SQL UPDATE STATEMENT
Introduction to SQL UPDATE
SQL (Structured Query Language) plays a pivotal role in manipulating data stored within relational databases. One of the most essential SQL operations is the UPDATE statement, which allows you to modify existing records.
The SQL UPDATE STATEMENT is a powerful tool that can be immensely useful in complex data scenarios.
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of SQL UPDATE statements, providing you with an extensive understanding of how to use them effectively.
Understanding SQL Update Statements
SQL Update Statement Syntax Explained
UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ... WHERE condition;
table_name: Specifies the name of the table you want to update.column1, column2, ... : Identifies the columns you wish to modify.
value1, value2, ...: Represents the new values you want to assign to the specified columns.
WHERE condition: Optional, but crucial for targeting specific rows within the table. If omitted, all rows in the table will be updated.
Syntax of SQL UPDATE with SELECT
SQL UPDATE with SELECT is a versatile SQL operation that enables you to update records in one table based on values from another table. This is particularly useful when you want to synchronize data between two tables or make bulk updates based on specific criteria.
UPDATE table1 SET column1 = (SELECT column2 FROM table2 WHERE condition) WHERE condition;
SQL UPDATE with SELECT Example
UPDATE employees SET salary = (SELECT new_salary FROM salary_updates WHERE employees.employee_id = salary_updates.employee_id);
Syntax of SQL UPDATE from Another Table
SQL UPDATE from another table is a powerful database operation that enables you to update records in one table using data from a different table. This is particularly useful when you want to make bulk updates or synchronize data between related tables.
UPDATE table1 SET column1 = table2.column2 FROM table2 WHERE table1.key_column = table2.key_column;
SQL UPDATE from Another Table Example
UPDATE products SET price = price_updates.new_price FROM price_updates WHERE products.product_id = price_updates.product_id;
Click below to access free SQL quizzes which will be helpful in your placement exams
Understanding SQL UPDATE for Multiple Rows and Columns
SQL UPDATE for multiple rows and columns is a powerful database operation that allows you to modify data across several rows and columns simultaneously. This is particularly valuable when you need to update a substantial amount of data in one go.
Syntax of SQL UPDATE for Multiple Rows and Columns
UPDATE table_name
SET
column1 = value1,
column2 = value2,
...
WHERE condition;
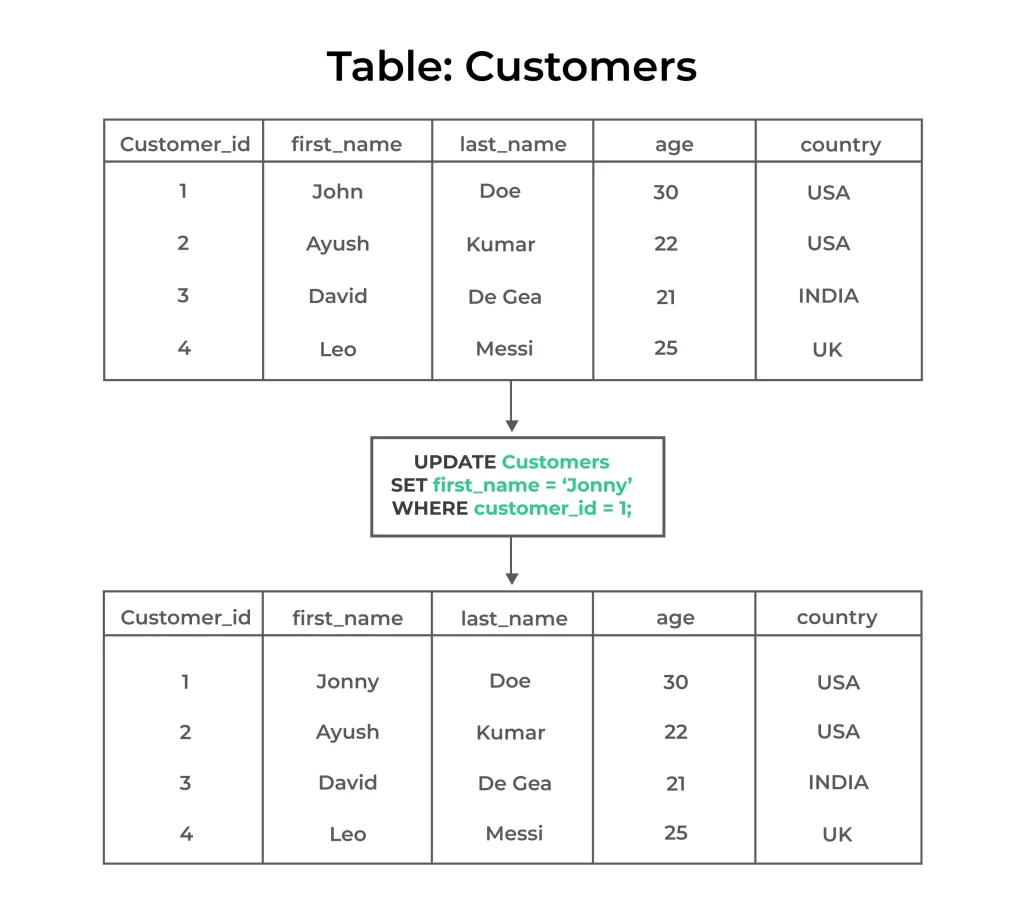
Practical Example : Updating Customer Information
Suppose you have a “customers” table, and you want to update the names and email addresses of customers who reside in a specific city (e.g., “New York”):
UPDATE customers
SET
first_name = 'John',
last_name = 'Doe',
email = 'johndoe@example.com'
WHERE city = 'New York';
SQL UPDATE STATEMENT EXAMPLES
UPDATE products SET price = price * 1.10;
UPDATE orders SET status = 'shipped' WHERE payment_received = 1;
Advantages of Using FULL OUTER JOIN :
Conclusion
SQL UPDATE statements is crucial for maintaining efficient database operations. By following the strategies outlined in this article, you can ensure that your SQL updates are not only speedy but also maintain data integrity.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription

Question 1.
What’s the difference between a Full Outer Join and other types of joins?
The key difference lies in inclusivity. A Full Outer Join retrieves all rows from both tables, whereas other joins may exclude certain records.

Question 2.
When should I use a Full Outer Join?
Use a Full Outer Join when you need a comprehensive view of your data, want to handle unmatched records, or are merging datasets from various sources.

Question 3.
Are Full Outer Joins supported in all SQL database systems?
Most modern SQL database systems support Full Outer Joins, but it’s essential to check the specific documentation for your database to ensure compatibility.

Question 4.
Where can I learn more about SQL joins and query optimization?
To further enhance your SQL skills, explore online resources, SQL tutorials, and documentation provided by your database management system.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




