SQL Left Join

Introduction to SQL Left Join
SQL (Structured Query Language) stands as the cornerstone. SQL allows us to interact with relational databases efficiently, and one of its most potent features is the “LEFT JOIN.”
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of the SQL Left Join, its syntax, equipping you with the knowledge and skills needed to harness the full potential of your database queries.
Understanding the SQL LEFT JOIN
A SQL LEFT JOIN (also known as a LEFT OUTER JOIN) is a type of SQL JOIN operation that combines rows from two or more tables based on a related column, and it returns all the rows from the left table (the table specified before the LEFT JOIN) and the matched rows from the right table (the table specified after the LEFT JOIN). If there is no match in the right table for a row in the left table, the result will contain NULL values for columns from the right table.
Exploring Types of SQL Left Joins :
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM left_table LEFT JOIN right_table ON left_table.column_name = right_table.column_name;
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM left_table LEFT JOIN right_table ON left_table.column_name = right_table.column_name WHERE right_table.column_name = some_value;
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM left_table LEFT JOIN right_table ON left_table.column_name = right_table.column_name WHERE right_table.column_name IS NULL;
SQL Left Join Syntax Explained
- SELECT: Specifies the columns you want to retrieve in the result.
- FROM: Specifies the left table (the table from which you want all rows).
- LEFT JOIN: Specifies the type of join operation. In this case, it’s a LEFT JOIN.
- right_table: Specifies the right table (the table from which you want matched rows).
- ON: Specifies the condition on which the tables are joined. It specifies the columns that should be compared to establish the relationship between the tables.
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM left_table LEFT JOIN right_table ON left_table.column_name = right_table.column_name;
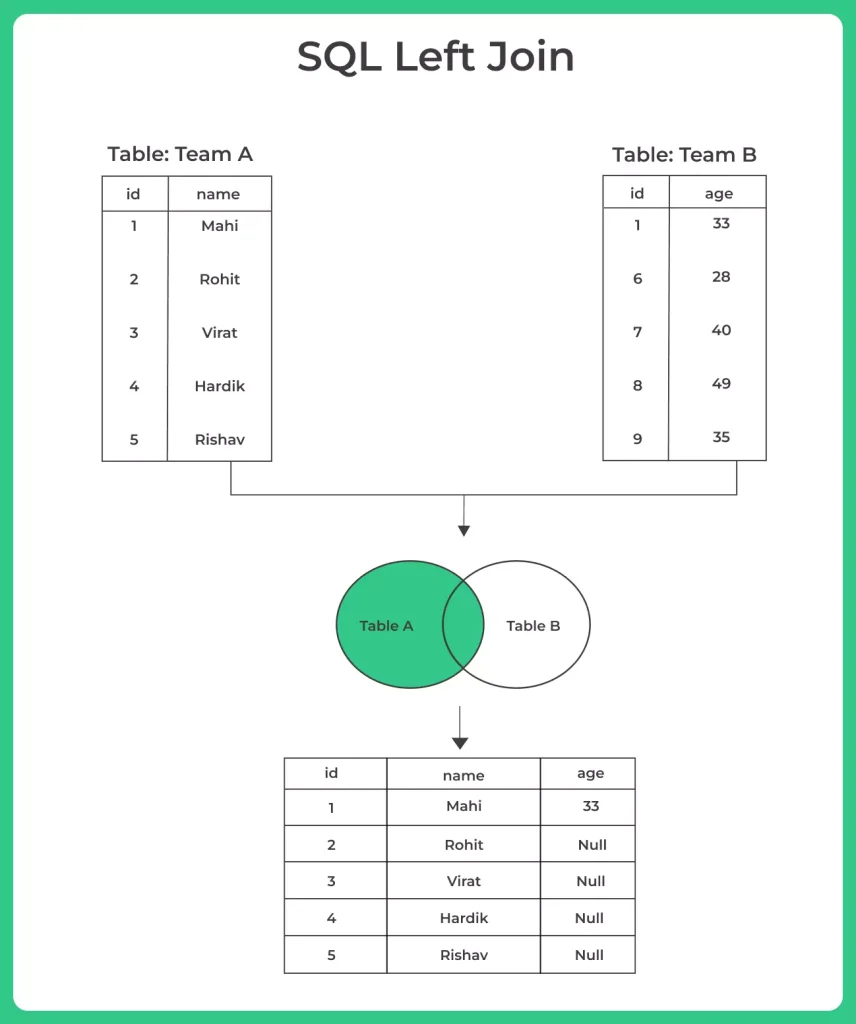
SQL Left Join Examples
Example 1: Employee-Department Relationship
SELECT Employees.EmployeeID, Employees.EmployeeName, Departments.DepartmentName FROM Employees LEFT JOIN Departments ON Employees.DepartmentID = Departments.DepartmentID;
Example 2: Products and Product Reviews
SELECT Products.ProductID, Products.ProductName, ProductReviews.ReviewText FROM Products LEFT JOIN ProductReviews ON Products.ProductID = ProductReviews.ProductID;
Click below to access free SQL quizzes which will be helpful in your placement exams
SQL Left Join vs Inner Join
| Aspect | LEFT JOIN | INNER JOIN |
|---|---|---|
| Included Rows | All rows from the left table are included. | Only rows with matching values in both tables are included. |
| Excluded Rows | Rows with no matching values in the right table are included with NULL values for right table columns. | Rows with no matching values in the right table are excluded. |
| Result Size | Typically, the result size is equal to or greater than the left table’s size. | Typically, the result size is equal to or less than the smaller of the two tables’ sizes. |
| Use Cases | Useful when you want all rows from the left table and related data from the right table. | Useful when you only want rows with matching values from both tables. |
| Syntax | SELECT * FROM left_table LEFT JOIN right_table ON left_table.column = right_table.column; | SELECT * FROM left_table INNER JOIN right_table ON left_table.column = right_table.column; |
Advantages of SQL Left Join :
Conclusion
SQL Left Join is a powerful tool that unlocks the potential of relational databases, allowing businesses to extract valuable insights from their data. By mastering Left Join and adhering to best practices, organizations can make informed decisions, drive efficiency, and stay competitive in today’s data-driven world.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription

Question 1.
What is an SQL LEFT JOIN, and how does it work?
An SQL LEFT JOIN is a type of join that combines rows from two tables based on a related column. It returns all rows from the left table and matching rows from the right table. If there is no match, it includes NULL values for columns from the right table.

Question 2.
When should I use an SQL LEFT JOIN?
You should use an SQL LEFT JOIN when you want to retrieve all records from the left table along with any matching records from the right table. It’s useful for scenarios where you want to preserve data integrity and include unmatched rows.

Question 3.
Can you provide an example of SQL LEFT JOIN in a real-world scenario?
Sure, consider a scenario where you have a “Customers” table and an “Orders” table. You can use LEFT JOIN to retrieve all customers and their associated orders (if any), ensuring that even customers with no orders are included in the result.

Question 4.
What happens if there are multiple matches in the right table for a row in the left table in a LEFT JOIN?
If there are multiple matches, a LEFT JOIN will return multiple rows in the result, with each row corresponding to a different match from the right table. This can result in duplication of data from the left table.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




