Linked List Applications
Click Here - Circular Linked List in –
- Insertion in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion at the beginning–
- Insertion at the end –
- Insertion at nth position –
- Deletion in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from beginning in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from nth position in Circular Linked List –
- Deletion from end in Circular Linked List –
- Insertion and Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves –
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List –
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List –
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List –
Circular Linked List
- Introduction to Circular Linked List
- Circular Linked List Applications
- Circular Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in a Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Split a Circular Linked List in two halves – C | C++ | Java
- Count nodes in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Sorted Insert In Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in Circular Linked List – C | C++ | Java






Login/Signup to comment