Deletion at the beginning of the Singly Linked List in C
How to Delete the node at the beginning of the Singly Linked List?
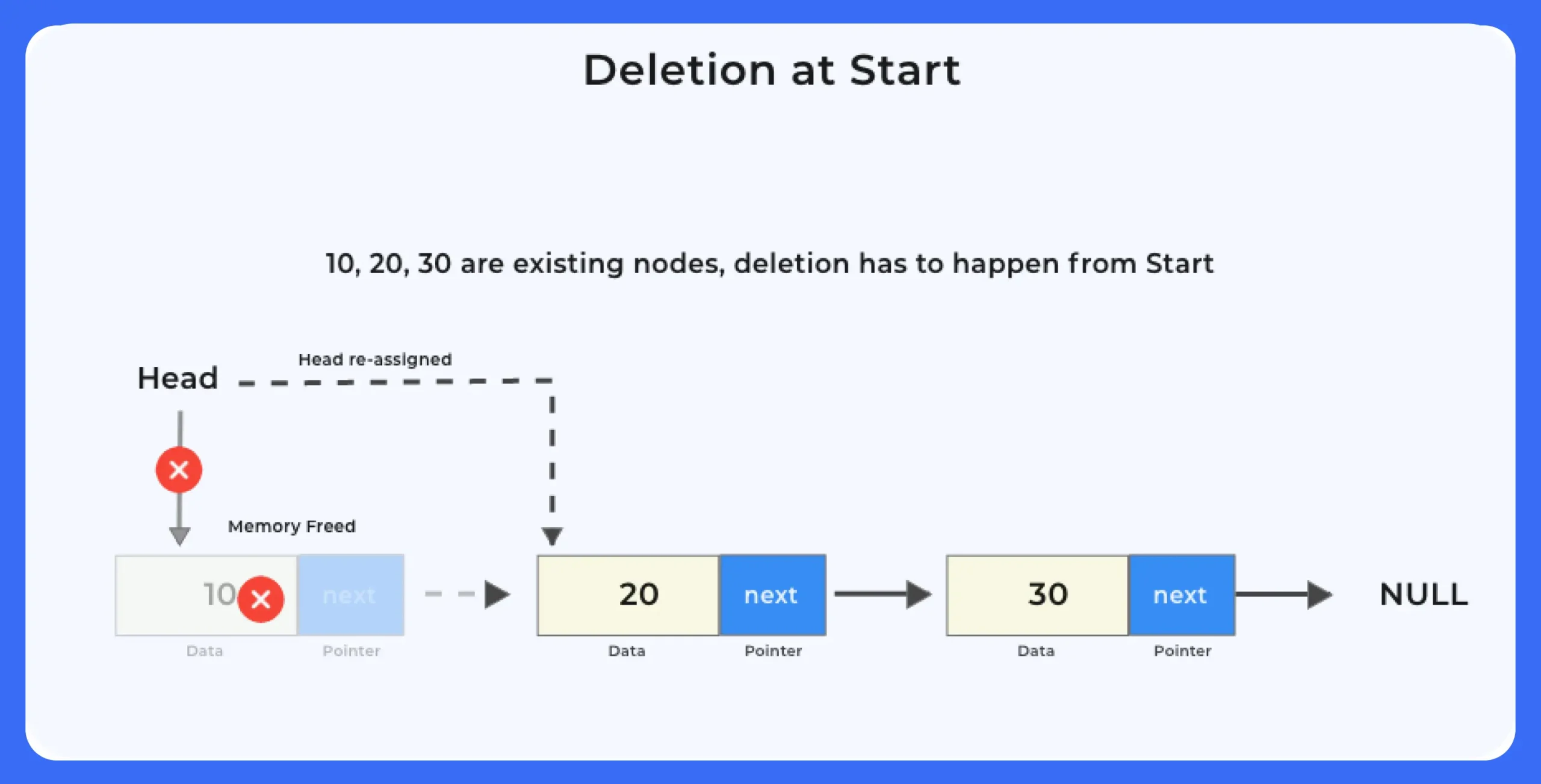
Let’s have a look at the code to delete from a singly linked list from the beginning i.e. the start or first node. We will discuss all possible ways of doing so in this post.

Deletion at The Beginning
Steps needed for deletion at the beginning of the Singly Linked List
- Move the current head from 1st node to the next node
- Delete the first node using the free method
- If the Linked List is empty that it is not possible to delete
Determine how to make Deletion node Structure:-
The following code will do the job –void deleteStart (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
printf ("Deleted: %d\n", temp->data);
free (temp);
}
C Code for deletion at the beginning of the Singly Linked List:-
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void deleteStart (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
// if there are no nodes in Linked List can't delete
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete");
return;
}
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
printf ("Deleted: %d\n", temp->data);
free (temp);
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
//creating 4 pointers of type struct Node
//So these can point to address of struct type variable
struct Node *head = NULL;
struct Node *node2 = NULL;
struct Node *node3 = NULL;
struct Node *node4 = NULL;
// allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node2 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node3 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node4 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
head->data = 22; // data set for head node
head->next = node2; // next pointer assigned to address of node2
node2->data = 30;
node2->next = node3;
node3->data = 24;
node3->next = node4;
node4->data = 20;
node4->next = NULL;
/*No need for & i.e. address as we do not
need to change head address
*/
printf ("Linked List Before Operations : ");
display (head);
deleteStart (&head);
deleteStart (&head);
printf ("Linked List After Operations : ");
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List Before Operations : 22 30 24 20 Deleted: 22 Deleted: 30 Linked List After Operations : 24 20



Login/Signup to comment