Binary Search in C
Binary Search in C
In this article, you will learn what binary search in C is, how it works, how to implement it in C (both iterative and recursive ways), along with its time and space complexity, all explained in simple language with example code.
Searching is one of the most common operations performed on data structures. Whether you are looking for a name in a contact list or a product in an online store, search algorithms play a vital role.
One of the fastest and most efficient ways to search in a sorted list is Binary Search.

What is Binary Search in C?
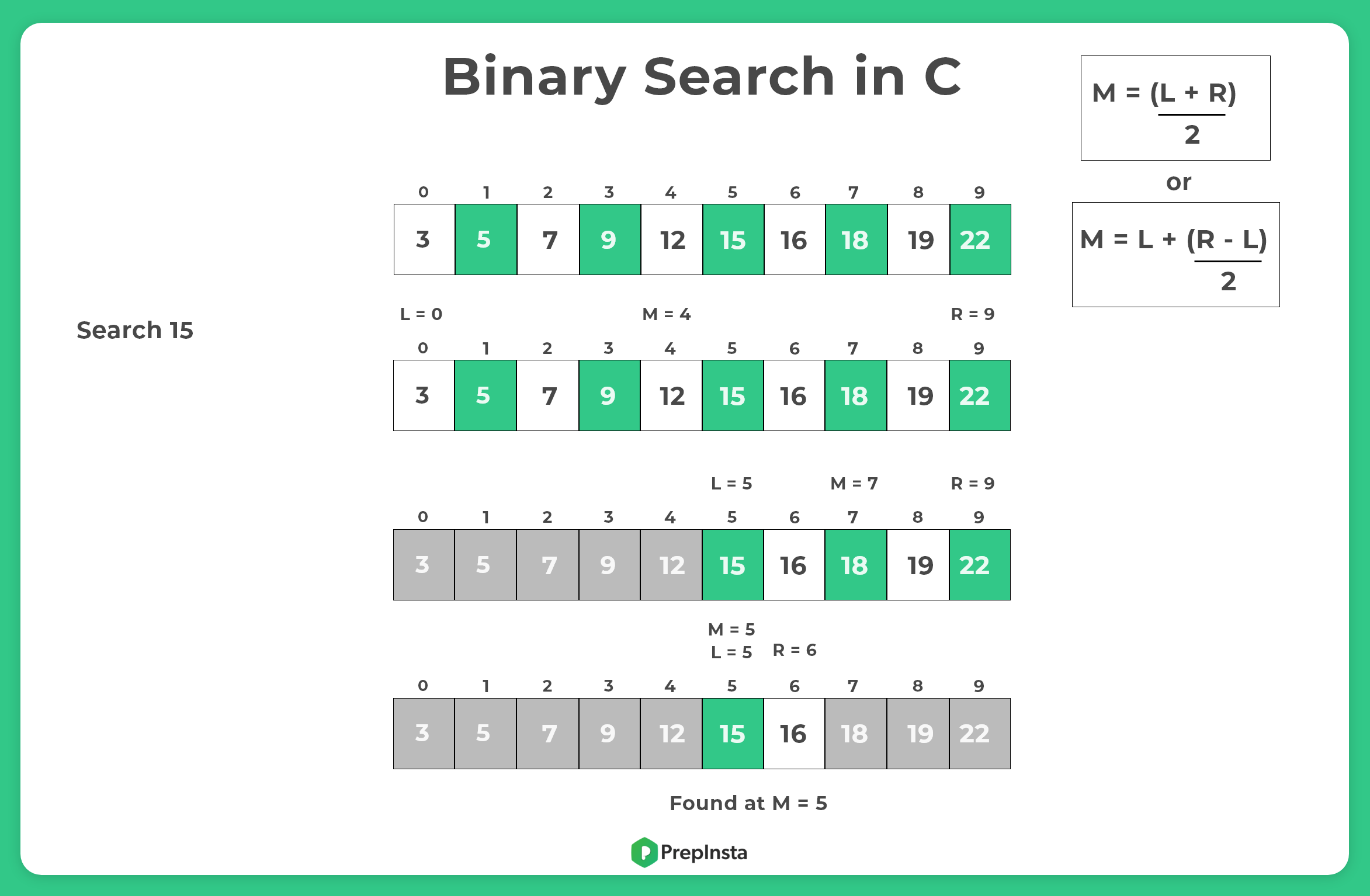
Binary Search is one of the most efficient algorithms to search for an element in a sorted array.
