SQL Subquery
Introduction to SQL Subquery:
The SQL LIKE Operator is a powerful tool used in database queries to perform pattern matching on text data. It allows users to search for specific patterns within strings, making it an essential component in SQL queries for tasks like data filtering and searching.
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of the SQL LIKE Operator, its syntax, usage of wildcard characters, performance considerations, best practices, and real-world use cases.
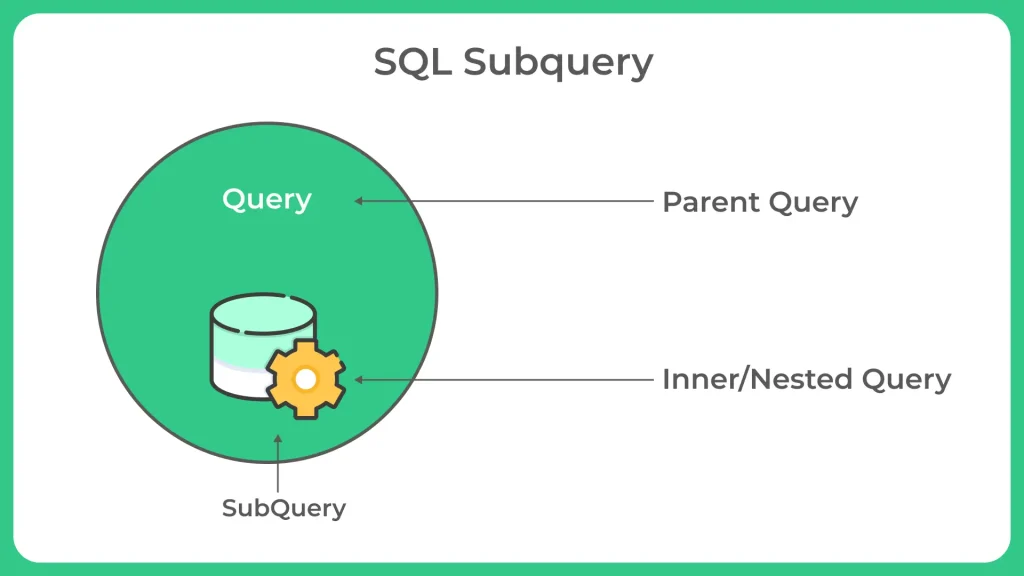
What is subquery in SQL?
In SQL, a subquery (also known as an inner query or nested query) is a query nested within another SQL statement, such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE. It allows you to retrieve data by executing a query within another query.
A subquery can be used in various parts of a SQL statement, including:
- SELECT statement: To retrieve data from one or more tables based on the result of the subquery.
- FROM clause: To use the result of the subquery as a derived table within the main query.
- WHERE clause: To filter rows based on the result of the subquery.
- INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements: To perform operations using the result of a subquery.
Types of Subqueries in SQL
- Single-row subquery: A single-row subquery returns only one row and one column. It is used where an expression expects a single value.
SELECT employee_name FROM employees WHERE salary = (SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees);
- Multiple-row subquery: A multiple-row subquery returns multiple rows and can have one or more columns in its result set. It is used with operators that expect multiple values.
SELECT product_name FROM products WHERE category_id IN (SELECT category_id FROM categories WHERE category_name = 'Electronics');
Correlated subquery: A correlated subquery is a type of subquery that depends on the outer query. It references columns from the outer query, and for each row processed by the outer query, the subquery is executed.
SELECT employee_name FROM employees e WHERE salary > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees WHERE department_id = e.department_id);
- Nested subquery or nested subselect: A nested subquery is a subquery within another subquery. It can be a single-row or multiple-row subquery. These subqueries are enclosed within parentheses.
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE customer_id IN (SELECT customer_id FROM customers WHERE country = 'USA' AND city = 'New York');
Click below to access free SQL quizzes which will be helpful in your placement exams
SQL Subquery Join
In SQL, a subquery join involves using a subquery as a part of the join condition in a query. This approach allows for more complex criteria to be applied when joining tables together.
Subquery joins can be performed using different types of joins like INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN, etc., combined with subqueries to fetch the desired data.
Here’s an example to illustrate the use of a subquery in a join:
Let’s say we have two tables, employees and departments. We want to retrieve the employees who belong to departments with a specific location.
Table : Employees
employee_id | employee_name | department_id 1 | John | 101 2 | Alice | 102 3 | Smith | 101 4 | Emily | 103
Table: departments
employee_id | employee_name | department_id 1 | John | 101 2 | Alice | 102 3 | Smith | 101 4 | Emily | 103
Now, if we want to find employees who work in departments located in ‘New York‘, we can use a subquery join like this:
SELECT e.employee_id, e.employee_name, e.department_id FROM employees e INNER JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id WHERE d.location = 'New York';
This query performs an INNER JOIN between the employees and departments tables on the department_id column and filters the result using a WHERE clause to only include departments located in ‘New York’.
How to use subquery in WHERE SQL?
In SQL, using a subquery in the WHERE clause allows you to filter data based on the result of a nested query. Subqueries in the WHERE clause are often used to compare values, retrieve specific records, or perform more complex filtering operations.
Here’s an example demonstrating how to use a subquery in the WHERE clause:
- Suppose we have two tables:
studentsandgrades. We want to retrieve the names of students who have scored above the average grade. - Table: students
student_id | student_name 1 | Alice 2 | Bob 3 | Claire 4 | David
In SQL, using a subquery in the WHERE clause allows you to filter data based on the result of a nested query. Subqueries in the WHERE clause are often used to compare values, retrieve specific records, or perform more complex filtering operations.
Here’s an example demonstrating how to use a subquery in the WHERE clause:
Table : Students
student_id | grade 1 | 85 2 | 72 3 | 90 4 | 68
Table : Grade
student_id | grade 1 | 85 2 | 72 3 | 90 4 | 68
To find students who scored above the average grade, you can use a subquery in the WHERE clause like this:
SELECT student_name
FROM students
WHERE student_id IN (
SELECT student_id
FROM grades
WHERE grade > (SELECT AVG(grade) FROM grades)
);
- The innermost subquery (SELECT AVG(grade) FROM grades) calculates the average grade.
- The subquery (SELECT student_id FROM grades WHERE grade > (SELECT AVG(grade) FROM grades)) retrieves the student_id of students who scored above the average grade.
- The outer query SELECT student_name FROM students WHERE student_id IN (subquery) fetches the names of those students by checking if their student_id exists in the result obtained from the subquery.
This query retrieves the names of students who have grades higher than the average grade from the grades table.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




