C++ program to count possible decoding of a given digit sequence
Counting possible decoding of a given digit sequence in C++
Here we will discuss how to count all the possible decoding of a given digit sequence in C++. Before counting the number of decoding’s first let’s see how the numbers are assumed to be coded. The decoding programs are the most possible questions asked and are largely practiced in C ++ programming. The program counts the number of possible decoding’s of the entered digit by the user of the given sequence.

Explanation
1 = A, 2 = B, 3 = C, . . . . , 26 = Z.
The decoding programs are the most possible questions asked and are largely practiced in C programming. The program counts the number of possible decoding’s of the entered digit by the user of the given sequence.
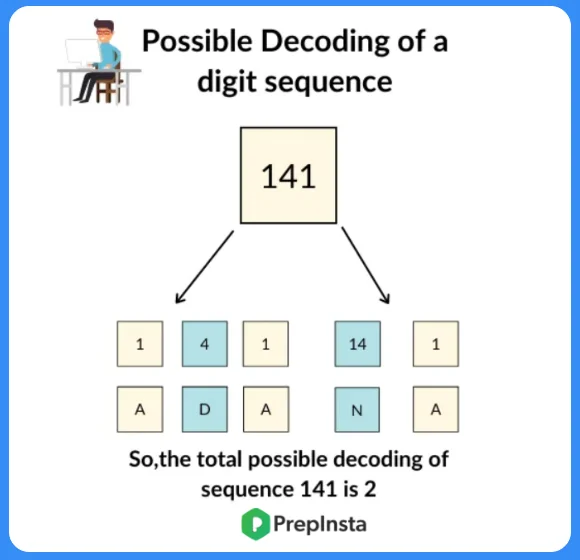
For example :- if the digit sequence is “12” then there are two possible decoding’s for this – One of them is ‘AB’ when we decode 1 as ‘A’ and 2 as ‘B’. Now we can also decode this digit sequence “12” as ‘L’ when we decode digits 1 and 2 taken together as an integer 12.
Now let’s take another example for reference,
Sequence = 131
- Possible decoding (1, 3, 1,) = ACA
- Possible decoding (13, 1) = MA
So, the total possible decoding’s of sequence 131 is 2.
Algorithm
- Initialize a array cnt of size 1 + length of input and store 1 at 0 & 1 position
- Iterate from 2 to a using variable k
- If the last digit not equal to 0, then last digit must added to the number of words if (dig[k-1] > ‘0’)
- In case second last digit is smaller than 2 and last digit is smaller than 7, then last two digits form a valid character
- Print cnt[a]
C++ code
//C Program to Count possible decodings of a given digit sequence
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int cnt_decoding_digits(char *dig, int a)
{
// Initializing an array to store results
int cnt[a+1];
cnt[0] = 1;
cnt[1] = 1;
for (int k = 2; k <= a; k++)
{
cnt[k] = 0;
// If the last digit not equal to 0, then last digit must added to the number of words
if (dig[k-1] > '0')
cnt[k] = cnt[k-1];
// In case second last digit is smaller than 2 and last digit is smaller than 7, then last two digits form a valid character
if (dig[k-2] == '1' || (dig[k-2] == '2' && dig[k-1] < '7'))
cnt[k] += cnt[k-2];
}
return cnt[a];
}
int main()
{
char dig[15];
cout<<"Enter the sequence : "; cin>>dig;
int a = strlen(dig);
cout<<"Possible count of decoding of the sequence : "<< cnt_decoding_digits(dig, a);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the sequence : 141 Possible count of decoding of the sequence : 2
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription






Login/Signup to comment