- It works by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half and comparing the middle element of the array with the target value.
- If the target matches the middle element, the search is complete. If the target is smaller than the middle element, the search continues in the left half.
- If the target is larger, the search continues in the right half.
Methods of Implementing Binary Search in C
There are 2 common ways to implement Binary Search:
- Iterative Method
- Recursive Method
Both give the same result and efficiency but have different styles of coding.
Methods to Implement Binary Search
1. What is Algorithm for Binary Search?
(Iterative Method)
- Start with two pointers: low = 0 and high = size – 1.
- Find the middle index: mid = low + (high – low) / 2.
- Compare array[mid] with the target value:
- If equal, return the index.
- If target < array[mid], search in the left half (high = mid – 1).
- If target > array[mid], search in the right half (low = mid + 1).
- Repeat the process until low > high.
- If not found, return -1.
Code for Binary Search using C:
#include<stdio.h>
// Binary Search Function (Iterative)
int binarySearch(int arr[], int size, int target) {
int low = 0, high = size - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target)
return mid; // Target found at index mid
if (arr[mid] < target)
low = mid + 1; // Search in right half
else
high = mid - 1; // Search in left half
}
return -1; // Target not found
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 23, 38, 56, 72, 91};
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int target = 23;
int result = binarySearch(arr, size, target);
if (result != -1)
printf("Element %d found at index %d\n", target, result);
else
printf("Element %d not found in the array\n", target);
return 0;
}
Example Input and Output:
Input:
Array: {2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 23, 38, 56, 72, 91}
Target: 23
Output:
Element 23 found at index 5
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banner
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
2. What is Algorithm for Binary Search
(Recursive Method)
Base case: if low > high, return -1 (not found).
Calculate mid: mid = low + (high – low) / 2.
Compare:
If arr[mid] == target, return mid.
If target < arr[mid], recursively search in left half.
If target > arr[mid], recursively search in right half.
Code for Binary Search using C:
#include<stdio.h>
// Binary Search Function (Recursive)
int binarySearchRecursive(int arr[], int low, int high, int target) {
if (low > high)
return -1; // Base case: not found
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (arr[mid] > target)
return binarySearchRecursive(arr, low, mid - 1, target); // Left half
return binarySearchRecursive(arr, mid + 1, high, target); // Right half
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 23, 38, 56, 72, 91};
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int target = 38;
int result = binarySearchRecursive(arr, 0, size - 1, target);
if (result != -1)
printf("Element %d found at index %d\n", target, result);
else
printf("Element %d not found in the array\n", target);
return 0;
}
Example Input and Output:
Input:
Array: {2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 23, 38, 56, 72, 91}
Target: 38
Output:
Element 38 found at index 6
Average Case:O(log n)
Worst Case:O(log n)
Logarithmic time comes from the fact that the search space is halved each time.
Recursive: O(log n)
Iterative version uses constant space.
Recursive version uses O(log n) stack space because of recursive calls.
Final Thoughts on Binary search are:
Binary Search is much faster than linear search for large sorted arrays.
- It is widely used in searching problems, interview questions, and in many system-level implementations.
- Always remember: Binary Search requires the array to be sorted, if it is not, sort the array first.

FAQ's related to Binary Search
Answer:
Binary search in C programming language is an efficient algorithm used to search for an element in a sorted array. It works by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half and comparing the middle element with the target value, drastically reducing the search time.
Answer:
To implement binary search in C, you can use an iterative method (with a while loop) or a recursive method (function calling itself). The array must be sorted in ascending or descending order for binary search to work correctly. Example C programs for binary search typically demonstrate how to find the index of a target element in a sorted array.
Answer:
Time complexity of binary search in C is O(log n), where ‘n’ is the number of elements in the array. Because the search space is halved with each comparison, binary search is much faster than linear search for large sorted arrays.
Answer:
Key advantages of binary search in C are its efficiency and speed. It has a time complexity of O(log n), making it much faster than linear search (O(n)) for large datasets. Binary search is ideal for scenarios where the array is already sorted.
Answer:
Main limitation of binary search in C is that it only works on sorted arrays. If the data is unsorted, you must sort the array first before applying binary search. Also, binary search is not suitable for linked lists unless they support random access.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment